Facts about Anemia

Regardless of one's philosophy about the classification of anemia, however, any methodical clinical evaluation should yield equally good results.

Two major approaches of classifying anemias include the "kinetic" approach, which involves evaluating production, destruction, and loss, and the "morphologic" approach, which groups anemia by red blood cell size.

Hypoxemia (lack of oxygen in cells) resulting from anemia can worsen the cardio-pulmonary status of patients with pre-existing chronic pulmonary disease.

The principal cause of iron deficiency anemia in premenopausal women is blood lost during menses.

The treatment for vitamin B12-deficient macrocytic and pernicious anemias was first devised by the scientist William Murphy.

During pregnancy, women should be especially aware of the symptoms of anemia, as an adult female loses an average of two milligrams of iron daily.

People with more severe anemia sometimes report shortness of breath.

The cause of megaloblastic anemia is primarily a failure of DNA synthesis with preserved RNA synthesis, which result in restricted cell division of the progenitor cells.

Anemia affects 20 percent of all females of childbearing age in the United States.

Anemia diminishes the capability of affected individuals to perform physical labor.

When the cause is not obvious, clinicians use other tests to further distinguish the cause for anemia.

Finally, cuneiform writing became a general purpose writing system for logograms, syllables, and numbers.

Many physicians use the reticulocyte production index, which is a calculation of the ratio between the level of anemia and the extent to which the reticulocyte count has risen in response.

Cold intolerance occurs in 20 percent of patients with iron deficiency anemia and it becomes visible through numbness and tingling.

The "kinetic" approach to anemia yields what many argue is the most clinically relevant classification of anemia.

Anemia (American English) or anaemia (British English), from the Greek (???????) meaning "without blood," refers to a deficiency of red blood cells (RBCs) and/or hemoglobin.
The lack of sustainability suggests the need for small scale, slow growth, and locally based ecotourism.
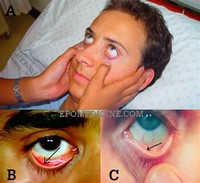
Pallor (pale skin and mucosal linings) is only notable in cases of severe anemia and is therefore not a reliable sign.

The megaloblastic anemias often present with neutrophil (type of white blood cell) hypersegmentation (6-10 lobes).

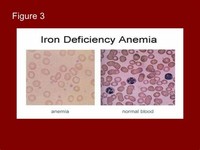
Macrocytic anemia can be further divided into "megaloblastic anemia" or "non-megaloblastic macrocytic anemia."

Studies have shown that iron deficiency without anemia causes poor school performance and lower IQ in teenage girls.