Facts about Riboflavin

Beef liver is a particular rich source of riboflavin, and milk and dairy products (yogurt, cottage cheese, cheese) also provide substantial amounts.

The fact that riboflavin deficiency does not immediately lead to gross clinical manifestations indicates that the systemic levels of this essential vitamin are tightly regulated.

Hence the requirement for riboflavin-5'-phosphate (E101a), a more expensive but more soluble form of riboflavin.

Riboflavin attaches itself to the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in cells, and when light is applied, the nucleic acids are broken, effectively killing those cells.

The light used to irradiate the infants breaks down not only the toxin causing the jaundice, but the naturally occurring riboflavin within the infant's blood as well.

Riboflavin, being yellow or yellow-orange in color, also is used in food coloring.

Riboflavin is continuously excreted in the urine of healthy individuals (Brody 1999), making deficiency relatively common when dietary intake is insufficient.

Riboflavin deficiency is classically associated with the oral-ocular-genital syndrome.

Riboflavin has been used in several clinical and therapeutic situations.

Riboflavin is essential for the production of enzymes for the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates into energy.

In animals, riboflavin deficiency results in lack of growth, failure to thrive, and eventual death.

More recently there has been growing evidence that supplemental riboflavin may be a useful additive along with beta-blockers in the treatment of migraine headaches (Sбndor et al.

Experimental riboflavin deficiency in dogs results in growth failure, weakness, ataxia, and inability to stand.

Riboflavin is one of three vitamins known to be involved in the regulation of circadian rhythms in humans and other mammals (Turner and Frey 2005).

The concentrations of riboflavin in their modified strain are so high, that the mycelium has a reddish/brownish color and accumulates riboflavin crystals in the vacuoles, which will eventually burst the mycelium.

Riboflavin is used in baby foods, pastas, sauces, processed cheese, fruit drinks, vitamin-enriched milk products, some energy drinks, and is widely used in vitamin supplements.

Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a water-soluble, yellow-orange organic compound in the vitamin B complex that is required for a number of metabolic processes in living organisms.

Recently, riboflavin has been used in a new treatment to slow or stop the progression of the corneal disorder keratoconus.

A positive diagnostic test for measuring levels of riboflavin in serum is ascertained by measuring erythrocyte levels of glutathione reductase.

Large quantities of riboflavin are often included in multi-vitamins; often, the dose is far more than a normal human can use in a day.

The chemical company BASF has installed a plant in South Korea, which is specialized on riboflavin production using Ashbya gossypii.

Post-mortem studies in rhesus monkeys fed a riboflavin-deficient diet revealed that about one-third the normal amount of riboflavin was present in the liver, which is the main storage organ for riboflavin in mammals.

Riboflavin is not toxic when taken orally, as its low solubility keeps it from being absorbed in dangerous amounts from the gut (Unna and Greslin 1942).

Riboflavin is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals.

Riboflavin also is found naturally in asparagus, bananas, okra, chard, meat, and fish.

Riboflavin is normally converted in the body to coenzymes, which are organic, non-protein, freely diffusing molecules that are associated with and essential for the activity of enzymes.

Both folic acid (vitamin B9) and pyridoxine (vitamin B6) are activated by riboflavin, and riboflavin is used in the formation of healthy erythrocytes (red blood cells) (Turner and Frey 2005).
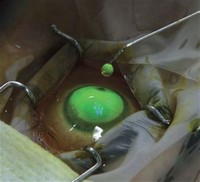
Once the riboflavin has penetrated through the cornea, Ultraviolet A light therapy is applied.
