Facts about Biology

Developmental biology involves study of life at the level of the development or ontogeny of an individual organism.

The word ology is thus misleading as the “o” is actually part of the word stem that receives the -logy ending, such as the bio part of biology.

Developmental biology studies the process by which organisms grow and develop.

Molecular biology chiefly concerns itself with understanding the interactions between the various systems of a cell, especially by mapping the interactions between DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis and learning how these interactions are regulated.

Biology, or "life science," offers a window into fundamental principles shared by living organisms.

Aspects of biology raising issues of bioethics include cloning, genetic engineering, population control, medical research on animals, creation of biological weapons, and so forth.
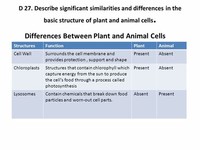
Appreciating the similarities and differences between cell types is particularly important to the fields of cell and molecular biology.

A speculative new field is astrobiology (or xenobiology) which examines the possibility of life beyond the Earth.

The field overlaps with other areas of biology, particularly genetics and biochemistry.

The word "biology" derives from Greek and is generally rendered as "study of life."
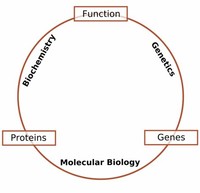
Among these are molecular biology, biochemistry, cell biology, physiology, anatomy, developmental biology, genetics, ecology, paleontology, and evolutionary biology.
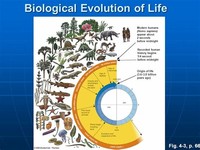
Evolutionary biology is concerned with the origin and descent of species, and their change over time, i.e., their evolution.

Related fields which are often considered part of evolutionary biology are phylogenetics, systematics, and taxonomy.

Biology has become such a vast research enterprise that it is not generally studied as a single discipline, but as a number of clustered sub-disciplines.

Two broad disciplines within biology are botany, the study of plants, and zoology, the study of animals.

Originating in embryology, today, developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation, and "morphogenesis," which is the process that gives rise to tissues, organs, and anatomy.

Biologists study life over a wide range of scales: Life is studied at the atomic and molecular scale in molecular biology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics.

The word "biology" in its modern sense seems to have been introduced independently by Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus (Biologie oder Philosophie der Lebenden Natur, 1802) and by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (Hydrogйologie, 1802).

A central, organizing concept in biology is that all life has descended from a common origin through a process of evolution.
Cell biology researches both single-celled organisms like bacteria and specialized cells in multicellular organisms like humans.

Evolutionary biology is an inclusive field because it includes scientists from many traditional taxonomically oriented disciplines.

The suffix "-logy" is common in science, in such words as geology, ecology, zoology, paleontology, microbiology, and so forth.

Model organisms for developmental biology include the round worm Caenorhabditis elegans, the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, the zebrafish Brachydanio rerio, the mouse Mus musculus, and the small flowering mustard plant Arabidopsis thaliana.

The purview of biology extends from the origin of life to the fundamental nature of human beings and their relationship to all other forms of life.

At the level of the cell, life is studied in cell biology, and at multicellular scales, it is examined in physiology, anatomy, and histology.

Changes over time, whether within populations (microevolution) or involving either speciation or the introduction of major designs (macroevolution), is part of the field of inquiry of evolutionary biology.

The common genetic and developmental mechanisms of animals and plants is studied in molecular biology, molecular genetics, and developmental biology.

Cell biology studies the physiological properties of cells, as well as their behaviors, interactions, and environment; this is done both on a microscopic and molecular level.
Depending on individual interests, biology careers can lead you on to study living organisms such as animals, plants, humans or even bacteria, to help develop biological knowledge and understanding of living processes for a number of different purposes, including treatment of disease and sustaining the natural ...Aug 15, 2014
The Biology major provides students with a broad base for understanding principles governing life processes at all levels–molecular, cellular, organismal, and ecological. An evolutionary perspective guides all areas of the curriculum–development, behavior, physiology, genetics, and more.
The term biology in its modern sense appears to have been introduced independently by Thomas Beddoes (in 1799), Karl Friedrich Burdach (in 1800), Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus (Biologie oder Philosophie der lebenden Natur, 1802) and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (Hydrogéologie, 1802).
Find Schools, Degrees or ProgramsAnimal Biology.Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics.Bioinformatics.Biology.Cellular Biology and Anatomy.Evolutionary Biology and Ecology.Genetic Sciences.Immunology and Microbiological Sciences.More items...
Biology is important to everyday life because it allows humans to better understand their bodies, their resources and potential threats in the environment. Biology is the study of all living things, so it helps people to understand every organism alive, from the smallest bacteria to California redwoods and blue whales.
There are many types of biologists. Some work on microorganisms, while others study multicellular organisms. There is much overlap between different fields of biology such as botany, zoology, microbiology, genetics and evolutionary biology, and it is often difficult to classify a biologist as only one of them.
From ecology to molecular biology, the science of biology studies them all. ... Biologists study the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution and distribution of living organisms.Aug 9, 2017
Biology is the study of life and living organisms. It is a broad field including many branches and subdisciplines. Biologists study structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, identification and taxonomy.Sep 27, 2016
Marine biologists must complete at least a bachelor's degree, which takes about four years. Marine biologists who pursue master's degrees may take an additional two to three years to complete their education, and earning a PhD will take up to six years more.



