Facts about Calcium

Subsequent methods of extraction have included electrolysis of calcium fluoride or calcium chloride.

Recommended daily calcium intake varies from 1,000 to 1,500 milligrams (mg), depending upon the person's stage of life.

The element calcium, however, was not isolated until 1808 in England, when Sir Humphry Davy electrolyzed a mixture of lime and mercuric oxide.

Calcium requirements must be met throughout life, but requirements are greatest during periods of growth, such as childhood, during pregnancy and when breast-feeding.

Medicinally, calcium carbonate is widely used as an inexpensive calcium supplement and antacid.

Calcium (chemical symbol Ca, atomic number 20) is the fifth most plentiful chemical element in the Earth's crust, occurring in various rocks, minerals, coral, and shells of marine animals.

Calcium oxide (CaO)—commonly known as lime, quicklime, or burnt lime—is a white, caustic, and alkaline crystalline solid.

Calcium burns with a yellow-red flame and forms a white nitride coating when exposed to air.

The ancient Romans are known to have prepared lime (calcium oxide) as early as the first century.

Calcium oxide is usually made by the thermal decomposition of materials (such as limestone) that contain calcium carbonate.

Calcium carbonate exhibits the properties typical of other carbonates.

Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), known as slaked lime, is a colorless crystal or white powder.

Long-term calcium deficiency can lead to osteoporosis, in which the bone deteriorates and there is an increased risk of fractures.
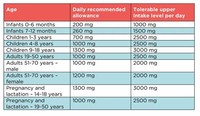
Calcium requirements must be met throughout life, but requirements are greatest during periods of growth, such as childhood, during pregnancy and when breast-feeding.

Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).

A suspension of fine calcium hydroxide particles in water, called lime water (or milk of lime), is a medium-strength chemical base that reacts violently with acids and attacks many metals.

Calcium carbonate is used in construction materials; calcium oxide is used for treating water, sewage, and acidic soils; and calcium hydroxide is used for processing water for beverages and neutralizing acids in the tanning industry.

Calcium hydroxide is also a filler used in the preparation of dry mixes for painting and decorating; manufacturing mixes for pesticides; and manufacturing brake pads.

Other important calcium compounds are its nitrate, sulfide, chloride, carbide, cyanamide, and hypochlorite.
Hyena (or Hyжna) is any terrestrial mammal in the subfamily Hyaeninae of the family Hyaenidae of the order Carnivora, typically characterized by a dog-like appearance, powerful jaws, and hind limbs shorter than fore limbs.

Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body and is an important component of a healthy diet.
Your body uses 99 percent of its calcium to keep your bones and teeth strong, thereby supporting skeletal structure and function. The rest of the calcium in your body plays key roles in cell signaling, blood clotting, muscle contraction and nerve function.
Top 10 Calcium Rich Foods1) Raw Milk. 1 cup: 300 mg (30% DV)2) Kale (cooked) 1 cup: 245 mg (24% DV)3) Sardines (with bones) 2 ounces: 217 mg (21% DV)4) Yogurt or Kefir. 6 oz: 300 mg (30% DV)5) Broccoli. 1 ½ cup cooked: 93 mg (9% DV)6) Watercress. 1 cup: 41 mg (4% DV)7) Cheese. 1 oz: 224 mg (22% DV)8) Bok Choy.More items...
Although calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the earth's crust, it is never found free in nature since it easily forms compounds by reacting with oxygen and water. Metallic calcium was first isolated by Sir Humphry Davy in 1808 through the electrolysis of a mixture of lime (CaO) and mercuric oxide (HgO).
The benefits of calcium. Your body needs calcium to build and maintain strong bones. Your heart, muscles and nerves also need calcium to function properly. Some studies suggest that calcium, along with vitamin D, may have benefits beyond bone health: perhaps protecting against cancer, diabetes and high blood pressure.Aug 5, 2015
If your body doesn't get enough calcium and vitamin D to support important functions, it takes calcium from your bones. This is called losing bone mass. Losing bone mass makes the inside of your bones become weak and porous. This puts you at risk for the bone disease osteoporosis.
Avoid soft drinks.Avoid soft drinks. ... Get enough vitamin D. Calcium is absorbed by the body and used only when there is enough vitamin D in your system. ... Eat your beans. ... Try canned salmon. ... Choose calcium-fortified foods. ... Include oatmeal in more than just breakfast.
Calcium and Milk. Calcium is important. But milk isn't the only, or even best, source. ... Good, non-dairy sources of calcium include collards, bok choy, fortified soy milk, baked beans, and supplements that contain both calcium and vitamin D (a better choice than taking calcium alone).
During menopause, women should also increase their calcium intake to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and calcium deficiency disease. ... People with this condition don't produce enough parathyroid hormone, which controls calcium levels in the blood. Other causes of hypocalcemia include malnutrition and malabsorption.Aug 25, 2017
In hypocalcemia, the calcium level in blood is too low. A low calcium level may result from a problem with the parathyroid glands, as well as from diet, kidney disorders, or certain drugs. ... Usually, the disorder is detected by routine blood tests. Calcium and vitamin D supplements may be used to treat hypocalcemia.
Deficiency. Low calcium or vitamin D levels may produce subtle symptoms or no noticeable symptoms at all, at least initially. Low blood calcium levels may make you feel tired, a symptom that may be accompanied by numbness in the extremities, muscle cramps and decreased appetite.




