Facts about Protein

Protein is an important macronutrient in the human diet, supplying the body's needs for amino acids, particularly the essential amino acids that humans are unable to synthesize.

When dietary proteins and carbohydrates are deficient, proteins may be broken down to synthesize glucose to supply organs, like the brain, that normally utilize glucose as a fuel.

Proteins are assembled from amino acids based on information encoded as genes, specific nucleotide sequences in the DNA.

Given the central importance of proteins to life, particularly the importance of strong muscles for survival, animals are designed to minimize the loss of protein from muscle during periods of starvation.

A full understanding of why incorrect protein folding occurs might lead to advances in the treatment of diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Other proteins play structural or mechanical roles, such as those that form the struts and joints of the cytoskeleton, which is like a system of scaffolding within a cell.

The incorrect folding of proteins can lead to illnesses such as Alzheimer’s disease, in which brain function is limited by deposits of incorrectly-folded proteins that can no longer perform their functions.

Proteins are involved in practically every function performed by a cell, including regulation of cellular functions such as signal transduction and metabolism.
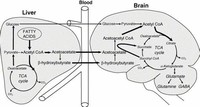
The brain’s transition from glucose to ketone bodies occurs quite rapidly, so that hardly any protein in muscle is lost, enabling them to make their arduous, 2,400-kilometer flight.

Proteins are generally large molecules (e.g., the muscle protein titin or connectin has a single amino acid chain that is 27,000 subunits long).

The word protein was first mentioned in a letter sent by the Swedish chemist Jцns Jakob Berzelius to Gerhardus Johannes Mulder on July 10, 1838.

The exact amount of dietary protein needed to satisfy protein requirements for humans, known as a Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA), may vary widely depending on age, sex, level of physical activity, and medical condition.

Severe protein deficiency is most commonly encountered in developing countries in times of famine, when diets are high in starch and low in protein.

Through genetic engineering, researchers can alter the amino acid sequence and hence the structure, targeting, susceptibility to regulation, and other properties of a protein.

Protein deficiency can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, insulin resistance, hair loss, loss of hair pigment, loss of muscle mass, low body temperature, hormonal irregularities, and loss of skin elasticity.

Kwashiorkor is a type of childhood malnutrition that is linked to insufficient protein intake (and may also result from deficiencies in various nutrients), though its causes are not fully understood.

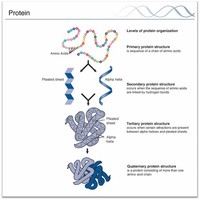
The question of how proteins arrive at their native state is an important area of biochemistry, called the study of protein folding.

Discovered by Jцns Jakob Berzelius in 1838, proteins are among the most actively studied molecules in biochemistry.

Biochemists are interested in determining a protein's unique amino acid sequence, which is presumed to govern its three-dimensional structure and, in turn, its biological function.

Soy products such as tofu are particularly important to many vegetarians and vegans as a source of complete protein (a protein that contains significant amounts of all the essential amino acids).

The sequence of amino acids in a protein is defined by a gene and encoded in the genetic code, which selects protein components from a set of 20 "standard" amino acids.
The functionality of a protein is dependent upon its ability to fold into a precise three-dimensional shape.

That is, by careful control of solution conditions to separate a denatured protein from the denaturing chemical, a denatured protein could be converted to its native form.

The best way to obtain the full range of essential amino acids is to consume a variety of protein-rich foods.

The genetic sequences of different proteins may be spliced together to create chimeric proteins that possess properties of both.

Along with polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids, proteins are one of the major classes of macromolecules that make up the primary constituents of biological organisms.

The shape into which a protein naturally folds is known as its native state, which is presumed to be determined by its sequence of amino acids.

Another area of protein research attempts to engineer proteins with entirely new properties or functions, a field known as protein engineering.

From the DNA, the protein-coding nucleotide sequences are each transcribed into an immature messenger RNA (mRNA), which is then cleaned up and modified to form the mature mRNA that is translated into a protein.

Such long chains of amino acids are almost universally referred to as proteins, but shorter strings of amino acids may be referred to as polypeptides, peptides, or, less commonly, oligopeptides.

Charting the amino acid sequences of proteins contributes to a reconstruction of the history of early life, as proteins resemble one another in sequence only if they evolved from a common ancestor.
Protein is made up of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of your muscles and body. Without them, it would be impossible to build, repair or even maintain muscle tissue. Protein is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.Dec 12, 2011
Protein is made up of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of your muscles and body. Without them, it would be impossible to build, repair or even maintain muscle tissue. Protein is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.Dec 12, 2011
They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. ... These proteins provide structure and support for cells.Feb 13, 2018
When you eat foods that contain protein, the digestive juices in your stomach and intestine go to work. They break down the protein in food into basic units, called amino (say: uh-MEE-no) acids. The amino acids then can be reused to make the proteins your body needs to maintain muscles, bones, blood, and body organs.
Proteins also carry vitamins, such as vitamin A, from your organs to your cells. A specific protein in your red blood cells, hemoglobin, is responsible for carrying oxygen from your lungs to your cells. Hemoglobin also takes carbon dioxide from your cells to your lungs, so that it can be expelled from the body.
When you consume more protein than your body needs, the excess protein is used to provide your body with energy or turned into fat. You can't store extra amino acids or protein for later use, so if you consume too many calories in an effort to increase your protein intake you will gain weight.
When you consume more protein than your body needs, the excess protein is used to provide your body with energy or turned into fat. You can't store extra amino acids or protein for later use, so if you consume too many calories in an effort to increase your protein intake you will gain weight.
However, if we eat more than we need, the excess protein will be broken down and used for energy. Even though a relatively high protein intake is healthy and safe, eating massive amounts of protein is unnatural and may cause harm. Traditional populations got most of their calories from fat or carbs, not protein.Jun 4, 2017


