Facts about Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles (compartments) found in plant cells and eukaryotic algae that conduct photosynthesis.

Utilizing chlorophyll and water, chloroplasts capture light energy from the sun to produce the free energy stored in ATP and NADPH through a process called photosynthesis.

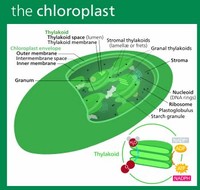
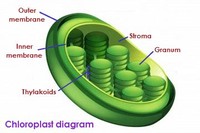
The chloroplast has a two membrane envelope termed the inner membrane and outer membrane, respectively.
The term chloroplast is derived from the Greek words chloros which means "green" and plast which means "form" ( in biological terms, it can be more roughly translated as organelle or cell ).

The chloroplast genome is considerably reduced compared to that of free-living cyanobacteria, but the parts that are still present show clear similarities.

Chloroplasts are flat discs usually two to ten micrometers (?m) in diameter and one micrometer thick.

Most of the sugars created in the chloroplast are converted by the plants into starch, which is stored in the plastids.

The theorized origin of chloroplasts—developed through a mutually-beneficial symbiotic relationship between a cyanobacteria and a prokaryote—reflects a view, advocated by Lynn Margulis, that life developed more through cooperation than through competition.

Chloroplasts are generally considered to have originated as endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
Chloroplasts absorb sunlight and use it in conjunction with water and carbon dioxide gas to produce food for the plant. Chloroplasts capture light energy from the sun to produce the free energy stored in ATP and NADPH through a process called photosynthesis.
The main role of chloroplasts is to conduct photosynthesis, where the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight and converts it and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water.
A chloroplast is an organelle unique to plant cells that contains chlorophyll (which is what makes plants green) and is responsible for enabling photosynthesis to occur so that plants can convert sunlight into chemical energy.
They are found in vascular plants, mosses, liverworts, and algae. Chloroplast organelles are responsible for photosynthesis , the process by which sunlight is absorbed and converted into fixed chemical energy in the form of simple sugars synthesized from carbon dioxide and water.
Two membranes contain and protect the inner parts of the chloroplast. They are appropriately named the outer and inner membranes. The inner membrane surrounds the stroma and the grana (stacks of thylakoids). One thylakoid stack is called a granum.
At various places within the chloroplast these are stacked in arrays called grana (resembling a stack of coins). Four types of protein assemblies are embedded in the thylakoid membranes: Photosystem I which includes chlorophyll and carotenoid molecules.

