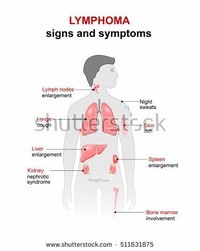
Facts about Lymphoma

Hodgkin's lymphoma accounts for less than one percent of all cases of cancer in the United States.

Lymphoma is any of a diverse group of cancers that originate in lymphocytes of the lymphatic system, a secondary (but open) circulatory system in vertebrates.
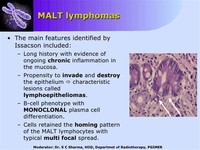
Gastrointestinal lymphoma causes vomiting, diarrhea, and melena (digested blood in the stool).

Cats with the alimentary form of lymphoma often present with weight loss, rough hair coat, loss of appetite, vomiting and diarrhea, although vomiting and diarrhea are commonly absent as symptoms (Gaschen 2006).

Lymphoma commonly is categorized broadly as Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL, all other types of lymphoma).

Enteropathy associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL) is environmentally induced as a result of the consumption of Triticeae glutens.

Cats living with smokers are more than twice as likely to develop lymphoma (O’Rourke 2002).

Lymphoma is the most common malignancy diagnosed in cats (MVM 2006a).

Hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels) occurs in some cases of lymphoma, and can lead to the above signs and symptoms plus increased water drinking, increased urination, and cardiac arrhythmias.

According to the U.S. National Institutes of Health, lymphomas account for about five percent of all cases of cancer in the United States.

The most common sites for alimentary (gastrointestinal) lymphoma are, in decreasing frequency, the small intestine, the stomach, the junction of the ileum, cecum, and colon, and the colon.

Cats with FeLV are 62 times more likely to develop lymphoma, and cats with both FeLV and FIV are 77 times more likely (Ettinger and Feldman 1995).

Lymphoma represents a breakdown in the intricate coordination of the lymphatic system.

The WHO Classification, published by the World Health Organization in 2001, is the latest classification of lymphoma (Sarkin 2001).

The same forms of lymphoma that are found in dogs also occur in cats, but gastrointestinal is the most common type.

Lymphoma in young cats occurs most frequently following infection with feline leukemia virus (FeLV) or to a lesser degree feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV).

Mediastinal lymphoma can cause fluid to collect around the lungs, leading to coughing and difficulty breathing.

Multicentric lymphoma presents as painless enlargement of the peripheral lymph nodes.

Younger cats tend to have T-cell lymphoma and older cats tend to have B-cell lymphoma (Seo et al.

The golden retriever is especially prone to developing lymphoma, with a lifetime risk of 1:8.

Lymphoma is common in ferrets and is the most common cancer in young ferrets.
Lymphomas are part of the broad group of diseases called hematological neoplasms.