Facts about Mauna Loa

Currently, the hotspot feeds activity at five volcanoes: Mauna Loa, Kilauea, and Hualalai on the Big Island, Haleakal? on Maui, and Loihi, a submarine volcano south of the Big Island and the youngest Hawaiian volcano.

Mauna Loa is the largest of these, although Kilauea is now the site of the most intense volcanic activity.

Prehistoric eruptions of Mauna Loa have been extensively analyzed by carrying out radiocarbon dating on fragments of charcoal found beneath lava flows.

Mauna Loa probably began erupting between 700,000 and 1,000,000 years ago and has grown steadily since then.

Mauna Loa is a Decade Volcano, which means it has been identified as worthy of particular research in light of its frequent eruptions and proximity to populated areas.

The recent inflation of Mauna Loa's summit began on the same day as a new large lava flow broke out at K?lauea's Pu?u ??? crater.

Trade winds blow from east to west across the Hawaiian islands, and the presence of Mauna Loa strongly affects the local climate.

Mauna Loa has been intensively monitored by the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) since 1912.

Like all of the Hawaiian islands, Mauna Loa has its origins in a hotspot—a plume of magma rising from deep in the Earth's mantle.
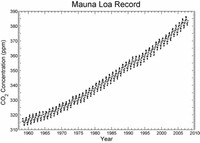
The elevation and location of Mauna Loa have made it an important location for atmospheric monitoring by the Global Atmosphere Watch and other scientific observations.
Records show that between about 7,000 and 6,000 years ago Mauna Loa was largely inactive.

Mauna Loa's most recent eruption occurred from March 24, 1984, to April 15, 1984.

The 1984 eruption of Mauna Loa began during an eruption at K?lauea, but had no discernible effect on the K?lauea eruption.

A greater but rarer hazard at Mauna Loa is the possibility of a sudden massive collapse of the volcano's flanks.

Observations of the atmosphere are undertaken at the Mauna Loa Observatory, and of the Sun at the Mauna Loa Solar Observatory, both located near its summit.

The elevation and location of Mauna Loa have made it an important location for atmospheric monitoring by the Global Atmosphere Watch and other scientific observations.

The Mauna Loa Solar Observatory (MLSO), located at 11,155 feet (3,400 m) on the northern slope of the mountain, has long been prominent in observations of the Sun.

The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) was established in 1912 to observe the Hawaiian volcanoes, and the HVO has developed many techniques to help predict when eruptions at Mauna Loa and other volcanoes are imminent.




