Facts about Diamond

A diamond simulant is defined as a non-diamond material that is used to simulate the appearance of a diamond.

Ayer's multifaceted marketing campaign included product placement, advertising the diamond itself rather than the De Beers brand, and building associations with celebrities and royalty.

A weekly diamond price list, the Rapaport Diamond Report is published by Martin Rapaport, CEO of Rapaport Group of New York, for different diamond cuts, clarity and weights.

The Kimberley Process provides documentation and certification of diamond exports from producing countries to ensure that the proceeds of sale are not being used to fund criminal or revolutionary activities.

A well-executed round brilliant cut should reflect light upwards and make the diamond appear white when viewed from the top.

One such substance, which is heavily advertised, is what scientists refer to as "diamond-like carbon."

The company and its subsidiaries own mines that produce some 40 percent of annual world diamond production.

A poorly cut diamond with facets cut only a few degrees out of alignment can result in a poorly performing stone.

The diamond supply chain is controlled by a limited number of powerful businesses, and is also highly concentrated in a small number of locations around the world.

The conditions for diamond formation to happen in the lithospheric mantle occur at considerable depth corresponding to the aforementioned requirements of temperature and pressure.

Fire refers to the spectral colors which are produced as a result of the diamond dispersing the white light.

A diamond is a transparent crystal of tetrahedrally bonded carbon atoms and crystallizes into the face centered cubic diamond lattice structure.

A diamond that is cut and polished to produce a high level of these qualities is said to be high in light performance.
WFDB's additional activities also include sponsoring the World Diamond Congress every two years, as well as the establishment of the International Diamond Council (IDC) to oversee diamond grading.

An inferior cut will produce a stone that appears dark at the center and in some extreme cases the ring settings may show through the top of the diamond as shadows.

The skill with which a diamond is cut determines its ability to reflect and refract light.

In bezel settings the diamond or gemstone is completely surrounded by a rim of metal, which can be molded into any shape to accommodate the stone.

The popularity of the diamond ring as an engagement ring for a much wider audience can be traced directly to the marketing campaigns of De Beers, starting in 1938.

A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond is perfectly transparent with no hue, or color.

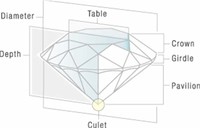
The function of the crown is to diffuse light into various colors and the pavilion's function to reflect light back through the top of the diamond.

Traditional diamond cutting centers are Antwerp, Amsterdam, Johannesburg, New York, and Tel Aviv.

The De Beers company, as the world's largest diamond miner holds a clearly dominant position in the industry, and has done so since soon after its founding in 1888 by the British imperialist Cecil Rhodes.

Pliny wrote that a diamond baffles poison, keeps off insanity and dispels vain fears.

The princess cut is also popular amongst diamond cutters: of all the cuts, it wastes the least of the original crystal.

In 2005, Russia produced almost one-fifth of the global diamond output, reports the British Geological Survey.

The GIA has developed a set of criteria for grading the cut of round brilliant stones that is now the standard in the diamond industry and is called "Facetware."

Tolkowsky's mathematical model is now superseded by the GIA Facetware software that is the culmination of 20 years of studies on diamond cuts.

Diamond prospectors continue to search the globe for diamond-bearing kimberlite and lamproite pipes.

is also widely used for diamond necklaces, bracelets and other similar jewelry pieces.

The process of shaping a rough diamond into a polished gemstone is both an art and a science.

Other characteristics not described by the four Cs influence the value or appearance of a gem diamond.

The oldest dated printed book in the world is called the Diamond Sutra, dates from 868 C.E.

Diamond-bearing volcanic pipes are closely related to the oldest, coolest regions of continental crust (cratons).

Recently, diamond cutting centers have been established in China, India, and Thailand.

Common industrial adaptations of this ability include diamond-tipped drill bits and saws, or use of diamond powder as an abrasive.

The settled areas of Tasmania have an extensive network of good-quality roads, the primary form of transport.

The cut of a diamond describes the manner in which a diamond has been shaped and polished from its beginning form as a rough stone to its final gem proportions.

Specialized applications include use in laboratories as containment for high pressure experiments (see diamond anvil), high-performance bearings, and limited use in specialized windows.

The gemological and industrial uses of diamond have created a large demand for rough stones.

Coatings are more and more used to give a diamond simulant such as Cubic Zirconia a more "Diamond like" appearance.

Traditionally, diamond cutters in these cities are Orthodox Jews or Chasidim.

Diamond's hardness has been known since antiquity, and is the source of its name.

The company announced that it asked the president of the World Federation of Diamond Bourses to make the examination next week.

A number of factors, including proportion, polish, symmetry, and the relative angles of various facets, are determined by the quality of the cut and can affect the performance of a diamond.

The Romans valued the diamond entirely on account of its supernatural powers.

According to the Gospel of Matthew, after Jesus' resurrection, many of the dead saints came out of their tombs and entered Jerusalem, where they appeared to many.

Inclusions may be crystals of a foreign material or another diamond crystal, or structural imperfections such as tiny cracks that can appear whitish or cloudy.

Observations indicate that the core is a diamond crystal 4000 km in diameter, with a corresponding weight of over 5?Ч?1026 carats.

Several different theories on the "ideal" proportions of a diamond have been and continue to be advocated by various owners of patents on machines to view how well a diamond is cut.

The diamond is the birthstone for people born in the month of April, and is also used as the symbol of a 60-year anniversary, such as a Diamond Jubilee (see hierarchy of precious substances).

Not all rain reaches the surface, however—some evaporates while falling through dry air.

Australia boasts the richest diamondiferous pipe with production reaching peak levels of 42 Mct per year in the 1990s.

In 1919, Marcel Tolkowsky developed an ideal round brilliant cut design that has set the standard for comparison of modern gems; however, diamond cuts have continued to be refined.

New diamond cuts are now all the rage in the diamond industry as for example a design invented in 2003 and called the "Genesis cut."

The name diamond derives from the ancient Greek adamas (??????), meaning "invincible."

Garnering much excitement is the possible use of diamond as a semiconductor suitable to build microchips from, or the use of diamond as a heat sink in electronics.

Diamond crystals are formed deep within the Earth, under conditions of high pressure and high temperature.

Diamond wedding rings didn't gain widespread social significance until the De Beers company started marketing the idea through cinema beginning in the 1940s.
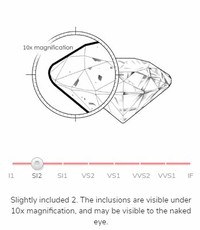
Clarity is a measure of internal defects of a diamond called inclusions.

Ownership was restricted among various castes by color, with only kings being allowed to own all colors of diamond.

India led the world in diamond production from the time of their discovery in approximately the ninth century B.C.E.

Most diamond impurities replace a carbon atom in the crystal lattice, known as a carbon flaw.

which, because of the axes' specular surfaces, the scientists believe were polished using diamond powder.

When a diamond is cut for too much "fire," it looks like a cubic zirconia, which gives off much more "fire" than real diamond.

Diamond formation requires exposure of carbon-bearing materials to high pressure, ranging approximately between 45 and 60 kilobars, but at a comparatively low temperature range between approximately 1652–2372 °F (900–1300 °C).

So a poorly cut 1.0 carat diamond may have the same diameter and appear as large as a 0.85 carat diamond.

One of the first occurrences of the diamond engagement (or wedding) ring can be traced back to the marriage of Maximilian I (then Archduke of Austria) to Mary of Burgundy in 1477.

The dominant industrial use of diamond is in cutting, drilling, grinding, and polishing.

The toughness of natural diamond has been measured as 3.4 MN m-3/2, which is good compared to other gemstones, but poor compared to most engineering materials.

Large cracks close to or breaking the surface may reduce a diamond's resistance to fracture.

The color of a diamond may be affected by chemical impurities and/or structural defects in the crystal lattice.

The largest flawless and colorless (grade D) diamond is the Centenary Diamond which weighs 273.85 carats.

At the high temperatures created by high speed machining, carbon is soluble in iron, leading to greatly increased wear on diamond tools as compared to other alternatives.

Long residence in the cratonic lithosphere allows diamond crystals to grow larger.

Naturally occurring diamond has a density ranging from 3.15 to 3.53 g/cmі, with very pure diamond typically extremely close to 3.52 g/cmі.

Scintillation refers to the small flashes of light that are seen when the diamond, light source or the viewer is moved.

Maintaining a clean diamond can sometimes be difficult as jewelry settings can obstruct cleaning efforts and oils, grease, and other hydrophobic materials adhere well to a diamond's surface.

The cut of a diamond describes the quality of workmanship and the angles to which a diamond is cut.

Diamond-bearing rock is brought close to the surface through deep-origin volcanic eruptions.

Water, dirt, or grease on the bottom of a diamond interferes with the diamond's brilliance and fire.

The magma itself does not contain diamond; instead, it acts as an elevator that carries deep-formed rocks (xenoliths), minerals (xenocrysts), and fluids upward.

Travis Metcalfe, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, believes that the galaxy's largest diamond is the core of the white dwarf star BPM 37093.

Today, most commercially viable diamond deposits are in Russia, Botswana, Australia and the Democratic Republic of Congo.

Diamond cutting is the art and science of creating a gem-quality diamond out of mined rough.

The further the diamond's characteristics are from Tolkowsky's ideal, the less light will be reflected.

The past decades have seen the development of new diamond cuts, often based on a modification of an existing cut.

The Auschwitz camps were a major element in the perpetration of the Holocaust.

The WFDB consists of independent diamond bourses in major cutting centers such as Tel Aviv, Antwerp, Johannesburg and other cities across the USA, Europe and Asia.

The most common impurity, nitrogen, replaces a small proportion of carbon atoms in a diamond's structure and causes a yellowish to brownish tint.

Diamond is the hardest known natural material and the third-hardest known material after aggregated diamond nanorods and ultrahard fullerite.

By 1375, a guild of diamond polishers had been established at Nuremberg.

The number, size, color, relative location, orientation, and visibility of inclusions can all affect the relative clarity of a diamond.

The Cullinan Diamond, part of the British crown jewels, was the largest gem-quality rough diamond ever found (1905), at 3,106.75 carats.

Diamond is therefore more fragile in some orientations than others.

The De Beers diamond advertising campaign is acknowledged as one of the most successful and innovative campaigns in history.

A clean diamond is more brilliant and fiery than the same diamond when it is "dirty."

Advertising suggests (righfully so or not) that such a coating would transfer some of these diamond-like properties to the coated stone, hence enhancing the diamond simulant.

Materials which have similar gemological characteristics to diamond but are not mined or synthetic diamond are known as diamond simulants.

Diamond solitaire earrings, for example, are usually quoted in t.c.w.
Try the 'Fog Test' (or 'Breath Test'): Since diamonds are efficient heat conductors, once you breathe on a real diamond the fog should disperse immediately. If the stone is a fake diamond the top will stay foggy for a few seconds longer. This test works best with a clean stone.
Because of heat conduction, Diamonds are cold to the feel at or below room temperature. ... The luster of Diamond is excellent. Diamond exhibits great "fire" and brilliance, which gives it a shiny, freshly polished look. Rough Diamonds exhibit a greasy luster, but proper cutting give them a powerful adamantine luster.
The most notable use of Diamonds is in the jewelry market. Due to the brilliance, hardness, and rarity of Diamond, it is the most famous of all gemstones. Colorless Diamonds are most often used in jewelry, although recently yellow and brown gems have picked up in popularity.
Because diamonds are so strong (scoring a 10 on the Mohs Hardness Scale), they are extremely effective at polishing, cutting, and drilling. Many industries – including automotive, mining, and military – use diamond saws and drills. ... Diamond particles are also important to the “circle of diamond life”.Dec 11, 2014
The popularity of diamond-eating suggests internal organs are an optimal hiding place for stolen hardware. But what happens to your innards when you swallow a diamond? As one of the hardest materials on Earth, there's little risk of diamonds decomposing inside your body, but can they hurt you in some other way?Sep 5, 2012
Diamond membranes are durable, resistant to heat, and transparent, making them highly useful. Because diamonds are so hard and durable, they are ideal for grinding, cutting, drilling, and polishing. When used as an abrasive, very small pieces of diamond are embedded into grinding wheels, saw blades, or drill bits.
(it seems like a diamond is somewhat stronger…) Actually Titanium is not stronger nor harder than a good grade steel, the only advantage it has over steel is the fact it is a much lighter metal with similar to steel qualities. Though it doesn't even come close to a Diamond in strength or hardness.