Facts about Nitrogen

The most prominent ones are nitrogen monoxide (NO) (known more commonly as nitric oxide in biology) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).

Some nitrides, such as lithium nitride (Li3N), are salt-like, in which the nitrogen exists as an ion with three negative charges (N3?).

Animal metabolism of nitrogen in proteins generally results in the excretion of urea, while animal metabolism of nucleic acids results in the excretion of urea and uric acid.

At ordinary temperatures and pressures, free nitrogen (unbound to any other element) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas.

Nitrogen gas was inert (unreactive) enough that Antoine Lavoisier referred to it as "azote," from the Greek word ?????? meaning "lifeless."

Isolated in the liquid form, this nitrogen is often referred to by the quasi-formula LN2, but it is more accurately written as N2(l).

Nitrogen is an essential element in the molecules of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, and other substances vital to life.

The Earth's nitrogen continually cycles through the atmosphere, biosphere, and lithosphere, effected by such processes as nitrogen fixation by bacteria, metabolic processing in living things, and decomposition of dead organic matter.

Specific bacteria (such as those of the genus Rhizobium) possess certain enzymes ("nitrogenases") that can fix atmospheric nitrogen (see nitrogen fixation) into a form (ammonium ion) that is chemically useful for higher organisms.

The two nitrogen atoms in each molecule are attached to each other by a strong, triple covalent bond.

Nitrogen makes up 78.084 percent of the volume (and 75.5 percent of the mass) of air.
Ammonia, a significant compound of nitrogen, is useful for fertilizers and for the synthesis of nitric acid and other valuable compounds.

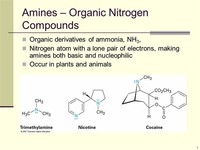
Nitrogen is also an important element in many organic compounds, in which it is directly bound to one or more carbon atoms.

When breathed at high partial pressures (higher than 3 atmospheres, encountered at diving depths below about 30 meters) nitrogen begins to act as an anesthetic agent.

Technologies that isolate nitrogen from gaseous air include methods known as pressure swing adsorption and membrane separation.

The ability to combine or "fix" molecular nitrogen is a key feature of modern industrial chemistry, where nitrogen and hydrogen are made to react to form ammonia, by what is called the Haber process.

The decay of organisms and their waste products may produce small amounts of nitrate, but most decay processes eventually return nitrogen content to the atmosphere, as molecular nitrogen.
By far the most common is 14N (99.634 percent), which is thought to be produced in stars by a set of nuclear fusion reactions called the "carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle" (CNO cycle).

Other notable nitrogen-containing drugs, such as morphine, are derived from plant alkaloids.

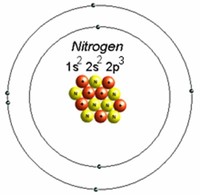
Nitrogen is a chemical element in the periodic table, situated at the head of group 15 (former group 5A), just above phosphorus.

Ammonia: The main neutral hydride of nitrogen is ammonia (NH3), although hydrazine (N2H4) is also common.

Nitrogen is produced industrially in large quantities by a method known as the fractional distillation of liquefied air.

Direct skin contact with liquid nitrogen causes severe frostbite (cryogenic burns) within seconds, depending on the form of liquid nitrogen (liquid versus mist) and surface area of the nitrogen-soaked material.

Liquid nitrogen is a cryogen (low-temperature refrigerant) used for freezing and transport of food and other perishable products.

Nitrogen gas consists of diatomic molecules, each of which has the chemical formula N2.
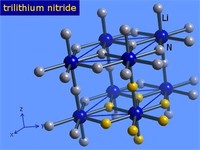
Nitrides: In the molecule of a nitride compound, a nitrogen atom is attached to an atom of a more electropositive element.

The characteristic odor of animal flesh decay is caused by nitrogen-containing long-chain amines, such as putrescene and cadaverine.

Nitrogen-fixing bacteria can also be symbiotic with other plant species, such as alders, lichens, casuarina, myrica, liverwort, and gunnera.

Compounds that contain this element have been observed by astronomers, and molecular nitrogen has been detected in interstellar space by David Knauth and coworkers using the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer.
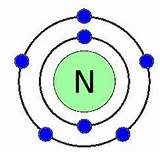
Each atom of nitrogen has five electrons in its outer shell, and it forms three covalent bonds in most compounds.
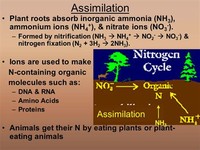
Animals use nitrogen-containing amino acids from plant sources as starting materials for all nitrogen-compound animal biochemistry, including the manufacture of proteins and nucleic acids.

Nitrogen gas has a wide variety of applications, including serving as an inert replacement for air where oxidation is undesirable.

Molecular nitrogen occurs in trace amounts in the atmospheres of various planets, but it is a major constituent of Titan, the planet Saturn's largest moon.

When appropriately insulated from ambient heat, liquid nitrogen serves as a compact, readily transportable source of nitrogen gas without pressurization.

Rapid release of nitrogen gas into an enclosed space can displace oxygen, thus representing an asphyxiation hazard.

Nitrogen is present in all living organisms, as part of the molecular structures of proteins, nucleic acids, and other important substances.

Nitrogen was also studied at about the same time by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, Henry Cavendish, and Joseph Priestley, who referred to it as "burnt air" or "phlogisticated air."

Compounds that contain this element have been observed by astronomers, and molecular nitrogen has been detected in interstellar space by David Knauth and coworkers using the Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer.

Nitrogen forms part of various inorganic compounds, some of which are noted below.

Nitrogen (symbol N, atomic number 7) is the chief constituent of the Earth's atmosphere and a vital element in all known forms of life.

The alchemists of the Middle Ages experimented with various compounds of nitrogen.
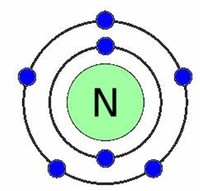
Each atom of nitrogen has five electrons in its outer shell, and it forms three covalent bonds in most compounds.
Nitrogen is a naturally occurring element that is essential for growth and reproduction in both plants and animals. It is found in amino acids that make up proteins, in nucleic acids, that comprise the hereditary material and life's blueprint for all cells, and in many other organic and inorganic compounds.
Liquid nitrogen is nitrogen in a liquid state at an extremely low temperature. It is a colorless clear liquid with a density of 0.807 g/ml at its boiling point (−195.79 °C (77 K; −320 °F)) and a dielectric constant of 1.43.
Animals get the nitrogen they need by eating plants or other animals that contain nitrogen. When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into soil on land or into ocean water. Bacteria alter the nitrogen into a form that plants are able to use.May 7, 2007
Nitrogen is so vital because it is a major component of chlorophyll, the compound by which plants use sunlight energy to produce sugars from water and carbon dioxide (i.e., photosynthesis). It is also a major component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
The visual symptoms of nitrogen deficiency mean that it can be relatively easy to detect in some plant species. Symptoms include poor plant growth, and leaves that are pale green or yellow because they are unable to make sufficient chlorophyll.
Nitrogen is used by plants for lots of leaf growth and good green color. Phosphorous is used by plants to help form new roots, make seeds, fruit and flowers. It's also used by plants to help fight disease. Potassium helps plants make strong stems and keep growing fast.
