Facts about Plants

Plant fossils include roots, wood, leaves, seeds, fruit, pollen, spores, phytoliths, and amber (the fossilized resin produced by some plants).

Plants like onion (Allium cepa), hyacinth (Hyacinth), narcissus (Narcissus) and tulips (Tulipa) reproduce by forming bulbs.

Other plants or plant parts that are eaten include fruits, vegetables, legumes, herbs, and spices.

The chloroplasts of green plants are surrounded by two membranes, suggesting they originated directly from endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.

Most conspicuous are the seaweeds, multicellular algae that may roughly resemble terrestrial plants, but are classified among the green, red, and brown algae.

Vascular plants first appeared during the Silurian (444 - 417 mya) period, and by the Devonian (417 - 359 mya) had diversified and spread into many different land environments.

Some plants, known as myco-heterotrophs, parasitize mycorrhizal fungi, and hence act as epiparasites on other plants.

Leaf cutting propagation of certain chimeral variegated plants, such as snake plant, will produce mainly nonvariegated plants.

Bryophytes—the Bryophyta (mosses), the Hepaticophyta (liverworts), and the Anthocerotophyta (hornworts)—are the only nonvascular plants grouped within the Kingdom Plantae.

Among the vascular plants, perennials include both evergreens that keep their leaves the entire year, and deciduous plants which lose their leaves for some part.

Much of human nutrition depends on plants, whether directly or indirectly via animals that consume or pollinate plants.

Pteridophyta (previously known as Filicophyta) is a vast group of 20,000 species of plants found globally, and known as ferns.
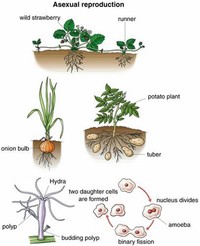
Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants, and is also called vegetative propagation or vegetative multiplication.

The spermatophytes (also known as phanerogams) comprise those plants that produce seeds.

The spoil heaps of coal mines are the best places to collect; coal itself is the remains of fossilized plants, though structural detail of the plant fossils is rarely visible in coal.

Fossil land plants are recorded in terrestrial, lacustrine, fluvial, and nearshore marine sediments.

Early fossils of these ancient plants show the individual cells within the plant tissue.

Early seed plants are referred to as gymnosperms (naked seeds), as the seed embryo is not enclosed in a protective structure at pollination, with the pollen landing directly on the embryo.

The so-called "seed ferns" (Pteridospermae) were one of the earliest successful groups of land plants, and forests dominated by seed ferns were prevalent in the late Paleozoic (359 - 253 mya).

The remains of fossil plants are not as common as fossil animals, although plant fossils are locally abundant in many regions worldwide.

Aristotle divided all living things between plants, which generally do not move or have sensory organs, and animals exhibiting sensory movement and motility.

The photosynthesis and carbon fixation conducted by land plants and algae are the ultimate source of energy and organic material in nearly all ecosystems.

Trees and flowering plants are used in landscaping and decoration, and are featured in works of art.

The fossil record contains evidence of many extinct taxa of seed plants.

Whereas other vascular plants, such as ferns, reproduce by means of spores and so need moisture to develop, some seed plants can survive and reproduce in extremely arid conditions.

Seed-bearing plants were traditionally divided into angiosperms, or flowering plants, and gymnosperms, which includes the gnetae, cycads, ginkgo, and conifers.

The angiosperms, comprising the flowering plants, were the last major group of plants to appear, emerging from within the gymnosperms during the Jurassic (201-147 mya) and diversifying rapidly during the Cretaceous (147-66 mya).

The most familiar plants are the multicellular land plants with specialized reproductive organs, called embryophytes.

The Lycopodiophyta are one of several classes of plants that expanded onto land during the Silurian and Devonian periods.

Non-vascular plants include those land plants (embryophytes) without a vascular system.

Plants are distinguished from green algae, from which they are considered to have evolved, by having specialized reproductive organs protected by non-reproductive tissues.

Psilotophyta, or Psilotales (the "whisk ferns") is a grouping of nonseed plants that sometimes is considered as an order of the Class Ophioglossopsida.

Plants rely on soil primarily for water (in quantitative terms), but also obtain nitrogen, phosphorus and other crucial elemental nutrients.

Some vascular plants, referred to as trees and shrubs, produce woody stems and are an important source of building material or raw material for producing paper.
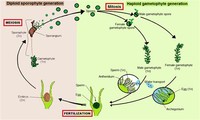
Alternation of generations is a reproductive cycle of those plants, fungi and protists in which a sexual reproductive phase alternates with an asexual reproductive phase.

Many plants are epiphytes, meaning they grow on other plants, usually trees, without parasitizing them.

Plants are found throughout the world, both on land and in water bodies.

Plants are most abundant where resources (water, sunlight, adequate growth temperatures, and fertile soil) are most abundant, and accordingly, the tropics overwhelmingly contain the greatest biomass and species diversity.

Vascular plants include the seed plants—flowering plants (angiosperms), and gymnosperms—as well as non-seed (vascular) plants, such as ferns, clubmosses, and horsetails.

The first primitive seed plants, Pteridosperms (seed ferns) and Cordaites, both groups now extinct, appeared in the late Devonian and diversified through the Carboniferous, with further evolution through the Permian and Triassic periods.

Only the green algae are still considered relatives of the plants, although these also are generally classified as protists rather than as plants.

All of these plants comprise eukaryotic cells with cell walls composed of cellulose, and most obtain the energy through photosynthesis, using light and carbon dioxide to synthesize food.

snake-tongue-leaved') are a small group of plants, the adders'-tongues and the moonworts and grape-ferns.

The Coal Measures are a major source of Palaeozoic plant fossils, with many groups of plants in existence at this time.

Vascular plants comprise those embryophytic plants that have specialized tissues for conducting water.

Other plants like potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) and dahlia (Dahlia) reproduce by a similar method of producing tubers.

The horsetails were a much larger and more diverse group in the distant past before seed plants became dominant across the Earth.

Strict vegetarians rely entirely on plants (as well as some algae and fungi) for their nutrition.

Plants are found throughout the world, both on land and in water bodies.

Through a process known as photosynthesis, plants use the energy in sunlight to convert carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into simple sugars.

Plants also provide valuable products, such as lumber, paper, and medicines.

The pattern generally applies to the flowering plants even though the application is not apparent because the gametophyte, haploid generation is vastly reduced in size.

The embryophytes developed from green algae; the two groups are sometimes collectively referred to as the green plants or Viridiplantae.
We use plants for food because we get fruits and vegetables from plants and trees. Plants give us oxygen, and we give them carbon dioxide. The fresh gel of the aloe plant is used to treat sunburn and to keep skin soft and young. We use trees for heat, such as burning fire wood.Oct 3, 2013
One of the materials that plants produce as they make food is oxygen gas. This oxygen gas, which is an important part of the air, is the gas that plants and animals must have in order to stay alive. When people breathe, it is the oxygen that we take out of the air to keep our cells and bodies alive.
Plants provide us with food, fiber, shelter, medicine, and fuel. The basic food for all organisms is produced by green plants. In the process of food production, oxygen is released. This oxygen, which we obtain from the air we breathe, is essential to life.
Roses are not toxic to cats, but they do have thorns. If your cat plays in a rosebush or tries to eat its leaves and stems, he could get an upset stomach and scratch up his skin and face. Also, if you've used topical chemicals on your bush, they could make him sick.
Plants in wetlands. Several thousand plant species grow in wetlands, ranging from mosses and grasses to shrubs and trees. Different kinds of wetland are home to different types of plant, depending on 2 main factors: whether the wetlands have mostly fresh, salty or brackish (slightly salty) water.Dec 1, 2017
A fen is a fresh water peat wetland covered mostly by grasses sedges, reeds, and wildflowers of high pH (alkaline) ground water. Bogs have soil that is low in nutrients. Evergreen trees and shrubs, and a floor covered by a thick carpet of sphagnum moss. Some species of carnivorous plants are also found in bogs.
While the sharp teeth and jaw of a T. rex is obviously that of a fearsome superpredator and the blunt teeth of a Triceratops obviously belong to a plant eater, a lot of dinosaur teeth fall somewhere in the middle. ... Many of the supposedly carnivorous therapod dinosaurs were actually eating plants.Dec 20, 2010
MammalsBlack-tailed prairie dog (Cynomys ludovicianus)Bushy-tailed woodrat (Neotoma cinerea)Grizzly bear (Ursus arctos horribilis)Mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus)Pronghorn (Antilocapra americana)Swift fox (Vulpes velox)White-tailed jackrabbit (Lepus townsendii)
Cellulose is the substance that makes up most of a plant's cell walls. Since it is made by all plants, it is probably the most abundant organic compound on Earth. Aside from being the primary building material for plants, cellulose has many others uses.
Structure. Cellulose is a very important polysaccharide because it is the most abundant organic compound on earth. Cellulose is a major component of tough cell walls that surround plant cells, and is what makes plant stems, leaves, and branches so strong.
The Coolest Plants Found in the Amazon RainforestHeliconia Flower (Lobster-Claw) ... Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis) ... Orchids. ... Cacao (Theobroma cacao) ... Giant Water Lilies (Victoria amazonica) ... Passion Fruit Flower (Passiflora) ... Bromeliads (Bromeliaceae) ... Monkey Brush Vine (Combretum rotundifolium)More items...
The visual symptoms of nitrogen deficiency mean that it can be relatively easy to detect in some plant species. Symptoms include poor plant growth, and leaves that are pale green or yellow because they are unable to make sufficient chlorophyll.
Nitrogen is used by plants for lots of leaf growth and good green color. Phosphorous is used by plants to help form new roots, make seeds, fruit and flowers. It's also used by plants to help fight disease. Potassium helps plants make strong stems and keep growing fast.
Crops usually display no obvious symptoms of phosphorus deficiency other than a general stunting of the plant during early growth. By the time a visual deficiency is recognized, it may be too late to correct in annual crops. Some crops, such as corn, tend to show an abnormal discoloration when phosphorus is deficient.
Because wood ash raises the pH of your soil, always test the soil to ensure that it does not become overly alkaline. Never use wood ashes on acid-loving plants like berries, including raspberries, strawberries and blueberries. Other acid-loving plants include rhododendrons, fruit trees, azaleas, potatoes and parsley.
Vines like honeysuckle, clematis and Boston ivy thrive in alkaline soil. A wide range of flowering and ornamental plants are perfectly suited to these soil conditions as well. Options include lily, iris, bluebell, crocus, geranium, hyacinth, maidenhair fern, morning glory, poppy and daisy.
The Coolest Plants Found in the Amazon RainforestHeliconia Flower (Lobster-Claw) ... Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis) ... Orchids. ... Cacao (Theobroma cacao) ... Giant Water Lilies (Victoria amazonica) ... Passion Fruit Flower (Passiflora) ... Bromeliads (Bromeliaceae) ... Monkey Brush Vine (Combretum rotundifolium)More items...
There are approximately 10 million species of animals, plants and insects known to man and more than half of them call the rainforest home. There are approximately 3000 fruits that grow in the rainforest that are edible. Many plants around the world have medicinal qualities.
The smoothness of the bark may also make it difficult for other plants to grow on their surface. Lianas are climbing woody vines that drape rainforest trees. They have adapted to life in the rainforest by having their roots in the ground and climbing high into the tree canopy to reach available sunlight.
Desert succulents, such as cacti or rock plants (Lithops) for example, survive dry spells by accumulating moisture in their fleshy tissues. They have an extensive system of shallow roots to capture soil water only a few hours after it has rained.
Learn more about these areas, which are often barren but not always devoid of life.Tumbleweed. Most people recognize this mature Russian thistle as common tumbleweed. ... Prickly Pear Cacti. ... Cacti. ... Saguaro Cactus. ... Mexican Poppies. ... Weathered Trees. ... Wildflowers. ... Black Rock Desert, Nevada.More items...
There are at least 2,450 native plant species found in California's desert, according to a great article by Chris Clarke on desert life, posted at KCET.Jan 11, 2012
Boron helps control the transport of sugars in plants. It is important to cell division and seed development. As a micronutrient, the amount of boron in soil is minute, but among micronutrients, boron deficiency in plants is the most common.Nov 26, 2016
It is the most widespread micronutrient deficiency around the world and causes large losses in crop production and crop quality. Boron deficiency affects vegetative and reproductive growth of plants, resulting in inhibition of cell expansion, death of meristem, and reduced fertility.
Plants are essential for any ecosystem. They provide all the energy for the ecosystem, because they can get energy directly from sunlight. They use a process called photosynthesis to use energy from the sun to grow and reproduce. They also must get nutrients from the soil.
We use plants for food because we get fruits and vegetables from plants and trees. Plants give us oxygen, and we give them carbon dioxide. The fresh gel of the aloe plant is used to treat sunburn and to keep skin soft and young. We use trees for heat, such as burning fire wood.Oct 3, 2013
Plants make oxygen. ... This oxygen gas, which is an important part of the air, is the gas that plants and animals must have in order to stay alive. When people breathe, it is the oxygen that we take out of the air to keep our cells and bodies alive. All of the oxygen available for living organisms comes from plants.
Through a process called photosynthesis, plants use energy in sunlight to turn a gas called carbon dioxide and water into sugar. Plants then use this sugar to grow. At the same time, plants produce a gas called oxygen as a waste product, which is lucky for us and other animals because we need oxygen to breathe!
1. Plants reduce pollution by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the air and giving off oxygen – just what we need to survive! This is called photosynthesis.Jun 4, 2015
Plants Provide Air and Regulate the Water Cycle. Plants bring you oxygen which is a by-product of photosynthesis. Carbon is also stored by plants and they help in keeping a lot of the produced carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels out into the earth's atmosphere.May 27, 2014
Take the time to prepare the proper environment before new plants arrive. ... Don't smother new plants with too thick a soil blanket. ... Use fast foods or health foods, but nourish young plants well during growth spurts. ... Weed out bad influences when plants are young. ... Be overprotective at a plant's vulnerable seedling stage.More items...




