Facts about Jamaica

Jamaica is a full and participating member of the Caribbean Community, or CARICOM.

Internationally known reggae musician Bob Marley was born in Jamaica and has a large following there and around the world.

Jamaica has traditionally had a two-party system, with power often alternating between the People's National Party and Jamaica Labour Party (JLP).

Jamaica is a mixed, free-market economy with state enterprises as well as private sector businesses.

In 2006, Jamaica became part of the CARICOM Single Market and Economy (CSME) as one of the pioneering members.

Other religions in Jamaica include: Bahai, Buddhism, Islam, and Judaism.

Jamaica's current Constitution was drafted in 1962 by a bipartisan joint committee of the Jamaica legislature.

The Jamaican Athletics Team has been well represented at the Olympics over the years with leading athletes obtaining gold medals.

In 1980, for example, Hurricane Allen destroyed nearly all Jamaica's banana crop.

Jamaica is 391 miles (635 km) east of Nicaragua on the Central American mainland, 93 miles (150 km) south of Cuba, and 100 miles (160 km) west of Haiti on the island of Hispaniola.

The former capital of Jamaica was Spanish Town in the parish of Saint Catherine, the site of the old Spanish colonial capital.

The Jamaican head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who officially uses the title "Queen of Jamaica" when she periodically visits the country or performs duties overseas on Jamaica's behalf.

Overall, the Jamaican 2008 Olympic team finished ranking 13th out of 204 competing nations with 11 medals: 6 golds, 3 silvers and 2 bronze.

The Institute of Jamaica, a promoter of the arts, sponsors exhibitions and awards.

Jamaica began to lag economically with its gross national product falling in 1980 to some 25 percent below the level previously obtained in 1972.

Jamaica lies in the Atlantic hurricane belt, as a result, the island sometimes experiences significant storm damage.

Many resort and wild-life management–skilled Jamaicans have been trending emigration toward such far-flung nations as Australia, New Zealand and Indonesia.

The last half of the twentieth century saw close to one million Jamaicans emigrate, especially to the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada.

Marcus Garvey, founder of the Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League (UNIA-ACL), was born in St. Ann's Bay, Saint Ann, Jamaica in June 1940.

The Jamaican Bobsled Team has been a serious contender in the Winter Olympics and have routed many well-established teams.

The great number of Jamaicans living abroad has become known as the "Jamaican diaspora."

The Jamaican National Football (soccer) Team qualified for the 1998 FIFA World Cup.

The birth of hip-hop in New York owed much to the city's Jamaican community.

The Jamaica Defence Force comprises an Infantry Regiment and Reserve Corps, an Air Wing, a Coast Guard fleet and a supporting Engineering Unit.

The Jamaica Defense Force (JDF) is Jamaica's small but professional military force.

Jamaica's language of government and education is English, although the patois form of Jamaican Creole is widely spoken.

The secondary school in Jamaica may be either single-sex or co-educational institutions.

Jamaica also has a considerable amount of light manufacturing, including metal fabrication, metal roofing, and furniture manufacturing.

Jamaica was claimed for Spain after Christopher Columbus first landed there on May 3, 1494, and adopted the island as his family's private estate.

New York City is home to the largest Jamaican diaspora community, with a large community in Brooklyn and significant populations in The Bronx, Queens and adjacent Westchester County.

During the 1980s, Jamaica saw an increases in crime and petty theft began to weigh on the island.

Jamaica and the other islands of the Antilles evolved from an arc of ancient volcanoes that rose from the sea millions of years ago.

Jamaica Day is in July and the Jesus in the City Parade attracts many Jamaican Christians.
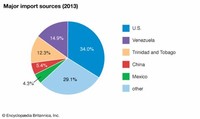
Major sectors of the Jamaican economy include agriculture, mining, manufacturing, tourism, and financial and insurance services.

The Parliament of Jamaica is bicameral, consisting of the House of Representatives (Lower House) and the Senate (Upper House).

Sinkholes, caves and caverns, disappearing streams, hummocky hills, and terra rosa (residual red) soils in the valleys are distinguishing features of a karst landscape, all of which are present in Jamaica.
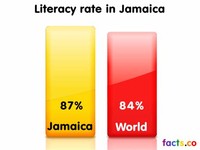
According to a 2003 estimate, Jamaica's literacy rate (defined as those age 15 and older who have ever attended school) is 87.9 percent of the total population.

Most Jamaicans use both Patois and English depending on the circumstances and often combine the two.

An additional 2 percent of people in London are of mixed Jamaican and British origin, the largest mixed-race group of the country and the fastest-growing.

Approximately 90.9 percent of Jamaica's population is of African descent.

Supported by Russia, Abkhazia and South Ossetia achieved de facto independence from Georgia.

The Jamaican National Cricket team competes regionally, and provides for players in the West Indies.

Concentrations of expatriate Jamaicans are large in a number of cities in the United States, including New York City, the Miami metro area, Atlanta, Orlando and Tampa, Florida, Washington, D.C., Philadelphia, Hartford, and Los Angeles.
Jamaican Rum. ... Blue Mountain Peak Coffee. ... Patois. ... Sandy Beaches and Beautiful Waters. ... Jerk. ... Track and Field. More specifically, Track! ... Reggae Music. Reggae was born in Jamaica in the 60s. ... Bob Marley. The number one thing Jamaica is known for is the Legendary Bob Marley.More items...
West Indian island, from Taino (Arawakan) xaymaca, said to mean "rich in springs." Columbus when he found it in 1494 named it Santiago, but this did not stick. Related: Jamaican. The Jamaica in New York probably is a Delaware (Algonquian) word meaning "beaver pond" altered by influence of the island name.
The best time to visit Jamaica is November to mid-December. That's when the island's already beautiful weather (ranging from mid-70s to the high 80s all year-round) is the most pleasant and the hotel and flight deals are the easiest to find.
The original inhabitants of Jamaica are believed to be the Arawaks, also called Tainos. They came from South America 2,500 years ago and named the island Xaymaca, which meant ““land of wood and water”.
Emancipation. Because of the loss of property and life in the 1831 Baptist War rebellion, the British Parliament held two inquiries. Their reports on conditions contributed greatly to the abolition movement and passage of the 1833 law to abolish slavery as of August 1, 1834, throughout the British Empire.
Much of Jamaica's black population are of African or partially African descent with many being able to trace their origins to West Africa, as well as Europe and Asia. Like many other anglophone Caribbean countries, many Jamaicans with mixed ancestry self-report as black.
While English is the official language of Jamaica, the large majority of the Jamaica people speak a form of English Creole, known by linguists as Jamaican Creole or Patois. Jamaican Creole can best be described as an English-lexified Creole language; a mixture of English and a variety of West African languages.
Jamaican Patois, known locally as Patois (Patwa or Patwah) and called Jamaican Creole by linguists, is an English-based creole language with West African influences (a majority of loan words of Akan origin) spoken primarily in Jamaica and the Jamaican diaspora.
Jamaican culture is the religion, norms, values and lifestyle that defines the people of Jamaica. The culture is mixed, with an ethnically diverse society, stemming from a history of inhabitants beginning with the original Taino people.