Facts about Nile

The cataracts are also significant because these define river segments where granite and other hard rocks come down to the edge of the Nile.

The Nile still supports much of the population living along its banks.

The Nile north of Aswan is a regular tourist route, with cruise ships and traditional wooden sailing boats known as feluccas.

The Blue Nile emerges from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian highlands, then flows about 850 miles (1,400 kilometers) to Khartoum, including sections that are channeled at great force through a narrow, rocky gorge.

The Nile is also home to a variety of fish and birds, mostly in the southern part.

Satellite imagery was used to identify dry watercourses in the desert to the west of the Nile.

The Nile provided the elements that make a vigorous civilization, and contributed much to its endurance for three thousand years.
An Eonile canyon, now filled by surface drift, represents an ancestral Nile called the Eonile that flowed during the later Miocene (23 to 5.3 million years ago).

North of Cairo, the Nile splits into two branches that empty into the Mediterranean Sea: the Rosetta Branch to the west and the Damietta to the east, forming the Nile Delta.

The Nile has been the lifeline for Egyptian culture since the Stone Age.

Water is also lost due to human usage, so that progressively less water flows in the Nile from Atbara, the Nile's last tributary, all the way to the Mediterranean Sea.

The Blue Nile is the source of most of the Nile's water and fertile soil, but the White Nile is the longer of the two.

The Blue Nile starts at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast.

The Nile was so significant to the lifestyle of the Egyptians that they created a god, Hapi, dedicated to the welfare of the Nile’s annual inundation.

The drainage basin of the Nile encompasses about 10 percent of the area of Africa.

The present Nile is at least the fifth river that has flowed north from the Ethiopian highlands.

Like the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Mesopotamia in modern Iraq, the Nile provided a hospitable environment for the emergence of one of the earliest and most dominant civilizations in history.

Despite the attempts of the Greeks and Romans (who were unable to penetrate the Sudd), the upper reaches of the Nile remained largely unknown.

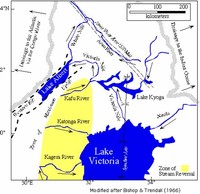
The Nile leaves Lake Victoria at Ripon Falls, near Jinja, Uganda, as the Victoria Nile.

During the dry season (January to June), however, the White Nile contributes between 70 and 90 percent of the total discharge from the Nile.

Today we have hydrographic information that explains why the Nile is a "summer river."

The White Nile rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source in southern Rwanda, and flows north from there through Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Uganda, and southern Sudan.

The Nile itself was also a convenient and efficient means of transportation for people and goods.

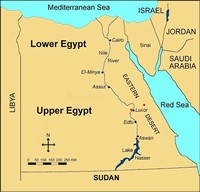
Two features define the Nile between Khartoum and Aswan: the cataracts and the Great Bend.

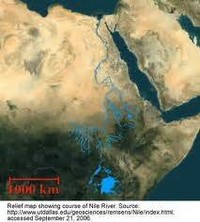
The Nile is one of the world's great waterways, at 4,180 miles (6,695 kilometers) generally regarded as the longest river in the world and among the most culturally significant natural formations in human history.

That would have made the Nile much longer, with its longest headwaters in northern Zambia.

The Nile south of the Great Bend in Sudan is really two hydraulic regimes: The White Nile maintains a constant flow over the year, because its flow is doubly buffered.

Without the waters of the Nile River for irrigation, Egyptian civilization would probably have been short-lived.

The White Nile Expedition, led by South African Hendri Coetzee, was to become the first to navigate the Nile's entire length.

Fish, especially the Nile perch and tilapia, are an important food source.

Formerly, Lake Tanganyika drained north into the Nile, until the Virunga Volcanoes blocked its course in Rwanda.

The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that "Egypt was the gift of the Nile," and in a sense that is correct.

The Nile also provided the resources, such as food or money, to quickly and efficiently raise an army.

The source of the Nile is sometimes considered to be Lake Victoria, but the lake itself has feeder rivers of considerable size.

Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Victoria, the queen of the United Kingdom.

The pharaoh, including female pharaohs, would often wear a false beard made of goat hair during rituals and ceremonies.

The Nile is unusual in that its last tributary (the Atbara) joins it roughly halfway to the sea.
The upper regions of the Nile are in mountain forests, but as it travels north the vegetation around the river changes to shrubs and short trees, then no plants in the desert.

After Aswan, there is less water due to evaporation of the Nile's waters during its leisurely passage through the Sahara Desert.
The word "Nile" comes from Greek Neilos (ὁ Νεῖλος). Neilos came from the word "river valley". In the ancient Egyptian language, the Nile is called Ḥ'pī or iteru, meaning "great river", represented by the hieroglyphs shown above (literally itrw, and 'waters' determinative).
When the floods went down it left thick rich mud (black silt) which was excellent soil to plant seeds in after it had been ploughed. The ancient Egyptians could grow crops only in the mud left behind when the Nile flooded. So they all had fields all along the River Nile.
Animals Living In and Around the River Nile. There are a vast number of animals that live in and around the River Nile, attracted by its fertile waters. ... Reptiles. The most well-known and common reptile to be found in the River Nile area is the famous Nile crocodile. ... Hippopotamus and Rhino. ... Fish.
They live throughout sub-Saharan Africa, the Nile Basin, and Madagascar in rivers, freshwater marshes, and mangrove swamps. The diet of the Nile crocodile is mainly fish, but it will attack almost anything unfortunate enough to cross its path, including zebras, small hippos, porcupines, birds, and other crocodiles.
The Blue Nile, however, is the source of most of the water and silt. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source still undetermined but located in either Rwanda or Burundi. It flows north through Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Uganda and South Sudan.
John Hanning Speke
The world's longest river, located in Egypt, the Nile flows 4,132 miles (6,650 kilometres) northward to the Mediterranean Sea (a very unusual direction for a river to take). It was considered the source of life by the ancient Egyptians and has played a vital role in the country's history.