Facts about Cloud

Red, orange, and pink clouds occur almost entirely at sunrise/sunset and are the result of the scattering of sunlight by the atmosphere.

The color of a cloud tells much about what is going on inside the cloud.

Yellowish clouds are rare but may occur in the late spring through early fall months during forest fire season.

Dense deep clouds exhibit a high reflectance (70-95 percent) throughout the visible range of wavelengths: they thus appear white, at least from the top.

Clouds form when relatively warm air containing water vapor is lighter than its surrounding air and this causes it to rise.

Cloud droplets tend to scatter light efficiently, so that the intensity of the solar radiation decreases with depth into the cloud, hence the gray or even sometimes dark appearance of the clouds at their base.

Orographic uplift also creates variable cloud forms depending on air stability, although cap cloud and wave clouds are specific to orographic clouds.

A cloud field is simply a group of clouds but sometimes cloud fields can take on certain shapes that have their own characteristics and are specially classified.

The scientific study of clouds is called nephology, which is a branch of meteorology.

The evening before the Edmonton, Alberta tornado in 1987, Edmontonians observed such clouds — deep black on their dark side and intense red on their sunward side.

Clouds are divided into two general categories: layered and convective.

Saturn's moon Titan has clouds which are believed to be composed largely of droplets of liquid methane.

The water in a typical cloud can have a mass of up to several million tonnes.

Conditions inside a cloud are not static: water droplets are constantly forming and re-evaporating.

Frontal uplift creates various cloud forms depending on the composition of the front (ana-type or kata-type warm or cold front).

The recently recognized phenomenon of global dimming is thought to be caused by changes to the reflectivity of clouds due to the increased presence of aerosols and other particulates in the atmosphere.

On Earth, clouds play an important part in the water cycle (hydrologic cycle).

The bluish color is evidence that such scattering is being produced by rain-sized droplets in the cloud.

A cumulonimbus cloud which shows green is a pretty sure sign of imminent heavy rain, hail, strong winds and possible tornadoes.

Both Jupiter and Saturn have an outer cloud deck composed of ammonia clouds, an intermediate deck of ammonium hydrosulfide clouds and an inner deck of water clouds.
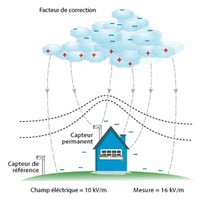
The effect of such electric fields has been suggested as an explanation of cloud formation.

Clouds can be formed when two air masses below saturation point mix.

At this altitude, water frequently freezes so clouds are composed of ice crystals.

The scientific study of clouds is called nephology, which is a branch of meteorology.

A typical cloud droplet has a radius on the order of 1 x 10-5 m and a terminal velocity of about 1-3 cm/s.

The actual form of the cloud created depends on the strength of the uplift and on air stability.

The clouds are not that color; they are reflecting the long (and unscattered) rays of sunlight which are predominant at those hours.

A cloud is a visible mass of condensed droplets, frozen crystals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of the Earth or other planetary body, such as a moon.

A few clouds can be found above the troposphere; these include noctilucent and polar stratospheric clouds (or nacreous clouds), which occur in the mesosphere and stratosphere respectively.

Clouds are divided into two general categories: layered and convective.
Precipitation: What makes clouds, rain, snow, hail and sleet. When warm, wet air rises, it cools, and water vapor condenses out to form clouds. A cloud is made up of small drops of water or ice crystals, depending on its height and how cold is the surrounding air.
Clouds consist of tiny drops of condensed water vapor, small enough to float in the air. If you have ever been in a thick fog at ground level , you know what clouds feel like. You will get damp or maybe slightly wet.