Facts about Sand

Parabolic: 'U'-shaped mounds of sand with convex noses trailed by elongated arms are well-known in coastal deserts and are called parabolic dunes.

The chlorite-glauconite bearing sands are typically green, as are sands derived from basalts (made from lavas) with a high olivine content.

Linear dunes may occur as isolated ridges, but they generally form sets of parallel ridges separated by miles of sand, gravel, or rocky interdune corridors.

The gypsum sand dunes of the White Sands National Monument in New Mexico are famous for their bright, white color.

Counting the number of grains of sand on a seashore seems like an impossible task.

An erg (or sand sea or dune sea) is a large, relatively flat area of desert covered with sand, with little or no vegetation cover.

Sand is used in preparing concrete and manufacturing bricks, and it is sometimes added to paint to obtain a textured finish.

Material in the size class just above sand is called gravel, with particles ranging from two millimeters up to 64 millimeters.

Sand fences might also work, but researchers are still trying to figure out the best possible fence design.

Sand threatens buildings and crops in Africa, the Middle East, and China.
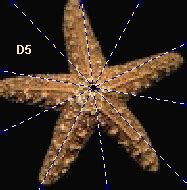
Star: Radially symmetrical, star dunes are pyramidal sand mounds with slipfaces on three or more arms that radiate from the high center of the mound.

The composition of sand varies according to local rock sources and conditions.
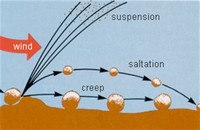
Sand is transported by wind or water and deposited in various forms, such as beaches, dunes, sand spits, and sand bars.

Sandy soils are ideal for some crops, including peanuts, peaches, and watermelon.

On the other hand, the migration of sand dunes threatens cities and agricultural lands in Africa, China, and the Middle East.

Sand dunes along shorelines play an important role in protecting the land from the potential devastation of storm waves.

Sand is generally harmless under controlled conditions, but one must be careful when engaging in some activities such as sandblasting.

The elongated arms of parabolic dunes follow rather than lead because they are fixed by vegetation, while the bulk of the sand in the dune migrates forward.

Sand feels gritty when rubbed between the fingers, while silt feels like flour.

Preventing sand dunes from overwhelming cities and agricultural areas has become a priority for the United Nations Environment Programme.

One of the biggest problems posed by sand dunes is their encroachment on human habitats.

Arkose is a sand or sandstone with considerable feldspar content, derived from the weathering and erosion of a nearby granite.

Some locations have sands that contain magnetite, chlorite, glauconite or gypsum.

Sand that is transported long distances through erosion by water or wind will be rounded, with characteristic abrasion patterns on the surface of the grains.

Dunes also form under the action of flowing water, such as on the sand or gravel beds of rivers, estuaries, and the sea.

One must take appropriate precautions, however, when engaging in such activities as sandblasting.

Quartz sand that is recently weathered from granite or gneiss quartz crystals will be angular.

The material safety data sheets (MSDS) for silica sand state that "excessive inhalation of crystalline silica is a serious health concern.

Drenching sand dunes with oil stops their migration, but this approach hurts the environment and uses a finite resource.

Like snow, the dunes may also move by sand avalanches, falling down the steep slopes of the dunes that face away from the winds.

Under controlled conditions, sand is usually harmless, and children have fun playing in the sand.

Sands rich in magnetite are dark gray to black in color, as are sands derived from volcanic basalts.

The bright white sands found in tropical and subtropical coastal settings are ground-up limestone.

Sand deposits in some areas contain garnets and other resistant minerals, including some small gemstones.

Technically, an erg is defined as a desert area that contains more than 125 square kilometers of wind-swept sand, where the sand covers more than 20 percent of the surface.
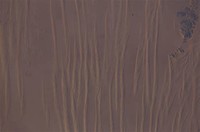
Linear: Straight or slightly sinuous sand ridges, typically much longer than they are wide, are known as linear dunes.

A different hazard arises when digging tunnels or "caves" in large dunes, sandhills, or beaches.
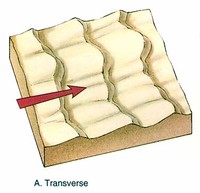
A transverse dune is horizontal to the prevailing wind, probably caused by a steady buildup of sand on an already existing, small mound.

Sand is a naturally occurring, finely divided rock, made up of small particles or granules called sand grains.

