Facts about Salt

A salt, in chemistry, is defined as the product formed from the neutralization reaction of acids and bases.

Salt is produced by evaporation of seawater or brine from other sources, such as brine wells and salt lakes, and by mining rock salt, called halite.

After the raw salt is obtained, it is refined to purify it and improve its storage and handling characteristics.

Mixtures of many different ions in solution—like in the cytoplasm of cells, in blood, urine, plant saps and mineral waters— usually do not form defined salts after evaporation of the water.

Most minerals and inorganic pigments as well as many synthetic organic dyes are salts.

Salts are often referred to only by the name of the cation (e.g., sodium salt or ammonium salt) or by the name of the anion (e.g., chloride or acetate).

Salt is used in the third item (which includes an Exorcism) of the Celtic Consecration (refer Gallican rite) that is employed in the Consecration of a Church.

Today, iodized salt is more common in the United States, Australia and New Zealand than in Britain.

Salt cravings may be caused by trace mineral deficiencies as well as by a deficiency of sodium chloride itself.

Refined salt is also prepared from rock salt: mineral deposits high in salt.

Other people think that raw sea and rock salts do not contain sufficient iodine salts to prevent iodine deficiency diseases like hypothyroidism.

Some isolated cultures, such as the Yanomami in South America, have been found to consume little salt.

Refined salt, which is most widely used presently, is mainly sodium chloride.

The Menzies Research Institute in Tasmania, Australia, maintains a website dedicated to educating people about the potential problems of a salt-laden diet.

Salt is even sometimes used as a health aid, such as in treatment of dysautonomia.

SACN states, "The target salt intakes set for adults and children do not represent ideal or optimum consumption levels, but achievable population goals.

Injected water dissolves the salt, and the brine solution can be pumped to the surface where the salt is collected.

Salt was often taxed; research has discovered this practice to have existed as early as the twentieth century B.C.E.
Note that this list is by no means a comprehensive list of contributors to early animation.

Table salt is also often iodized—a small amount of potassium iodide (in the US) or potassium iodate (in the EU) is added as an important dietary supplement.

Iodized table salt has significantly reduced disorders of iodine deficiency in countries where it is used.

Zwitterions contain an anionic center and a cationic center in the same molecule but are not considered to be salts.

Some assert that unrefined sea salt is more healthy than refined salts.

Until the 1900s, salt was one of the prime movers of national economies and wars.

Salt is a mineral, composed primarily of sodium chloride, which is commonly eaten by humans.

Too much or too little salt in the diet can lead to muscle cramps, dizziness, or even an electrolyte disturbance, which can cause severe, even fatal, neurological problems.

The manufacture and use of salt is one of the oldest chemical industries.

UK: The Food Standards Agency defines the level of salt in foods as follows: "High is more than 1.5g salt per 100g (or 0.6g sodium).

Salt may be added to the water "where it is customary" in the Roman Catholic rite of Holy water.

Salts of strong acids and strong bases ("strong salts") are non-volatile and odorless, while salts of either weak acids or weak bases ("weak salts") may smell after the conjugate acid (e.g.

Salts are ionic compounds composed of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negative ions) so that the product is electrically neutral (without a net charge).

All three electrolytes (sodium, potassium, and calcium) are available in unrefined salt, as are other vital minerals needed for optimal bodily function.

From the Phoenicians dates the evidence of harvesting solid salt from the sea.

When salts are dissolved in water, they are called electrolytes, and are able to conduct electricity, a property that is shared with molten salts.

A manufacturer, LoSalt, has issued an advisory statement that people taking the following prescription drugs should not use a salt substitute: Amiloride, Triamterene, Dytac, Spironolactone, Aldactone, Eplerenone and Inspra.

During his protests in India, Mohandas Gandhi performed the famous salt march to challenge the British-imposed monopoly on salt.

Salt substitutes have a taste similar to table salt and contain mostly potassium chloride, which will increase potassium intake.

shows Vishnu awakening and becoming both Brahm? to create the world, and Shiva to destroy it.

Salt is involved in regulating the water content (fluid balance) of the body.

Salt is also obtained by evaporation of sea water, usually in shallow basins warmed by sunlight; salt so obtained was formerly called bay salt, and is now often called sea salt or solar salt.

SACN aimed for an achievable target reduction in average intake of salt to 6 g per day (2.4 g or 100 mmol sodium) — this is roughly equivalent to a teaspoonful of salt.

United Kingdom: In 2003, the UK's Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) recommended that, for a typical adult, the Reference Nutrient Intake is 4 g salt per day (1.6 g or 70 mmol sodium).

Iodized salt (BrE: iodised salt), table salt mixed with a minute amount of sodium iodide, iodate, or sometimes potassium iodide, is used to help reduce the chance of iodine deficiency in humans.

The earliest Biblical mention of salt appears to be in reference to the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah (Genesis xix.

People's risk for disease due to salt intake that is too low or too high varies, due to biochemical individuality.

Another additive, especially important for pregnant women is Folic acid (B vitamin) giving the table salt a yellow color.

Other anticaking agents (and potassium iodide, for iodized salt) may be added after crystallization.

Among the ancients, as with ourselves, "sol" (sun) and "sal" (salt) were considered essential to the maintenance of life.

Salt intake can be reduced by simply reducing the quantity of salty foods in a diet, without recourse to salt substitutes.

Unfortunately for those paid with salt, it was easily ruined by rain and other weather conditions.

Food grade salt accounts for only a small part of salt production in industrialised countries (3% in Europe) although world-wide, food uses account for 17.5% of salt production.

Overconsumption of salt can increase the risk of health problems, including high blood pressure.

That slow, partial decomposition is usually accelerated by presence of water, since hydrolysis is the other half of the reversible reaction equation of formation of weak salts.

Salts can appear to be clear and transparent (sodium chloride), opaque, and even metallic and lustrous (iron disulfide).

Fleur de sel, natural sea salt harvested by hand, has a unique flavor varying from region to region.

Different salts can elicit all five basic tastes, e.g., salty (sodium chloride), sweet (lead diacetate; but which will cause lead poisoning if ingested), sour (potassium bitartrate), bitter (magnesium sulfate), and umami or savory (monosodium glutamate).

Some anticaking agents used are tricalcium phosphate, calcium or magnesium carbonates, fatty acid salts (acid salts), magnesium oxide, silicon dioxide, calcium silicate, sodium alumino-silicate, and alumino-calcium silicate.
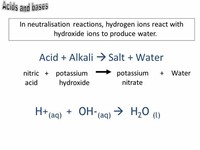
Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are basic salts and salts that produce hydronium ions in water acid salts.

Drinking too much water, with insufficient salt intake, puts a person at risk of water intoxication.

Different natural salts have different mineralities, giving each one a unique flavor.

Edible rock salts may be slightly greyish in color due to this mineral content.

The Latin word salarium meaning a payment made in salt, is the root of the word "salary."

Salts can also form if solutions of different salts are mixed, their ions recombine, and the new salt is insoluble and precipitates (see: solubility equilibrium).

In Aztec mythology, Huixtocihuatl was a fertility goddess who presided over salt and salt water.

Natural sea salt includes vital trace minerals in addition to the sodium chloride.
After years and years of river inflow and evaporation, the salt content of the lake water built up to the present levels. The same process made the seas salty. Rivers carry dissolved salts to the ocean. Water evaporates from the oceans to fall again as rain and to feed the rivers, but the salts remain in the ocean.
Table salt is more heavily processed to eliminate minerals and usually contains an additive to prevent clumping. ... Sea salt and table salt have the same basic nutritional value, despite the fact that sea salt is often promoted as being healthier. Sea salt and table salt contain comparable amounts of sodium by weight.
In the absence of fresh water, it had also adapted to drinking salt water with a higher salt content than sea water. Domestic Bactrian camels cannot drink salt water with this degree of salt. Research to date does not show conclusively how the wild camel is absorbing and secreting the salt water.
In chemistry, a salt is an ionic compound that can be formed by the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. Salts are composed of related numbers of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negative ions) so that the product is electrically neutral (without a net charge).
Table salt is more heavily processed to eliminate minerals and usually contains an additive to prevent clumping. ... Sea salt and table salt have the same basic nutritional value, despite the fact that sea salt is often promoted as being healthier. Sea salt and table salt contain comparable amounts of sodium by weight.
White salt is produced by evaporating 'solution-mined' brine in pressure vessels. The rock salt we use for gritting roads comes from mining ancient deposits. In some countries the natural energy of the sun is used to evaporate brine produced from sea water.
Salt (NaCl) is a natural mineral made up of white cube-shaped crystals composed of two elements, sodium and chlorine. It is translucent, colourless, odourless (officially, though we think you can smell the freshness of the sea in one of our boxes) and has a distinctive and characteristic taste.
If you eat too much salt, the extra water stored in your body raises your blood pressure. So, the more salt you eat, the higher your blood pressure. The higher your blood pressure, the greater the strain on your heart, arteries, kidneys and brain. This can lead to heart attacks, strokes, dementia and kidney disease.
Table salt or common salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in its natural form as a crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite.
This amounts to about one teaspoon, or 6 grams of salt (it is 40% sodium, so multiply sodium grams by 2.5). However, about 90% of US adults consume a lot more than that (7). Eating too much salt is claimed to raise blood pressure, thereby increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.Jun 18, 2017
Many salts are commonly found and used in the home.Sodium Chloride. Table salt, or sodium chloride, is the ionic product of the combination of lye, or sodium hydroxide, and hydrochloric acid. ... Ammonium Dichlorate. ... Magnesium Sulfate. ... Sodium Bicarbonate.
Salt is a compound called sodium chloride. Its formula is NaCl. It can be formed in a variety of ways, including the direct reaction of sodium and chlorine and through neutralisation reactions involving hydrochloric acid and sodium or some sodium compounds (e.g. sodium hydroxide).















