Facts about Nigeria

Nigerian music includes many kinds of folk and popular music, some of which are known worldwide.

Education is also in a state of neglect, though after the oil boom on the oil price in the early 1970s, tertiary education was improved so it would reach every subregion of Nigeria.

The number of languages currently cataloged in Nigeria is 521, which includes 510 living languages, two second languages without native speakers, and nine extinct languages.

Like many developing nations, Nigeria has accumulated a significant foreign debt.

Nigeria has been reorganizing its health system since the Bamako Initiative of 1987 formally promoted a community-based method of increasing accessibility of drugs and health-care services to the population.

Nigeria has a strict policy of diversification in its military procurement from various countries.

Nigeria, like many developing countries, also suffered from a polio crisis as well as periodic outbreaks of cholera, malaria, and sleeping sickness.

Nigeria was also a founding member of the Organization for African Unity (now the African Union), and has tremendous influence in West Africa and Africa on the whole.

Homosexuality is illegal in Nigeria as it runs counter the country's deeply ingrained cultural and religious mores.

Nigeria has additionally founded regional cooperative efforts in West Africa, functioning as standard-bearer for ECOWAS and ECOMOG, economic and military organizations, respectively.

By its projections, Nigeria will be one of the countries in the world that will account for most of the world's total population increase by 2050.

Nigeria has a rich literary history, both prior to British imperialism and after, as Nigerians have authored several works of post-colonial literature in the English language.

Nigeria has a total area of 356,669 miІ (923,768 kmІ; its size makes it the world's 32nd-largest country (after Tanzania).

Nigeria, which in the 1960s grew 98 percent of its own food and was a net food exporter, now must import much of the same cash crops it once exported.

The middle belt of Nigeria is known for its diversity of ethnic groups, including the Pyem, Goemai, and Kofyar.

The first African Nobel Laureate, Wole Soyinka, is Nigeria's best-known writer and playwright.

Despite its vast government revenue from the mining of petroleum, Nigeria is beset by a number of societal problems due primarily to a history of inept governance.
Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa, with a population of close to 170 million.

The official language of Nigeria, English, was chosen to facilitate the cultural and linguistic unity of the country.

Nigeria is divided into 36 states and one Federal Capital Territory, which are further sub-divided into 774 Local Government Areas (LGAs).

The choice of English as the official language was partially related to the fact that a part of Nigerian population spoke English as a result of British colonial occupation.

Nigeria has pursued a policy of developing domestic training and military production capabilities.

The major political parties at present include the People's Democratic Party of Nigeria and the All Nigeria People's Party.

More than 2,000 years ago the Nok people in central Nigeria produced sculptures that have been discovered by archaeologists on the Jos Plateau.

Petroleum plays a large role in the Nigerian economy, accounting for 40 percent of the GDP.

Years of military rule, corruption, and mismanagement have hobbled economic activity and output in Nigeria, despite the restoration of democracy and subsequent economic reform.

Another prominent kingdom in southwestern Nigeria was the Kingdom of Benin, whose power lasted between the fifteenth and nineteenth centuries.

Abacha's death finally yielded an opportunity for return to civilian rule, and Nigeria elected Olusegun Obasanjo, a Yoruba and former military head of state, as the new president.

Unofficially Nigeria is invisibly divided into North Benue Niger and South Benue Niger by the Niger and Benue rivers.

Nigeria has more than 250 ethnic groups, with varying languages and customs, creating a country of rich ethnic diversity.

Mineral resources that are present in Nigeria but not yet fully exploited are coal and tin.

Nigeria has remained a key player in the international oil industry since the 1970s and maintains membership in the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) which it joined in 1971.

After a long decline in health, Francis Marion died at his plantation, Pond Bluff, on February 27, 1795.

Nigeria has the second largest newspaper market in Africa (after Egypt) with an estimated circulation of several million copies daily.

British goals were to have Nigeria produce raw materials such as tin and coal and consume manufactured goods.
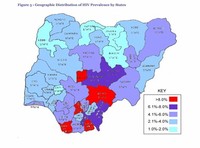
HIV/AIDS rate in Nigeria is much lower compared to the other African nations such as Kenya or South Africa whose prevalence (percentage) rates are in the double digits.

Active-duty personnel in the three Nigerian armed services total approximately 115,000.

The Nigerian side attacked Biafra, signaling the beginning of the 30-month war that ended in January 1970.

Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is the most populous country in Africa.

In April 2006, Nigeria became the first African country to fully pay off its debt (estimated at $30 billion) owed to the Paris Club.

Nigeria has significant production and manufacturing facilities such as factories for Peugeot (the French car maker), Bedford (the English truck manufacturer), now a subsidiary of General Motors, and also manufactures T-shirts and processed food.

After the imposition of sanctions by many Western nations, Nigeria turned to China, Russia, North Korea, and India for the purchase of military equipment and training.

Taking advantage of its role of sub-saharan Africa's most populated country, Nigeria has repositioned its military as an African peacekeeping force.

Nigeria won the gold medal for football in the 1996 Summer Olympics (in which they beat Brazil).

Nigeria is a member of the International Criminal Court, and the Commonwealth of Nations.

Following the war, which claimed the lives of more than 1.5 million Igbos, Nigeria became to an extent even more mired in ethnic strife.

Due to its multitude of diverse, sometimes competing ethno-linguistic groups, Nigeria has been beset since prior to independence with sectarian tensions and violence.

World famous musicians that come from Nigeria are Fela Kuti, Alhaji Sikiru Ayinde Barrister, King Sunny Ade, Ebenezer Obey, Femi Kuti, Lagbaja, Sade Adu.

Nigeria's national football team, known as the Super Eagles, has made the World Cup on three occasions:1994, 1998, and 2002.

The North Benue Niger, which consists of fourteen states, has ruled Nigeria for thirty-seven years, while the South Benue Niger, which consists of twenty-two states, has ruled for nine years.

Nigeria defaulted on its debt as arrears and penalty interest accumulated and increased the size of the debt.

During the oil boom of the 1970s, Nigeria helped initiate the founding of OPEC and billions of dollars generated by production in the oil-rich Niger Delta flowed into the coffers of the Nigerian state.

Ethnocentricism and sectarianism (especially religious) have played a dominant role in Nigerian politics prior to independence and afterward.
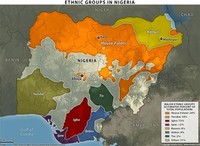
Nigeria's three largest ethnic groups have maintained historical preeminence in Nigerian politics; competition among these three groups, the Hausa-Fulani, Yoruba, and Igbo, has fueled corruption and graft.

The Nigerian air force (9,000 members) flies transport, trainer, helicopter, and fighter aircraft.

Nigeria re-achieved democracy in 1999 after a sixteen-year interruption; from 1966 until 1999, Nigeria had largely been ruled by military dictators from 1966-1979 and 1983-1998.

The drill monkey is only found in the wild in southeast Nigeria and neighboring Cameroon.

Abacha proved to be perhaps Nigeria's most brutal ruler and employed violence on a wide scale to suppress the continuing pandemic of civilian unrest.
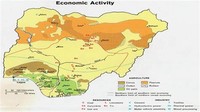
Despite huge deposits of these natural resources, the mining industry in Nigeria is almost non-existent.

Nigeria shares land borders with the Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, Niger in the north, and borders the Gulf of Guinea in the south.

Nigeria's foreign policy was soon tested in the 1970s after the country emerged united from its own civil war and quickly committed itself to the liberation struggles going on in Southern Africa.

According to the United Nations, Nigeria has been undergoing explosive population growth and one of the highest growth and fertility rates in the world.
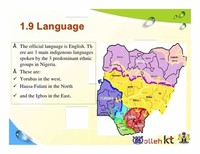
The major languages spoken in Nigeria represent three major families of African languages - the majority are Niger-Congo languages, such as Yoruba, Igbo.

A number of Cubans settled in Nigeria as political refugees following the Cuban Revolution.

JuJu music, which is percussion music fused with traditional music from the Yoruba nation and made famous by King Sunny Ade, is also from Nigeria.

The military in Nigeria have played a major role in the country's history since independence.

On October 1, 1960, Nigeria declared its independence from the United Kingdom after decades of colonial rule.

Newly independent Nigeria's government was a coalition of regionally based political parties.

Nigeria's main rivers are the Niger and the Benue, which converge and empty into the Niger Delta, the world's largest river delta.

According to the official November 2006 FIFA World Rankings, Nigeria is currently fifth-ranked football nation in Africa and the 36th highest in the world.
Nigeria has a total area of 356,669 miІ (923,768 kmІ; its size makes it the world's 32nd-largest country (after Tanzania).

Presently, Nigeria is the ninth most populous country in the world]], and even conservative estimates conclude that more than 20 percent of the world's black population lives in Nigeria.
Oil – The number one thing Africa's giant is most famous for is petroleum. ... Nigeria remains Africa's largest oil producer, though the country went from being 10th to 12th largest producer of oil in the world.Sep 3, 2015
Poverty has risen in Nigeria, with almost 100 million people living on less than a $1 (£0.63) a day, despite economic growth, statistics have shown. The National Bureau of Statistics said 60.9% of Nigerians in 2010 were living in "absolute poverty" - this figure had risen from 54.7% in 2004.Feb 13, 2012
The history of Nigeria can be traced to prehistoric settlers (Nigerians) living in the area as early as 11000 BC. Numerous ancient African civilizations settled in the region that is today Nigeria, such as the Kingdom of Nri, the Benin Empire, and the Oyo Empire. ... Nigeria became a British protectorate in 1901.
The country has 527 languages, seven of them are extinct. Nigeria also has over 1150 dialects and ethnic groups. The six largest ethnic groups are the Hausa and Fulani in the north, the Igbo in the southeast, and the Yoruba predominate in the southwest, Efik - Ibibio, and Ijaw of the south.
When you are not sure how to greet somebody, it is always appropriate to say “Kóyo ”.Mesiere. Mesiere is the Efik/Ibibio way of greeting. ... Sannu! This is the formal way to greet somebody and say: “hello” in the Northern region dominated by locals from the Hausa tribe. ... Abole.
According to official data, there are more than 520 languages spoken in Nigeria. By the way, nine of them are extinct. The other major languages are Igbo, Urhobo, Hausa, Yoruba, Ibibio, Fulfulde, Edo, Pidgin English, Ijaw, Kanuri, and Tiv.
The main languages spoken in the country include Hausa, Yoruba, Igbo, Edo, Ibibio, Eifk, and Annang language, Adamawa Fulfulde, French, and Cetral Kanuri, The diversity of language in Nigeria is a model of Africa as a whole that encompass 3 major African languages families – the Afro-Asiatic, Nilo-Saharan, and the ...
Arguably, the most useful, indigenous African languages for Americans to learn are Yoruba (primarily spoken in Nigeria), Xhosa (South Africa), Swahili (Kenya, Tanzania, and much of East Africa), and Amharic (mainly Ethiopia).Nov 10, 2015