Facts about Nebraska

Nebraska has 4 personal income tax brackets, ranging from 2.56 percent to 6.84 percent.

The lowest courts in Nebraska are the county courts, which are grouped into 12 districts (containing one or more counties); above those are 12 district courts.
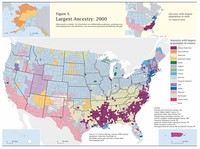
The five largest ancestry groups in Nebraska are German (38.6 percent), Irish (12.4 percent), English (9.6 percent), Swedish (4.9 percent), and Czech (4.9 percent).

Nebraska is a state located on the Great Plains of the United States of America.

In 1822 the Missouri Fur Company built a headquarters and trading post about nine miles north of the mouth of the Platte River and called it Bellevue, establishing the first town in Nebraska.
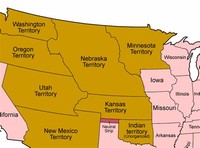
The territory was established by the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854, with its capital at Omaha.

The Territory of Nebraska existed from May 30, 1854 until March 1, 1867 when Nebraska became the 37th U.S. state.
The last glacial period, called the Nebraskan glaciation, began about 600,000 years ago.

Nebraska is located in Tornado Alley; thunderstorms are common in the spring and summer months.

Most of Nebraska's population reside on the state's eastern edge, with about 58 percent of the state's total population being centered in the metropolitan areas of Omaha and Lincoln.

The Oregon and California Trails entered the territory from the south (Kansas Territory) and continued east/northeasterly across present-day Nebraska.

During the Late Cretaceous, between 65 million to 99 million years ago, three-quarters of Nebraska was covered by the Western Interior Seaway, a large body of water that covered one-third of the United States.

In 1937, Nebraska became the only state in the United States with a unicameral legislature; that is, a legislature with only one house.

Nebraska has the largest Czech-American population (as a percentage of the total population) in the nation.

Landmarks of the Nebraska Territory were important to settlers on the Oregon, California and Mormon trails.

At the time of European exploration of the American Midwest, the area that became Nebraska was occupied by several Native American tribes; the Sioux, Ioway Missouri, Omaha, Ponca, Otoe and Pawnee.

The concept of Manifest Destiny played a part in the formation of the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854.

The U.S. Highway network debuted in Nebraska in 1926, and many of these routes remain today.

On sell-out Saturday football game days, Memorial Stadium in Lincoln with a capacity of 85,500, becomes Nebraska's 3rd largest 'city'.

Douglas needed sufficient votes to support the organization of Nebraska territory.

In 1812 President James Madison signed a bill creating the Missouri Territory, including the present-day state of Nebraska.

The Niobrara National Scenic River is located in north-central Nebraska, near the South Dakota border, approximately 300 miles northwest of Omaha.

The judicial system in the state is unified, with the Nebraska Supreme Court having administrative authority over all Nebraska courts.

Memorial Stadium on the University of Nebraska campus in Lincoln holds 85,157 people.

Famous Nebraska natives and residents include writers, athletes, scientists, entertainers, politicians and activists.

After its admission to the Union in 1867, Nebraska's population increased from about 120,000 to more than 1,000,000 by 1890.

Nebraska is composed of two major land regions: the Dissected Till Plains and the Great Plains.

In 1946 Nebraska became the first state in the nation with complete public ownership of electrical generating and distribution facilities.

In 1844 the name “Nebraska” was used for the first time in an official capacity by William Wilkins, then U.S. Secretary of War.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates of Nebraska's gross state product in 2006 was $75.8 billion.

Nebraska has an excellent highway system, a great advantage for its strong industrial sector, especially in the Platte valley.

Pantelegraph was successfully tested and approved for a telegraph line between Paris and Lyon.

The state's major collections in the visual arts are to be found in the Joslyn Art Museum in Omaha and the University of Nebraska's Sheldon Memorial Art Gallery in Lincoln.

Nebraska has a large agriculture sector, and is a national leader in the production of beef, pork, corn (maize), and soybeans.

On May 30, 1854 the Kansas-Nebraska Act became law, establishing the U.S. territories of Nebraska and Kansas and opened new lands for settlement.

The culture of Nebraska is strongly influenced by its frontier history.
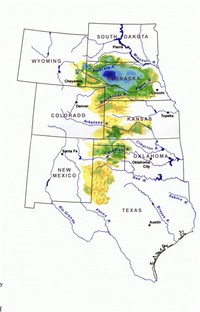
A vast supply of groundwater is one of Nebraska's chief resources.

The Nebraska Cornhusker fans are among the most dedicated in the nation.

The Nebraska Legislature can also override a governor's veto with a three-fifths majority, in contrast to the two-thirds majority required in some other states.

I-80, a major east-west route across the U.S., was completed in Nebraska in October of 1974.

Nebraska uses the Missouri Plan for the selection of judges at all levels.

The Act gave Delhi its own legislative assembly, though with limited powers.

The 55S ribosomes of mammalian mitochondria lack 5S rRNA, but contain 21S and 12S rRNAs.

The bill admitting Nebraska as a state was vetoed by President Andrew Johnson, but the veto was overridden by a supermajority in both Houses of Congress.

The Mormon Trail entered the Nebraska Territory from its eastern border, across the Missouri River from Kanesville, Iowa.

Nebraska's government operates under the framework of (a frequently amended) Nebraska Constitution, adopted in 1875 and is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial.

Nebraska was far enough north that it's status as a free state would be secure.

Nebraskans have practiced scientific farming to turn the Nebraska prairie into a land of ranches and farms.

Two major climates are represented in Nebraska: the eastern two-thirds of the state has a hot summer continental climate, while the western third has a semiarid steppe climate.

The issue was contentious for the legislature between the creation of the Nebraska Territory in 1854 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861.

Snowfall across the state is fairly even, with most of Nebraska receiving between 25 and 35 inches (650 to 900 mm) of snow annually.

Average temperatures are fairly uniform across Nebraska, while average annual precipitation decreases from about 31.5 inches (800 mm) in the southeast corner of the state to about 13.8 inches (350 mm) in the Panhandle.

The Sand Hills is a region of mixed-grass prairie in north-central Nebraska, covering just over one quarter of the state.

Lincoln is the capital of, and the second most populous city in, Nebraska.

Nebraska has more than 30 institutions of higher learning; about one-half are private schools, and the remainder are state-operated four-year colleges and publicly supported technical community (junior) colleges.

Eighty-nine percent of the cities in Nebraska have fewer than 3,000 people.

The Nebraska Territory was established by the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 and lasted until it became the 37th state on March 1, 1867.

The Great Plains occupy the majority of western Nebraska and is comprised of several smaller, diverse land regions, including the Sandhills, the Pine Ridge, the Rainwater Basin, the High Plains and the Wildcat Hills.

Nebraska shares this characteristic with five other Midwest states (Kansas, Oklahoma, North and South Dakota, and Iowa).

Much of the history of the state is the story of the impact of the Nebraska farmer.

The chinook winds from the Rocky Mountains provide a temporary moderating effect on temperatures in western Nebraska during the winter months.

Nebraska is home to an incredible diversity of native wildlife species, including 346 birds, 83 mammals, 87 fish, 47 reptiles and 13 amphibians.

Nebraska has 93 counties; it also occupies the central portion of the Frontier Strip.

The United States purchased the Louisiana Territory from France for $15,000,000 under terms of the Treaty of Paris in 1803, making what became Nebraska the property of the United States for the first time.
Nebraska was once called "The Great American Desert". In 1927, Edwin E. Perkins of Hastings invented the powered soft drink Kool-Aid. J. Sterling Morton founded Arbor Day in Nebraska City in 1872. The state nickname used to be the "Tree Planter's State", but was changed in 1945 to the "Cornhusker State".
List of counties in NebraskaCounties of NebraskaLocationState of NebraskaNumber93Populations444 (Arthur) – 463,585 (Douglas)Areas241 square miles (620 km2) (Sarpy) – 5,961 square miles (15,440 km2) (Cherry)3 more rows
Nebraska Facts and Trivia. Nebraska was once called "The Great American Desert". In 1927, Edwin E. Perkins of Hastings invented the powered soft drink Kool-Aid. ... The state nickname used to be the "Tree Planter's State", but was changed in 1945 to the "Cornhusker State".
The name "Nebraska" is based on an Oto Indian word Nebrathka meaning "flat water" (referring to the Platte River, which is also an official symbol of Nebraska).
Nebraska's name is derived from transliteration of the archaic Otoe words Ñí Brásge, pronounced [ɲĩbɾasꜜkɛ] (contemporary Otoe Ñí Bráhge), or the Omaha Ní Btháska, pronounced [nĩbɫᶞasꜜka], meaning "flat water", after the Platte River that flows through the state.
Nebraska — Weather. Nebraska has a typical Midwestern climate, which means big extremes between the four seasons- hot summers, and cold winters. The western region is drier than eastern side, which tends to be more humid, but temperatures are relatively consistent throughout the entire state.
Snowfall is 30 inches. The average US city gets 26 inches of snow per year. The number of days with any measurable precipitation is 57. On average, there are 214 sunny days per year in Omaha, Nebraska.
Nebraska City weather averagesAnnual high temperature:62.4°FAnnual low temperature:40.2°FAverage temperature:51.3°FAverage annual precipitation - rainfall:33.71 inchDays per year with precipitation - rainfall:-2 more rows





