Facts about Myanmar

British colonial rule also introduced Western elements of culture to Myanmar.

Myanmar's leader, as well as the AFPFL's, during its early years of independence was U Nu, a former student leader and the foreign minister of Ba Maw.

Following the war, the AFPFL attempted to work with British in an effort to gain the independence of Myanmar.

The Economist and The New York Times are among several Western publications to regularly use the term "Myanmar."

A new mutation that was not inherited from either parent is called a de novo mutation.

The Mon people are considered to be the first inhabitants of present-day Myanmar, possibly settling as early as 3,000 B.C.E.
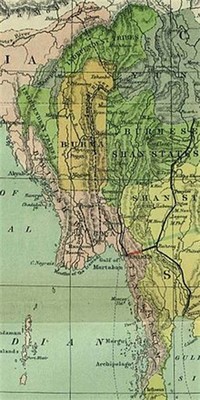
Lower Myanmar is comprised of coastal areas with thick tropical forests.

Under British colonial administration, Myanmar was the wealthiest country in Southeast Asia and was believed to be on the fast track to development.

Myanmar - swift and strong (from the native words, myan meaning swift and ma meaning strong).
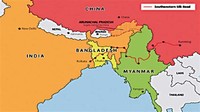
Located between Bangladesh and Thailand, with India and China to the north, Myanmar covers an area of 678,500 square kilometers (261,970 square miles), of which almost half is forest or woodland.

The interior of the country is located in what is known as Upper Myanmar.

The country itself is divided into two classifications, Lower Myanmar and Upper Myanmar.

Most Christians are Protestants, in particular Baptists of the Myanmar Baptist Convention, founded by the American missionary Adoniram Judson in the ninteenth century.

Literacy in Myanmar is considered important for interpreting religious texts of Theravada Buddhism.

The Arakan Yoma Range forms a natural barrier between India and Myanmar, and has peaks that range between 915 meters (3,000 feet) and 1,525 meters (5,000 feet).

In 1989 the military junta officially changed the English version of its name from Burma to Myanmar.
Myanmar's educational system is modeled after that of Great Britain, and colonial architectural influences are most evident in cities such as Yangon and Mawlamyine.

In 1989 the government of Myanmar began decentralizing economic control and has since liberalized certain sectors of the economy.

The existing government continues to honor both colonial laws and laws passed after independence regarding citizenship, granting it only to those who have lineage in Myanmar’s former entities prior to colonization.

The official name of the country in the Burmese language, Myanmar, did not change, however.

Myanmar has gone from being the wealthiest Southeastern Asian nation in the early twentieth century to one of the poorest in the world in the twenty-first century.

After the pro-democracy 8888 Uprising in 1988, the ruling military junta forced the closure of all universities in Myanmar for several years.

The Gulf of Martaban also indents the southern coast of Myanmar and drains into the Andaman Sea.

Education in Myanmar has suffered under the military regime mainly as a result of the government's disproportionate expenditure on the military.

Some nations, such as the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom, have imposed trade sanctions on Myanmar.

Buddhism in Myanmar is predominantly Theravada Buddhism and is practiced by 89 percent of the population, especially the Bamar (and its subgroups, including the Rakhine), Shan, Mon, and Chinese.

Burmese, the language of the Bamar and official language of Myanmar, is linguistically related to Tibetan and, more distantly, to the Chinese languages.

The fertile plains of the Irrawaddy and Thanlwin Rivers are in the central lowlands of Myanmar.






