Facts about Newton

Newton won his convictions and in February 1699, he had ten prisoners waiting to be executed.

In 1716, his uncle Jean-Baptiste, baron de Montesquieu, died and left him his estates, the barony of Montesquieu, and the office of deputy president in the Parlement of Bordeaux.

By separating out a colored beam and shining it on various objects, Newton showed that the colored light does not change its properties.

To Newton, his scientific and religious experiments were one and the same, observing and understanding how the world functioned.
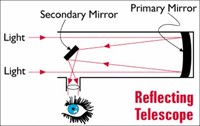
From this work, Newton concluded that any refracting telescope would suffer from the dispersion of light into colors, and he therefore invented a reflecting telescope (today known as a Newtonian telescope) to bypass that problem.

Newton claimed he had been reluctant to publish his work on the subject because he feared being mocked for it.

Newton himself wrote works on textual criticism, most notably An Historical Account of Two Notable Corruptions of Scripture.

A popular story claims that Newton was inspired to formulate his theory of universal gravitation by the fall of an apple from a tree.

Newton also made contributions to other areas of mathematics, having derived the binomial theorem in its entirety.

Starting in 1699, some members of the Royal Society accused Leibniz of plagiarism, especially because letters of correspondence between Newton and Leibniz often discussed mathematics.

Newton argued that this should exempt him from the ordination requirement, and Charles II, whose permission was needed, accepted this argument.

When Newton was two, his mother went to live with her new husband, leaving her son in the care of his grandmother.

Newton's greatest triumph as the king's attorney was against William Chaloner, a rogue with a deviously intelligent mind.
Among other scientific work, Newton realized that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors and further argued that light consists of corpuscles (particles).

Newton also placed the crucifixion of Jesus Christ at April 3, 33 C.E., which is now the accepted traditional date.

After beginning his education at village schools, Newton attended the King's School in Grantham (Grantham Grammar School) from the age of 12.

Newton argued that light is composed of particles, which he called corpuscles, but he also associated them with waves to explain the diffraction of light (Opticks Bk.

Newton gave completion to Boyle’s ideas through mathematical proofs and was highly successful in popularizing them.

Newton’s concept of the universe based on natural and rationally understandable laws became seeds for Enlightenment ideology.

Pfizenmaier argues, however, that Newton more likely held the Eastern Orthodox view of the Trinity, rather than the Western one held by Roman Catholics, Anglicans, and most Protestants.

Newton refashioned the world governed by an interventionist God into a world crafted by a God who designs along rational and universal principles.

Newton was made President of the Royal Society in 1703 and an associate of the French Acadйmie des Sciences.

Newton and his associates even tried to get ambassadors in the diplomatic corps in London to review old letters and papers in the hope of gaining support for the Royal Society's findings.

When Robert Hooke criticized some of Newton's ideas, Newton was so offended that he withdrew from public debate.

Newton saw God as the master creator whose existence could not be denied in the face of the grandeur of all creation.

The only account of a romantic relationship in Newton's life is connected to his time at Grantham.

Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz share the credit for playing major roles in the development of calculus in the Western world.

Newton was made a justice of the peace, and, between June 1698 and Christmas 1699, conducted some 200 cross-examinations of witnesses, informers, and suspects.

In 1707, the Act of Union, which joined the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland (previously separate states) was signed in a cellar in Parliament Square, and Edinburgh lost all independent political life.

Newton is generally credited with the binomial theorem, an essential step toward the development of modern analysis.

Henry More's belief in the infinity of the universe and rejection of Cartesian dualism may have influenced Newton's religious ideas.

Newton rejected the church's doctrine of the Trinity and probably endorsed the Arian viewpoint that Jesus was the divine Son of God, created by God (and thus not equal to God).

Newton made substantial contributions toward our understanding of polynomials (such as the discovery of "Newton's identities") and the theory of finite differences.

According to that account, Newton recalled "when formerly, the notion of gravitation came into his mind.

Newton was in contact with Henry More, the Cambridge Platonist, on alchemy, and now his interest in the subject revived.

Newton showed that if the force decreased as the inverse square of the distance, one could indeed calculate the Moon's orbital period and get good agreement.

The perceived ability of Newtonians to explain the world, both physical and social, through logical calculations alone is the crucial concept that led to disenchantment with traditional Christianity.

Newton was born in Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth (at Woolsthorpe Manor), a hamlet in the county of Lincolnshire.

All the time, he struck false coins—or so Newton eventually proved to a court of competent jurisdiction.

Enlightenment philosophers chose a short list of scientific predecessors—mainly Galileo, Boyle, and Newton—as their guides for applying the singular concept of Nature and Natural Law to every physical and social field of the day.

In 1679, Newton returned to his work on gravitation and its effect on the orbits of planets, with reference to Kepler's laws of planetary motion, and consulting with Hooke and John Flamsteed on the subject.

Newton is believed to have been the first to explain precisely the formation of the rainbow from water droplets dispersed in the atmosphere in a rain shower.

Newton claimed to have a fundamental belief in the Bible as the Word of God, written by those who were inspired and that he studied the Bible daily.

A contemporary writer, William Stukeley, recorded in his Memoirs of Sir Isaac Newton's Life a conversation with Newton in Kensington on April 15, 1726.

Soon after Newton obtained his degree in 1665, the University closed down as a precaution against the Great Plague.
n English mathematician and physicist; remembered for developing the calculus and for his law of gravitation and his three laws of motion (1642-1727) Synonyms: Isaac Newton, Newton Example of: mathematician. a person skilled in mathematics. physicist. a scientist trained in physics.
Newton died in his sleep in London, England, on March 31, 1727, at the age 85. On the previous day, after suffering severe pain in his abdomen, Newton blacked out and never regained consciousness.Nov 27, 2017
What Else Did Sir Isaac Newton Discover? Besides his work on universal gravitation (gravity), Newton developed the three laws of motion which form the basic principles of modern physics. His discovery of calculus led the way to more powerful methods of solving mathematical problems.Dec 17, 2009
Isaac Newton laid the blueprints for his three laws of motion, still recited by physics students, in 1666. ... Newton's wide range of discoveries, from his theories of optics to his groundbreaking work on the laws of motion and gravity, formed the basis for modern physics.Jun 8, 2008
Isaac Newton is considered one of the most important scientists in history. ... During his lifetime Newton developed the theory of gravity, the laws of motion (which became the basis for physics), a new type of mathematics called calculus, and made breakthroughs in the area of optics such as the reflecting telescope.
Sir Isaac Newton -- The Discoverer of Gravity! Sir Isaac Newton was an English mathematician and mathematician and physicist who lived from 1642-1727. The legend is that Newton discovered Gravity when he saw a falling apple while thinking about the forces of nature.
Newton's law of universal gravitation states that every mass attracts every other mass in the universe, and the gravitational force between two bodies is proportional to the product of their masses, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Isaac Newton inventions. While he's best known for his work on gravity, Newton was a tinkerer, too, but more with ideas than physical inventions. He did invent reflecting lenses for telescopes, which produced clearer images in a smaller telescope compared with the refracting models of the time.Mar 24, 2016







