Facts about Isotopes

Given that the chemical behavior of an atom is largely determined by its electronic structure, the isotopes of a particular element exhibit nearly identical chemical behavior.

Several applications capitalize on properties of the various isotopes of a given element.

After the initial coalescence of the solar system, isotopes were redistributed according to mass (see also Origin of the Solar System).

The main exception to this rule is what is called the "kinetic isotope effect": heavier isotopes tend to react somewhat more slowly than lighter isotopes of the same element.

Many people are aware that specific radioactive isotopes are used to produce nuclear power and nuclear weapons.
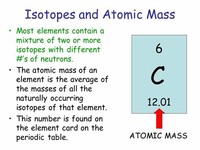
The tabulated atomic mass of an element is an average that takes into account the presence of multiple isotopes with different masses and in different proportions.

The isotopes of a given element have nearly identical chemical properties but their physical properties show somewhat greater variation.

According to generally accepted cosmology, virtually all nuclides—other than isotopes of hydrogen and helium, and traces of some isotopes of lithium, beryllium, and boron—were built in stars and supernovae.

The term isotope comes from Greek and means "at the same place"—all the different isotopes of an element are placed at the same location on the periodic table.

Based on these differences, the element can have different forms known as isotopes, each of which is made up of atoms with the same atomic structure.


