Facts about Dinosaur
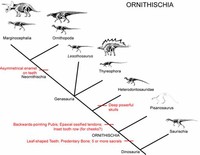
Ornithischians ('bird-hipped', from the Greek ornitheos (?????????) meaning 'of a bird' and ischion (??????) meaning 'hip joint') is the other dinosaurian order, most of which were quadrupedal herbivores.

There has been much speculation about the use of technology to bring dinosaurs back to life.

The well-preserved feathered dinosaurs in China have further consolidated the link between dinosaurs and their conjectured living descendants, modern birds).

Modern birds are classified by most paleontologists as belonging to the subgroup Maniraptora, which are coelurosaurs, a kind of theropods, which are saurischians, which are dinosaurs (Padian 2004).

The atmosphere's composition during the dinosaur era was vastly different as well.

The popular preoccupation with dinosaurs is also reflected in a broad array of fictional and non-fictional works.

The field of dinosaur research has enjoyed a surge in activity that began in the 1970s and is ongoing.

Most discussions of dinosaur endothermy tend to compare them to average birds or mammals, which expend energy to elevate body temperature above that of the environment.

Large meat-eating dinosaurs had a complex system of air sacs similar to those found in modern birds, according to an investigation which was led by paleontologist Patrick O'Connor.

Birds and non-avian dinosaurs (dinosaurs in common, non-cladistic terminology) share many features.

A vigorous debate on the subject of temperature regulation in dinosaurs has been ongoing since the 1960s.

A recently discovered troodont fossil demonstrates that the dinosaurs slept like certain modern birds, with their heads tucked under their arms (Xu and Norell 2004).
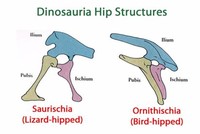
Dinosaurs are divided into Ornithischia (bird-hipped) and Saurischia (lizard-hipped), depending upon the pelvic girdle structure.

Interpretations of dinosaur behavior are generally based on the pose of body fossils and their habitat, computer simulations of their biomechanics, and comparisons with modern animals in similar ecological niches.

Modern birds are generally considered to be the direct descendants of theropod dinosaurs.

Dinosaurs may have congregated in herds for defense, for migratory purposes, or to provide protection for their young.

Many fields of study contribute to our understanding of dinosaurs, including physics, chemistry, biology, and the earth sciences (of which paleontology is a sub-discipline).

Dinosaur remains have been found on every continent on Earth, including Antarctica.

Paleontologists mostly use cladistics, which classifies birds as dinosaurs, although some biologists do not.

The discovery of primitive, dinosaur-like ornithodirans such as Marasuchus and Lagerpeton in Argentinian Middle Triassic strata supports this view; analysis of recovered fossils suggests that these animals were indeed small, bipedal predators.

The term dinosaur is sometimes used informally to describe other prehistoric reptiles, such as the pelycosaur Dimetrodon, the winged pterosaurs, and the aquatic ichthyosaurs, plesiosaurs, and mosasaurs, although technically none of these were dinosaurs.

Current evidence suggests that dinosaur average size varied through the Triassic, early Jurassic, late Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods (Holtz, 1998).

One of the best examples of soft tissue impressions in a fossil dinosaur was discovered in Petraroia, Italy.

There have not been any few indications climbing species of dinosaurs, and no indication of a burrowing species.

Comparison of bird and dinosaur skeletons, as well as cladistic analysis, strengthens the case for the link, particularly for a branch of theropods called maniraptors.

Major new dinosaur discoveries have been made by paleontologists working in previously unexploited regions, including India, South America, Madagascar, and most significantly in China.

Regardless of body type, nearly all known dinosaurs were well-adapted for a predominantly terrestrial—that is, land-bound—rather than aquatic or aerial, habitat.

The term "pain" is a subjective experience that typically accompanies nociception, but can also arise without any stimulus, and thus it includes the emotional response.

Scientists are not certain whether dinosaurs were thriving or declining before the impact event.

The fight between the two scientists lasted for over 30 years, ending in 1897 when Cope died after spending his entire fortune on the dinosaur hunt.

The open, or "perforate," hip joint of dinosaurs had significant implications for dinosaur movement and behavior.

During the period of dinosaur predominance, which encompassed the ensuing Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, nearly every known land animal larger than 1 meter in length was a dinosaur.
Using the strict cladistical definition that all descendants of a single common ancestor are related, modern birds are dinosaurs and dinosaurs, therefore, are not extinct.

Nests and eggs have been found for most major groups of dinosaurs, and it appears likely that dinosaurs communicated with their young, in a manner similar to modern birds and crocodiles.

The Mesozoic is often called the "Age of Dinosaurs" after the dominant fauna of the era.

The feathered dinosaurs discovered so far include Beipiaosaurus, Caudipteryx, Dilong, Microraptor, Protarchaeopteryx, Shuvuuia, Sinornithosaurus, Sinosauropteryx, and Jinfengopteryx.

After dinosaurs were discovered, paleontologists first posited that they were ectothermic creatures: "terrible lizards" as their name suggests.

Dinosaurs are an extinct, diverse, largely terrestrial group of vertebrate animals of the Sauropsid orders Saurischia (lizard-hipped) and Ornithischia (bird-hipped) and were the dominant land reptiles for over 160 million years, during the Mesozoic era.

The fossil includes portions of the intestines, colon, liver, muscles, and windpipe of this immature dinosaur (Dal Sasso and Signore 1998).

Modern evidence indicates that dinosaurs thrived in cooler temperate climates, and that at least some dinosaur species must have regulated their body temperature by internal biological means (perhaps aided by the animals' bulk).

Despite their unrefined methods, the contributions of Cope and Marsh to paleontology were vast; Marsh unearthed 86 new species of dinosaur and Cope discovered 56, for a total of 142 new species.

Ornithischian dinosaurs had a four-pronged pelvic configuration, incorporating a caudally-directed (rear-pointing) pubis bone with (most commonly) a forward-pointing process.

Birds are cited in the definition of Saurischia because there is an almost universal consensus among paleontologists that birds are the descendants of theropod dinosaurs (bipedal saurischian dinosaurs).

The sudden mass extinction of non-avian dinosaurs, an event that occurred approximately 65 million years ago, is one of the most intriguing mysteries in paleontology.

Paleontologist Jack Horner's 1978 discovery of a Maiasaura ("good mother dinosaur") nesting ground in Montana demonstrated that parental care apparently continued long after birth among the ornithopods (Lessem and Glut 1993).

According to a 2006 study, 527 dinosaur genera have been identified with certainty so far, and 1,844 genera are believed to have existed (Wang and Dodson 2006, Fountain 2006).

Another piece of evidence that birds and dinosaurs are closely related is the use of gizzard stones.

Most dinosaurs, however, were much smaller than the giant sauropods.

In 1858, the first known American dinosaur was discovered, in marl pits in the small town of Haddonfield, New Jersey (although fossils had been found before, their nature had not been correctly discerned).

The widespread application of cladistics, which rigorously analyzes the relationships between biological organisms, has also proved tremendously useful in classifying dinosaurs.

Vertebrate paleontology, arguably the primary scientific discipline involved in dinosaur research, has become a global science.

Current dinosaur "hot spots" include southern South America (especially Argentina) and China.

Scrutiny under the microscope further revealed that the putative dinosaur soft tissue had retained fine structures (microstructures) even at the cellular level.

The longest complete dinosaur is the 27 m (89 ft) long Diplodocus, which was discovered in Wyoming in the United States and displayed in Pittsburgh's Carnegie Natural History Museum in 1907.

William Buckland, a professor of geology at Oxford University, unearthed more fossilized bones of Megalosaurus and became the first person to describe dinosaurs in a scientific journal.

Under phylogenetic taxonomy (classification centered on evolutionary relatedness), dinosaurs are defined as descendants of the most recent common ancestor of Triceratops and modern birds.

Birds share over a hundred distinct anatomical features with theropod dinosaurs, which are generally accepted to have been their closest ancient relatives (Mayr 2005).

The study of these "great fossil lizards" soon became of great interest to European and American scientists, and in 1842 the English paleontologist Richard Owen coined the term "dinosaur."

Unfortunately, many valuable dinosaur specimens were damaged or destroyed due to the pair's rough methods; for example, their diggers often used dynamite to unearth bones (a method modern paleontologists would find appalling).

Foulke's discoveries sparked a wave of dinosaur mania in the United States.

Skeletal structures suggest that theropods and other dinosaurs had active lifestyles better suited to an endothermic cardiovascular system, while sauropods exhibit fewer endothermic characteristics.

At the peak of the dinosaur era, there were no polar ice caps, and sea levels are estimated to have been from 100 to 250 meters (330 to 820 feet) higher than they are today.

Dinosaur legs extend directly beneath the body, whereas the legs of lizards and crocodylians sprawl out to either side.

Megalosaurus was the first dinosaur to be formally described, in 1677, when part of a bone was recovered from a limestone quarry at Cornwell near Oxford, England.

Dinosaur ectothermy remained a prevalent view until Robert T. "Bob" Bakker, an early proponent of dinosaur endothermy, published an influential paper on the topic in 1968.

Archaeopteryx, the first good example of a "feathered dinosaur," was discovered in 1861.

Not including modern birds like the bee hummingbird, the smallest dinosaurs known were about the size of a crow or a chicken.

Paleontologists believe Eoraptor resembles the common ancestor of all dinosaurs (Hayward 1997).

Within the archosaur group, dinosaurs are differentiated most noticeably by their gait.

China in particular has produced many exceptional feathered dinosaur specimens due to the unique geology of its dinosaur beds, as well as an ancient arid climate particularly conducive to fossilization.

Collectively, dinosaurs are usually regarded as a superorder or an unranked clade.

Dinosaurs have become a part of world culture and remain consistently popular among children and adults alike.

The tallest and heaviest dinosaur known from good skeletons is Brachiosaurus brancai (also known as Giraffatitan).

The relatively sudden demise of dinosaurs, after a long period of dominance, provided the foundation for events such as the rise of mammals and birds.

From a behavioral standpoint, one of the most valuable dinosaur fossils was discovered in the Gobi Desert in 1971, when paleontologists unearthed a Velociraptor attacking a Protoceratops, illustrating interspecific predation.

The smallest dinosaur was bigger than two-thirds of all current mammals; the majority of dinosaurs were bigger than all but 2% of living mammals (Erickson 2005).

Radiometric dating of fossils from the early dinosaur genus Eoraptor establishes its presence in the fossil record at this time.

Note that the terms indicate the origin of the groups, not their modern distribution: the Chinese water deer, for example, is a New World species, but is found only in China and Korea.

By human standards, dinosaurs were creatures of fantastic appearance and often enormous size.

Notable examples of older fictional works featuring dinosaurs include Arthur Conan Doyle's book The Lost World; the 1933 film King Kong; and Godzilla.

The successful extraction of ancient DNA from dinosaur fossils has been reported on two separate occasions, but upon further inspection and peer review, neither of these reports could be confirmed (Wang et al.

Dinosaur fossils have been known for millennia, although their true nature was not recognized.

Numerous fossils of the same dinosaur species have been found on completely different continents, corroborating the generally-accepted theory that all land masses were at one time connected in a super-continent called Pangaea.

Vertical limb configuration also enabled dinosaurs to breathe easily while moving, which likely permitted stamina and activity levels that surpassed those of sprawling reptiles.

The second dinosaur species to be identified, Iguanodon, was discovered in 1822 by the English geologist Gideon Mantell, who recognized similarities between his fossils and the bones of modern iguanas.

A dinosaur embryo was found without teeth, suggesting that some parental care was required to feed the young dinosaur.

More recently, the presence of endothermy among dinosaurs has become the consensus view, and debate has focused on the mechanisms of temperature regulation.

The largest known carnivorous dinosaur was Spinosaurus, reaching a length of 16-18 meters (53-60 ft), and weighing in at 9 tons (dal Sasso et al.

Dinosaur-like birds like Confuciusornis, which are anatomically closer to modern avians, have also been discovered.

The lungs of theropod dinosaurs (carnivores that walked on two legs and had birdlike feet) likely pumped air into hollow sacs in their skeletons, as is the case in birds.

Anatomically, dinosaurs share many other archosaur characteristics, including teeth that grow from sockets rather than as direct extensions of the jawbones.

Another piece of evidence that birds and dinosaurs are closely related is the use of gizzard stones.

The Chinese, whose own word for dinosaur is konglong (??, or "terrible dragon"), considered them to be dragon bones and documented them as such.

Originally, scientists broadly disagreed as to whether dinosaurs were capable of regulating their body temperatures at all.

Dinosaurs first appeared approximately 230 million years ago (mya) during the Triassic and disappeared at the end of the Cretaceous period, approximately 65 mya, when a catastrophic extinction event ended their dominance on land.

Modern computerized tomography (CT) scans of a dinosaur chest cavity conducted in 2000 found the apparent remnants of a complex four-chambered heart, much like those found in today's mammals and birds (Fisher et al.
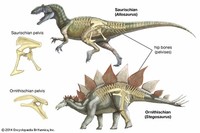
By contrast, the pelvic structure of saurischian dinosaurs was three-pronged, and featured a pubis bone directed cranially, or forwards, only (Benton 2004b).

Dinosaur exhibitions and displays at parks and museum exhibits around the world both cater to, and reinforce, this public interest.
A dinosaur the size of a Labrador retriever walked the Earth about 243 million years ago, suggesting the first reptiles were born much earlier than previously thought. Scientists who identified the newly identified species, Nyasasaurus parringtoni, believe it may have been the first dinosaur ever to have lived.Dec 5, 2012
Approximately 230 million years ago, during the Triassic Period, the dinosaurs appeared, evolved from the reptiles. Plateosaurus was one of the first large plant-eating dinosaurs, a relative of the much larger sauropods.
Troodon
The Fastest Running Dinosaur. The speediest dinosaurs were the ostrich mimic ornithomimids, such as Dromiceiomimus, which could probably run at speeds of up to 60 kilometres per hour.
Most of the largest herbivorous specimens on record were discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive titanosaur Argentinosaurus huinculensis, which is the largest dinosaur known from uncontroversial evidence, estimated to have been 96.4 metric tons (106.3 short tons) and 39.7 m (130 ft) long.
Huge dinosaurs with short legs, like Apatosaurus, Diplodocus, Brachiosaurus, and the other sauropods, were probably among the slowest of the dinosaurs.
That gives whales the advantage. Supersaurus weighed about as much as seven African elephants, a traditional unit of measurement for dinosaur size. The blue whale is the largest animal alive on Earth today, although the exact maximum size is something of a moving target in the literature.Apr 22, 2014
It may have acted as a radiator, helping Triceratops regulate its body temperature. This ceratopsian, or horned dinosaur, was one of the last dinosaurs in the late Cretaceous period. It lived just before the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction 65 million years ago.Sep 10, 2010
Most of the largest herbivorous specimens on record were discovered in the 1970s or later, and include the massive titanosaur Argentinosaurus huinculensis, which is the largest dinosaur known from uncontroversial evidence, estimated to have been 96.4 metric tons (106.3 short tons) and 39.7 m (130 ft) long.
Visitors were mesmerized by the tooth, specially compared to a modern shark's tooth, and liked to call Megalodon a “dinosaur shark.” Well, the Megalodon was definitely not a dinosaur, and is much younger than dinosaurs. It was still around 2 million years ago.Aug 12, 2013


