Facts about Asthma

A similar review of air ionizers found no evidence that they improve asthma symptoms or benefit lung function; this applied equally to positive and negative ion generators.

Smoking cessation and avoidance of secondhand smoke is strongly encouraged in asthmatics.
The mortality rate for asthma is low, with around six thousand deaths per year in a population of some ten million patients in the United States.

Given that some research has identified a negative association between helminth infection (hookworm) and asthma and hay fever, some have suggested that hookworm infestation, although not medically sanctioned, would cure asthma.

Asthma appears to be more prevalent in athletes than in the general population.

Finally, Jesus predicted Muhammad (Q61:6), based on the Arabic translation of "Comforter" (??????????) in John 14:16 as "Ahmad," a cognate of Muhammad.

The airways of asthmatics are "hypersensitive" to certain triggers, also known as stimuli (see below).

During an asthma episode, inflamed airways react to environmental triggers such as smoke, dust, or pollen.

Only a minority of asthma sufferers have an identifiable allergy trigger.

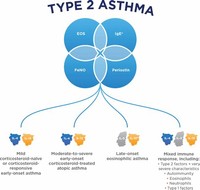
Asthma is categorized by the United States National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute as mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent.

The correlation seems to be not with the onset, but rather with accelerated loss of lung function in adults with new onset of non-atopic asthma.
In asthmatics, however, these cells transform into a different type of cell (TH2), for reasons that are not well understood.

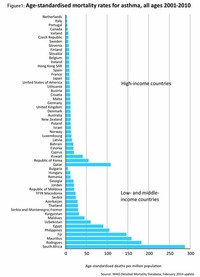
The prevalence of "severe persistent" asthma is also greater in low-income communities compared with communities with better access to treatment.

In 1968, Andor Szentivanyi first described The Beta Adrenergic Theory of Asthma; in which blockage of the Beta-2 receptors of pulmonary smooth muscle cells causes asthma.

One possible explanation is that some asthmatics may have altered immune response that facilitates long-term chlamydia pneumonia infection.

Moses Maimonides, an influential medieval rabbi, philosopher, and physician, wrote a treatise on asthma, describing its prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.

Many asthmatics, like those who suffer from other chronic disorders, use alternative treatments; surveys show that roughly 50 percent of asthma patients use some form of unconventional therapy.

A Cochrane systematic review of acupuncture for asthma found no evidence of efficacy.

The fundamental problem in asthma appears to be immunological: young children in the early stages of asthma show signs of excessive inflammation in their airways.

The study showed that children in the high ozone communities who played three or more sports developed asthma at a rate three times higher than those in the low ozone communities.

Epidemiological findings give clues as to the pathogenesis (or its origin): the incidence of asthma seems to be increasing worldwide, and asthma is now much more common in affluent countries.

A randomized, controlled trial of just 39 patients in 1998 suggested that this method may moderately reduce the need for beta-agonists among asthmatics, but found no objective improvement in lung function.

Current research suggests that the prevalence of childhood asthma has been increasing.

Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) (a mechanism where air is directly delivered into the airway) is used to treat OSA, but is not effective in patients with nocturnal asthma only.
Later, when an asthmatic inhales the same allergen, these antibodies "recognize" it and activate a humoral response.

Hippocrates thought that the spasms associated with asthma were more likely to occur in tailors, anglers, and metalworkers.

Asthma is strongly suspected if a patient suffers from eczema (an inflamed skin condition) or other allergic conditions—suggesting a general atopic (allergy-related) constitution—or has a family history of asthma.

Many studies have linked asthma, bronchitis, and acute respiratory illnesses to air quality experienced by children.

On the remote South Atlantic island Tristan da Cunha, 50 percent of the population are asthmatics due to heredity transmission of a mutation in the gene CC16.

Despite the severity of symptoms during an asthmatic episode, between attacks an asthmatic may show few signs of the disease.

The most effective treatment for asthma is identifying triggers, such as pets or aspirin, and limiting or eliminating exposure to them.

The inflammatory response is responsible for the clinical manifestations of an asthma attack.

The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that some 8 percent of the Swiss population suffers from asthma today, compared with just 2 percent some 25–30 years ago.

One survey of participants in the 1996 Summer Olympic Games showed that 15 percent had been diagnosed with asthma, and that 10 percent were taking asthma medication.

The specific medical treatment recommended to patients with asthma depends on the severity of their illness and the frequency of their symptoms.

Second, it has also been suggested that some professional athletes who do not suffer from asthma claim to in order to obtain special permits to use certain performance-enhancing drugs.
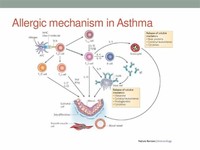
The mechanisms behind allergic asthma—i.e., asthma resulting from an immune response to inhaled allergens—are the best understood of the causal factors.

Specific treatments for asthma are broadly classified as relievers, preventers, and emergency treatment.

Testing peak flow at rest (or baseline) and after exercise can be helpful, especially in young asthmatics who may experience only exercise-induced asthma.
Once a diagnosis of asthma is made, a patient can use peak flow meter testing to monitor the severity of the disease.
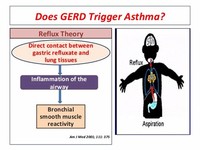
GERD may be common in difficult-to-control asthma, but generally speaking, treating it does not seem to affect the asthma.

There appears to be a relatively high incidence of asthma in sports such as cycling, mountain biking, and long-distance running, and a relatively lower incidence in weightlifting and diving.

Researchers at Harvard Medical School (HMS) have come up with convincing evidence that the answer to what causes asthma lies in a special type of natural "killer" cell.

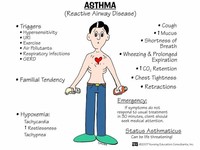
Asthma is a chronic disease of the respiratory system in which the airway occasionally constricts, becomes inflamed, and is lined with excessive amounts of mucus, often in response to one or more triggers.

In both asthmatics and non-asthmatics, inhaled allergens that find their way to the inner airways are ingested by a type of cell known as antigen presenting cells, or APCs.

Another theory is based on the correlation of air pollution and the incidence of asthma.

A recent meta-analysis of the roles of long-acting beta-agonists may indicate a danger to asthma patients.

The word asthma is derived from the Greek aazein, meaning "sharp breath."

Before diagnosing someone as asthmatic, alternative possibilities should be considered.

Public attention in the developed world has recently focused on asthma because of its rapidly increasing prevalence, affecting up to one in four urban children.

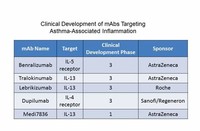
A novel therapeutic target currently under investigation is the A2B receptor, a cell surface G-protein coupled receptor expressed in the lungs and in inflammatory cells expressed in asthma.

The quality of asthma treatment varies along racial lines, likely because many low-income people cannot afford health insurance and because there is still a correlation between class and race.

During very severe attacks, an asthma sufferer can turn blue from lack of oxygen, and can experience chest pain or even loss of consciousness.

Asthmatics who smoke typically require additional medications to help control their disease.

The incidence of asthma is higher among low-income populations within a society (even though it is more common in developed countries than developing countries).

The use of bronchodilators started in 1901, but it was not until the 1960s that the inflammatory component of asthma was recognized, and anti-inflammatory medications were added to the regimen.

Six centuries later, Galen wrote much about asthma, noting that it was caused by partial or complete bronchial obstruction.

More than 6 percent of children in the United States have been diagnosed with asthma, a 75 percent increase in recent decades.

The prognosis for asthmatics is good, especially for children with mild disease.

The symptoms of asthma, which can range from mild to life threatening, can usually be controlled with a combination of drugs and environmental changes.

Pulmonary aspiration (the entry of secretions or foreign material into the trachea and lungs), whether direct due to dysphagia (swallowing disorder) or indirect (due to acid reflux), can show similar symptoms to asthma.

Asthmatics sometimes stop taking their preventive medication when they feel fine and have no problems breathing.
Asthma triggers. Exposure to various irritants and substances that trigger allergies (allergens) can trigger signs and symptoms of asthma. Asthma triggers are different from person to person and can include: Airborne substances, such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander or particles of cockroach waste.Aug 30, 2016
A child's asthma can get better or worse over time and some very young children with asthma may get much better as they (and their lungs) grow, but for most people, asthma is present the rest of their lives. Some very young children have asthma symptoms that go away when they get older.
Exposure to allergens or irritants such as cigarette smoke, chemicals, mold, dust, or other substances commonly found in the person's environment (e.g. home or work place) might trigger the first asthma symptoms in an adult. ... Different illnesses, viruses, or infections can be a factor in adult onset asthma.
Asthma is a chronic disease of the airways that makes breathing difficult. With asthma, there is inflammation of the air passages that results in a temporary narrowing of the airways that carry oxygen to the lungs. This results in asthma symptoms, including coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.Mar 1, 2016
Here, the different types:Allergic asthma. This type occurs when an allergy sets off an asthma flare up. ... Asthma without allergies. People may also have asthma not triggered by allergies. ... Aspirin Exacerbated Respiratory Disease (AERD) ... Exercise induced asthma. ... Cough variant. ... Occupational asthma.
Asthma attack: 6 things to do if you do not have an inhaler with you.Sit upright. Stop whatever you are doing and sit upright. ... Take long, deep breaths. This helps to slow down your breathing and prevent hyperventilation. ... Stay calm. ... Get away from the trigger. ... Take a hot caffeinated beverage. ... Seek emergency medical help.
Determining your risk for a fatal asthma attack is important. Only a third of asthma deaths occur in the hospital, which means many asthma patients who die are either not seeking care or are not being hospitalized with their worsening asthma. Asthma and every attack have the potential to be life-threatening.Dec 19, 2017
The life expectancy for mild asthmatics is the same as for those who do not have asthma, which is about 80 years. (This is great news. So take care of yourself and you can live long and prosper). Only 10% of asthmatics develop severe asthma (That comes to less than 1-2% of the population, yet still significant).May 12, 2009
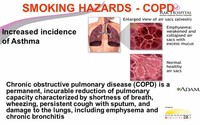
Having asthma doesn't up your odds of getting lung cancer, but if symptoms aren't controlled, it may eventually develop into chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD is basically an umbrella term used to describe treatable but irreversible lung conditions such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis.