Facts about Pollination

The largest managed pollination event in the world is in Californian almond orchards, where nearly half (about one million hives) of the U.S. honeybees are trucked to the almond orchards each spring.

Losey and Vaughan (2006) report that native insect pollination saves the United States agricultural pollination management industry nearly an estimated $3.1 billion annually through natural crop production.
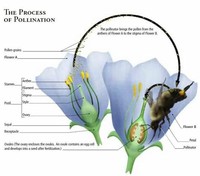
The process of pollination requires agents (pollinators) that carry or move the pollen grains from the anther to the receptive part of the female reproductive organ.

Pollination also requires consideration of pollenizers (the plant that provides the pollen).
Two examples of multiple mammal pollination are the genus Quararibea which is visited by 12 species and Combretum which is visited by eight (Carthewa 1997).

Zoophily is a form of pollination whereby pollen is transferred by vertebrates, particularly by hummingbirds and other birds, and bats, but also by monkeys, marsupials, lemurs, bears, rabbits, deer, rodents, lizards and other animals.

Pollination of food crops has become an environmental issue, due to two trends.

Of the geckos visiting this species, two-thirds of them carried large amounts of pollen, suggesting a main role in pollination.

Pollination syndromes are groups of adaptations of flowers that attract particular types of pollinators.

Good pollination management seeks to have bees in a "building" state during the bloom period of the crop, thus requiring them to gather pollen, and making them more efficient pollinators.

Many fruits are dependent on bats for pollination, such as mangoes, bananas, and guavas (USDA 2006).

Hybridization is effective pollination between flowers of different species of the same genus, or even between flowers of different genera (as in the case of several orchids).

Traits of the M. depressa flowers support non-flying mammal pollination.

Pollination management is a branch of agriculture that seeks to protect and enhance present pollinators and often involves the culture and addition of pollinators in monoculture situations, such as commercial fruit orchards.

Plant species that feed non-flying mammals will often exhibit similar characteristics to aid in pollination.

The study of pollination brings together many disciplines, such as botany, horticulture, entomology, and ecology.

Other plants have chemical or physical barriers to self-pollination and need to be cross-pollinated.

Pollination is important in horticulture because most plant fruits will not develop if the ovules are not fertilized.

Peaches are considered self-fertile because a commercial crop can be produced without cross-pollination, though cross-pollination usually gives a better crop.

Just as the combine harvesters follow the wheat harvest from Texas to Manitoba, beekeepers follow the bloom from south to north, to provide pollination for many different crops.

Well-documented studies of non-flying mammal pollination now involve at least 59 species of mammals distributed among 19 families and six orders (Carthewa 1997).

The United States solution to the pollinator shortage, so far, has been for commercial beekeepers to become pollination contractors and to migrate.

The ecological and financial importance of natural pollination by insects to agricultural crops, improving their quality and quantity, has become more and more appreciated and has given rise to new financial opportunities.

Entomophily is a form of pollination whereby pollen is distributed by insects, particularly bees, Lepidoptera (e.g., butterflies and moths), flies, and beetles.

Most bat species that pollinate flowers inhabit Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific Islands, although bat pollination occurs over a geographically wide range.

Pollination can be cross-pollination with a pollinator and an external pollenizer, self-pollenization with a pollinator, or self-pollination without any pollinator.

Many angiosperms have unique adaptations to attract animals, such as honeybees or hummingbirds, to act as the agents of pollination.

Bat pollination is an integral process in tropical communities with 500 tropical plant species completely, or partially, dependent on bats for pollination (Heithaus 1974).

