Facts about Armor

Machine gunners in that war also occasionally wore a crude type of heavy armor.

At the start of World War I the French Cuirassiers, in the thousands, rode out to engage the German Cavalry who likewise used helmets and armor.

Another tactic was to attempt to strike though the gaps between the armor pieces, using daggers to attack the Knight's eyes or joints.

Armor was also commonly used to protect war animals, such as war horses and elephants.

A variety of methods for improving the protection provided by mail were used as armorers seemingly experimented.

Chinese influence in Japan would result in the Japanese adopting Chinese styles, their famous "samurai armor" being a result of this influence.

Despite advances in the protection offered by ballistic armor against projectiles, as the name implies, modern ballistic armor is much less impervious to stabbing weapons unless they are augmented with anti-knife/anti-stab armor.

Armor has also been produced for hunting dogs that hunt dangerous game, such as boars.

Their armor was meant to protect only against sabres and light lances.

Armor has been used throughout recorded history, beginning with hides, leather, and bone, before progressing to bronze, then steel during the Roman Era, to modern fabrics such as Kevlar, Dyneema, and ceramics.

Full plate armor made the wearer virtually impervious to sword blows as well as providing some protection against arrows, bludgeons and even early musket shot.

The armor dates from the Mycenaean Era around 1400 B.C.E., some 200 years before the Trojan War.

Armor is protective clothing intended to defend its wearer from intentional harm in military and other combat engagements, typically associated with soldiers and riot police.

Hence, guns and cavalry in plate armor were "threat and remedy" together on the battlefield for almost 400 years.
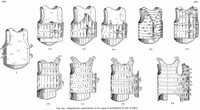
The coat of plates was developed, an armor made of large plates sewn inside a textile or leather coat.

the infrastructure to make plate was largely lost in Europe, as a result mail was the best available armor during the ensuing Early Medieval period.

Rather than dooming the use of body armor, the threat of small firearms intensified the use and further refinement of plate armor.

Armor often bore an insignia in the interior, that was only visible to the wearer upon removal.

Full suits of armor were actually worn by generals and princely commanders right up to the second decade of the 1700s.

The U.S. Army has adopted interceptor body armor, however, which uses Enhanced Small Arms Protective Inserts (E-S.A.P.I) in the chest and back of the armor.

Well-known constituent parts of plate-armor include the helm, gauntlets, gorget or 'neckguard', breastplate, and greaves worn on the lower legs.

Other significant factors in the development of armor include the economic and technological necessities of armor production.

Knights were instead increasingly felled by blunt weapons like maces or war hammers that could send concussive force through the plate armor resulting in injuries such as broken bones, organ haemorrhage and/or head trauma.

Armor is protective clothing intended to defend its wearer from intentional harm in military and other combat engagements, typically associated with soldiers and riot police.

By that period, the shiny armor plate was covered in dark paint and a canvas wrap covered their elaborate Napoleonic style helmets.

The function of a flower is to mediate the union of male and female gametes.


