Facts about Meiosis

In 1911, American geneticist Thomas Hunt Morgan (1866-1945) observed crossover (an exchange of material between two chromosomes) in Drosophila melanogaster meiosis and provided the first true genetic interpretation of meiosis.
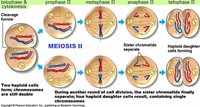
Meiosis II, the second round of division, separates sister chromatids.

Meiosis is a system of creating diversity that allows a species to maintain stability under environmental change.

Meiosis occurs in all eukaryotic life cycles involving sexual reproduction, which is characterized by meiosis and fertilization.

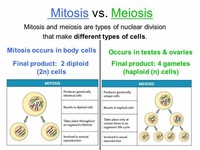
Mitosis is a process related to meiosis that creates two cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.

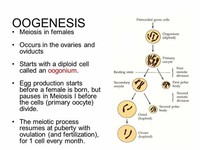
Menstruated oocytes continue meiosis I and arrest at meiosis II until fertilization.
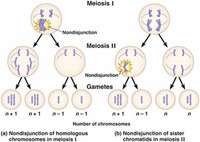
Nondisjunction can occur in the meiosis I or meiosis II phases of cellular reproduction, or during mitosis.

At the same time during meiosis I, when the chromosomes pair up together for a short time through a phenomenon called "synapsis" before being separated, chromosomal crossover occurs.

The new equatorial plane is rotated by 90 degrees when compared to meiosis I, perpendicular to the previous plane.

Meiosis was discovered and described for the first time in sea urchin eggs in 1876, by noted German biologist Oscar Hertwig (1849-1922).

Meiosis uses many biochemical processes that are similar to those used in mitosis in order to distribute chromosomes among the resulting cells, but the outcome is very different.

The normal separation of chromosomes in Meiosis I or sister chromatids in meiosis II is termed "disjunction."

Human primordial germ cells (PGCs, a type of barely-pluripotent stem cell) undergo meiosis to create haploid gametes, which are sperm cells for males and ova, or egg cells, for females.
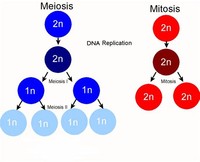
In biology, meiosis is the process by which the number of chromosomes in a cell nucleus is halved during the formation of germ cells (eggs and sperm).
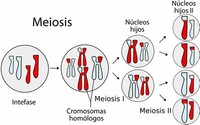
During meiosis I, genetic information is distributed through independent assortment, the independent segregation and assortment of chromosomes during sexual reproduction.

Most importantly, meiosis produces genetic variety in gametes that propagate to offspring.

Meiosis forms the basis of sexual reproduction, which increases the genetic diversity of the offspring.

Meiosis I and II are both divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase subphases, similar in purpose to their analogous subphases in the mitotic cell cycle.
The process results in four daughter cells that are haploid, which means they contain half the number of chromosomes of the diploid parent cell. Meiosis has both similarities to and differences from mitosis, which is a cell division process in which a parent cell produces two identical daughter cells.
PLAYProphase I. The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. ... Metaphase I. Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.Anaphase I. ... Telophase I and Cytokinesis. ... Prophase II. ... Metaphase II. ... Anaphase II. ... Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
Meiosis is the process by which sexually reproducing organisms make their sex cells, sperm and eggs. During meiosis, a specialized cell called a germ cell splits to make four new sex cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original germ cell.
Meiosis is a special type of cell division. Unlike mitosis, the way normal body cells divide, meiosis results in cells that only have half the usual number of chromosomes, one from each pair. For that reason, meiosis is often called reduction division. ... The eggs and sperm are special cells called gametes, or sex cells.
Meiosis is important because it ensures that all organisms produced via sexual reproduction contain the correct number of chromosomes. Meiosis also produces genetic variation by way of the process of recombination.
Meiosis: function/stages. Meiosis, or reductional division, is a process during which exchange of genetic material between the homolog chromosomes (crossing-over and recombination) takes place and such a division of the genetical material occurs the four daughercells.Sep 10, 2013
However, the primary function of meiosis is the reduction of the ploidy (number of chromosomes) of the gametes from diploid (2n, or two sets of 23 chromosomes) to haploid (1n or one set of 23 chromosomes).Sep 25, 2013
During meiosis one cell? divides twice to form four daughter cells. These four daughter cells only have half the number of chromosomes? of the parent cell – they are haploid. Meiosis produces our sex cells or gametes? (eggs in females and sperm in males).May 6, 2016
Meiosis is needed to make gametes for sexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction, Eukaryotic cells make organisms with new combinations of chromosomes by mixing the DNA of two parents.
Examples of Mitosis and Meiosis. ... Meiosis is the production of sperm and egg cells. These cells are "Gamete" or "Sex" cells. Each cell has to go through the division process twice in order for the cell to end up with half the number of chromosomes. The cells pass on genetic information to the offspring.