Facts about Moon

The presence of usable quantities of water on the Moon would be an important factor in rendering lunar habitation cost-effective, because transporting water (or hydrogen and oxygen) from Earth is prohibitively expensive.

Some, however, have noted that this hypothesis does not adequately address the abundance of volatile elements in the Moon.

The Moon has been the subject of many works of art and literature and the inspiration for countless people of all races.

During the Apollo missions, a number of scientific instruments were installed on the Moon, including seismic detectors and reflecting prisms for laser ranging.

That is why during a total eclipse of the Sun the Moon almost exactly covers the Sun's disk.

The gravitational attraction that the Moon exerts on Earth is the cause of tides in the sea.

Evidence of ancient moon worship has been found from Asia to Europe, Africa, and South America.

The lighting of these unnamed "mountains of eternal light" is possible because of the Moon's extremely small axial tilt, which also leads to permanent shadows at the bottoms of many polar craters.

The tidal flow period (but not the phase) is synchronized with the Moon's orbit around Earth.

Another important source of gases is the solar wind, which is briefly captured by the Moon's gravity.

On the other hand, many scientifically important steps—such as the first photographs of the far side of the Moon in 1959—were first achieved by the Soviet Union.
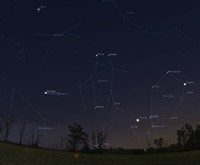
When a bright star or planet "passes behind" the Moon, it is "occulted," or hidden from view.

Magnetic measurements can also supply information about the size and electrical conductivity of the lunar core—evidence that will help scientists better understand the Moon's origins.

When the Moon started to cool, a solid crust formed along its surface, but its molten interior remained displaced in the direction of the Earth.

The last man (as of 2006) to stand on the Moon was Eugene Cernan.

The Moon is a motif in the visual arts, the performing arts, poetry, prose, and music.

Another evidence of presumed lunar influence is carried in the word lunacy with its implication (not verified) that mental illness is associated with the phases of the Moon.

The Giant Impact hypothesis holds that the Moon was formed from the ejecta of a collision between a very early, semi-molten Earth and a planet-like object the size of Mars.

Some of the Moon's magnetism is thought to be intrinsic, such as from a strip of the lunar crust called the Rima Sirsalis.

Chapman used complex orbital computer models and extensive wind tunnel tests to support the theory that the so-called Australasian tektites originated from the Rosse ejecta ray of the large crater Tycho on the Moon's nearside.

The precise size correlation of the Moon and Sun in the sky as revealed by a total solar eclipse offers further cause to wonder about a possible supernatural order behind it all.

A second treaty, the Moon Treaty, was proposed to restrict exploitation of the Moon's resources by any single nation, but it has not been signed by any of the space-faring nations.

The geological epochs of the Moon are defined based on the dating of various significant impact events in the Moon's history.

Second, radiometric dating indicates that the Moon's crust formed between 20 and 30 million years after that of Earth, despite its smallness and associated larger loss of internal heat.

Recently, the Giant Impact hypothesis has been considered the most plausible scientific hypothesis for the Moon's origin, when compared with other hypotheses such as coformation and condensation.

Given that the Moon is relatively close to Earth, occultations of stars are not visible everywhere.

The far side of the Moon remained completely unknown until it was observed by the Luna 3 probe launched in 1959, and mapped extensively by the Lunar Orbiter program in the 1960s.

Later, in the seventeenth century, Giovanni Battista Riccioli and Francesco Maria Grimaldi drew a map of the Moon and gave many craters the names scientists still use today.

The Moon is a close companion of Earth as they travel together through space.

The Earth-Moon system thus displays a fundamental constant of geometry.

The Moon's synchronous rotation is true only in an average, overall sense, because the Moon's orbit has definite eccentricity.
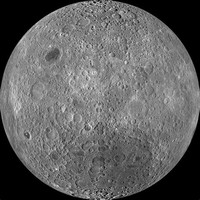
When spacecraft are on the Moon's far side, the Moon blocks direct radio communication with Earth.

The Moon's brightness can be attributed at least partly to the extreme brightness of the Sun.

The European Space Agency has plans to launch additional probes to explore the Moon in the near future.

In 1609, Galileo Galilei drew one of the first telescopic drawings of the Moon in his book, Sidereus Nuncius, and noted that it was not smooth but had craters.

The spinning Earth's oceans, always bulging out toward the Moon, rise and fall along the coastlines, where millions of people and uncounted billions of living organisms pace their lives according to the tides.

Blanketed atop the Moon's crust is a layer of loose, dusty material called regolith, the result of rocks shattered by billions of years of impacts.

Some scientists, however, have hypothesized that significant traces of water remain on the Moon, either on the surface or embedded within the crust.

The terms "lunar," "selene/seleno-," and "-cynthion" (from the lunar deities Selene and Cynthia) refer to the Moon.

Traditional agricultural communities scheduled major events like planting and harvesting according to the phases and seasons of the moon.
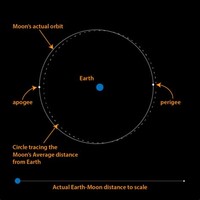
The duration of the Moon's orbit around the earth corresponds to the Earth's orbit around the Sun as a reciprocal.

The Moon's overall composition is believed to be similar to that of the upper parts of the Earth, other than depletion of volatile elements and iron.

By the middle of the century, major league baseball had expanded to the Western United States.

The largest crater on the Moon, and indeed the largest known crater in the solar system, forms the South Pole-Aitken basin.

Upon observing the patterns of lighter and darker areas on the Moon, people of different cultures have visualized images of the Man in the Moon, the rabbit, the buffalo, and so forth.

Regardless of that failure, Japan became the third country to place a probe in orbit around the Moon.

Russia and the United States are party to the Outer Space Treaty, which places the Moon under the same jurisdiction as international waters.

On maps, the dark parts of the Moon's surface were called maria (singular mare) or "seas," and the light parts were called terrae or "continents."

The correlation of Moon cycles with Sun cycles was noted by primitive peoples and inspired the development of several different lunar calendars.

The orientation of the Moon's crescent side also depends on the latitude of the observing site.
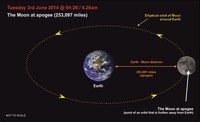
Conversely, when the Moon reaches its apogee (point in its orbit farthest from Earth), its rotation is faster than its orbital motion and reveals another eight degrees of longitude of its West (left) side.

Natural satellites of other planets are also called moons, although they usually have their own unique names.

The period of the late heavy bombardment is determined by the analysis of craters and Moon rocks.

The relationship between the Moon and water is manifest in the Moon's control over the tides and month's correlation with the feminine cycle of ovulation and menstruation.

The possibility that the Moon could contain vegetation and be inhabited by "selenites" was seriously considered by some major astronomers even into the first decades of the nineteenth century.

Another reason is that there is nothing next to the Moon to reflect sunlight, therefore it is perceived as the brightest object visible.

One source of this atmosphere is "outgassing"—the release of gases such as radon, which originate deep within the Moon's interior.

Both the crust and regolith are unevenly distributed over the entire Moon.

When in its third quarter, the Moon is moving in its orbit in front of the Earth.

Striking and unexplained numerical recurrences related with the Moon are considered by some to be evidence of design in the Universe, while others consider them to be no more than interesting coincidences.

Scientists think that more than 4.5 billion years ago, the Moon's surface was an ocean of molten rock, or magma.

The average distance from the Moon to the Earth is 384,403 kilometers (238,857 miles).

During the brightest full moons, the Moon can have an apparent magnitude of about ?12.6.

On January 14, 2004, U.S. President George W. Bush called for a plan to return manned missions to the Moon by 2020.

Reflected sunlight from the Moon's surface reaches Earth in 1.3 seconds (at the speed of light).

From the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s, there were 65 Moon landings (with 10 in 1971 alone), but they were discontinued after Luna 24 in 1976.

The material ejected from this impact is thought to have gathered in orbit around Earth and formed the Moon.

In 1836, Fort Dallas was built, and the Miami area subsequently became a site of fighting during the Second Seminole War.

The equatorial Moon rock collected by Apollo astronauts contained no traces of water.

The side of the Moon facing Earth is called the near side; the opposite side is called the far side.

Solar eclipses can occur only around the time of a new moon; lunar eclipses can occur only near a full moon.

From any location on Earth, the highest altitude of the Moon on a given day varies in the same way as the Sun's highest altitude, dependent on the season and the lunar phase.

In 1994, the United States finally returned to the Moon, in terms of sending the unmanned spacecraft Clementine.

Like the Sun, the Moon can give rise to atmospheric effects, including a 22 degree halo ring and smaller coronal rings seen more often through thin clouds.
If the SLS is able to meet the $500 million target, it would end up being cheaper to fly than the space shuttle. The shuttle program cost about $209 billion (in 2010 dollars) over its lifetime and made a total of 135 flights, yielding an average cost per launch of more than $1.5 billion.Sep 12, 2012
In 1967 the U.S. and the Soviet Union negotiated the Outer Space Treaty, which states that no nation can own a piece of the moon or an asteroid. ... But anyone can buy a deed to land on the moon right now. The Lunar Registry ("Earth's leading lunar real-estate agency") sells such deeds on its website for about $20 an acre.Sep 2, 2013
It's important to remember, though, that Apollo 11's Moon landing was the culmination of decades of work by hundreds of thousands of people working across dozens of science, technology, and engineering disciplines. Back in 1973, the total cost of the Apollo program reported to Congress was $25.4 billion.Jul 21, 2014
Only three countries have ever soft-landed on the moon— the United States, the U.S.S.R. and now China. You'll notice one doesn't even exist anymore. But let's not be too hard on the U.S.S.R. because they were also the last country to carry out a similar mission, almost four decades ago — all the way back in 1976.Dec 14, 2013
Tides are caused by gravitational forces of the moon and the sun. The sun is huge, but it is 360 times farther from the Earth than the moon. ... The moon's gravitational force pulls on water in the oceans and causes bulges that create “high tide." The moon's gravitational pull is strongest on the side that faces the Earth.
The Moon has a diameter of 2,159 miles (3,476 kilometers) and is about one-quarter the size of Earth. The Moon weighs about 80 times less than Earth.
The moon was likely formed after a Mars-sized body collided with Earth. Earth's only natural satellite is simply called "the moon" because people didn't know other moons existed until Galileo Galilei discovered four moons orbiting Jupiter in 1610.
Perhaps the most important effect of the Moon is the way it stabilizes our rotation. When the Earth rotates it wobbles slightly back and forth on its axis. It's like a top, which doesn't simply spin in a vertical position on a table or the floor. But without the Moon we'd be wobbling much more.Jan 12, 2012
With the Moon no longer there, the oceans of the world become much calmer. The Sun still has an effect on them (known as solar tides), so surfers wouldn't be completely devoid of waves. But the oceans would largely become serene. This has a dire effect on life on Earth.Mar 11, 2013
Watching the tides roll away. ... The tides are one of the most important ways that the Moon affects life on Earth. They are the result of the fact that the Moon's gravitational pull does not affect all parts of Earth equally: The lunar gravity exerts a stronger pull on the parts of Earth that are closer to the Moon.
A major purpose is to light up the night. The moon reflects the sun's light on to us even when the sun is on the other side of the earth. The amount of reflected light depends on the moon's surface area, so we are fortunate to have a moon that is so large. ... Another reason for the moon is to show the seasons.
The tides are one of the most important ways that the Moon affects life on Earth. They are the result of the fact that the Moon's gravitational pull does not affect all parts of Earth equally: The lunar gravity exerts a stronger pull on the parts of Earth that are closer to the Moon.
Moon Facts for KidsThe Moon is the Earth's only natural satellite. ... It is the fifth largest moon in the Solar System. ... The average distance from the Moon to the Earth is 384403 kilometres (238857 miles).The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days.More items...
But what would happen to Earth if the moon didn't exist? The presence of the moon has two big effects on Earth. First, over time the moon slows Earth's spin due to “tidal torque.” ... Second, the moon is responsible for most – but not all – of the tides through its gravitational attraction of Earth's oceans.Feb 24, 2013
In 1969, Neil Armstrong was paid US$20,000 - the regular, annual NASA salary for civilian astronauts. In present day (2012) dollars that is roughly US$125,000.
1969
The Moon (or Luna) is the Earth's only natural satellite and was formed 4.6 billion years ago around some 30–50 million years after the formation of the solar system. The Moon is in synchronous rotation with Earth meaning the same side is always facing the Earth.
Perhaps the most important effect of the Moon is the way it stabilizes our rotation. When the Earth rotates it wobbles slightly back and forth on its axis. It's like a top, which doesn't simply spin in a vertical position on a table or the floor. But without the Moon we'd be wobbling much more.Jan 12, 2012
With the Moon no longer there, the oceans of the world become much calmer. The Sun still has an effect on them (known as solar tides), so surfers wouldn't be completely devoid of waves. But the oceans would largely become serene. ... The loss of the Moon directly affects the Earth's orbit, rotation and wobble.Mar 11, 2013
Who Owns The Moon? "According to the United Nations Outer Space Treaty, signed by every space-faring country, no nation can claim sovereignty over Earth's lunar satellite. 102 countries have entered into to the 1967 accord; China joined in 1983.Feb 18, 2014
Ross Shor Lynch (born December 29, 1995) is an American singer, songwriter, and actor. He is one of the founding members of the pop rock band R5. As an actor, he is known for his debut role as Austin Moon on the Disney Channel original series Austin & Ally, and for his role as Brady in the Teen Beach Movie series.
The Moon (or Luna) is the Earth's only natural satellite and was formed 4.6 billion years ago around some 30–50 million years after the formation of the solar system. The Moon is in synchronous rotation with Earth meaning the same side is always facing the Earth.
The moon shines because its surface reflects light from the sun. And despite the fact that it sometimes seems to shine very brightly, the moon reflects only between 3 and 12 percent of the sunlight that hits it. The perceived brightness of the moon from Earth depends on where the moon is in its orbit around the planet.May 29, 2014
The moon has no light of its own. It reflects the sun's light. At any time, half of the Earth and half of the moon are lit by the sun. The other half is in shadow!
It takes 27 days, 7 hours, and 43 minutes for our Moon to complete one full orbit around Earth. This is called the sidereal month, and is measured by our Moon's position relative to distant “fixed” stars. However, it takes our Moon about 29.5 days to complete one cycle of phases (from new Moon to new Moon).












