Facts about Skin
Mammalian skin contains hairs, which in non-human mammals and sufficient density is called fur.

Epidermis also contains DNA repair enzymes, which help to reverse UV damage, and people who lack the genes for these enzymes suffer high rates of skin cancer.

Melanocytes are cells that produce melanin, a pigment that absorbs some of the potentially dangerous ultraviolet radiation in sunlight and gives color to the skin.

Historically, efforts have been made to designate various human populations as distinct "races" based on skin color, along with such other observable physical traits as hair type, facial features, and body proportions.

Individuals with ancestors from different parts of the world have highly visible differences in skin pigmentation.

The thicker the skin, the more layers of cells with melanin in them, and the darker the color (Smith and Burns 1999).
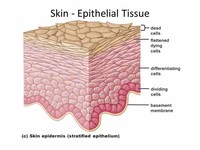
The skin is continuous with the inner epithelial lining of the body at the orifices, each of which supports its own complement of microbes.

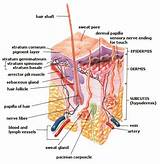
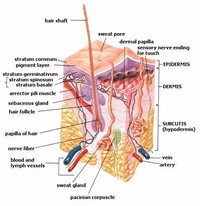
The hypodermis is not part of the skin, but attaches the skin to underlying bone and muscle as well as supplying it with blood vessels and nerves.

The use of natural or synthetic cosmetics to treat the appearance of the face and condition of the skin is common in many cultures.

The skin supports its own ecosystems of microorganisms, including yeasts and bacteria, which cannot be removed by any amount of cleaning.

The skin must be regularly cleaned; unless enough care is taken, it will become cracked or inflamed.

Skins and hides from different animals are used for clothing, bags, and other consumer products, usually in the form of leather, but also furs, rawhide, snakeskin, and hagfish.

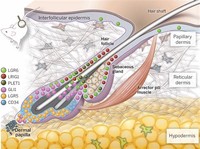
The papillae provide the dermis with a "bumpy" surface that interdigitates with the epidermis, strengthening the connection between the two layers of skin.

In biology, skin is a flexible organ (group of tissues which perform a specific function) that serves as the outer covering of an animal.
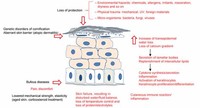
Functions of the skin are disturbed when it is excessively dirty; it becomes more easily damaged, the release of antibacterial compounds decreases, and dirty skin is more prone to develop infections.
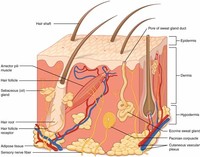
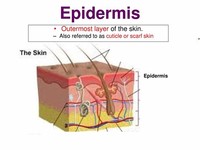
Skin is composed of two primary layers, the epidermis and the dermis.

Skin consists of two layers of tissues (collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function): A thin outer layer called the epidermis and a thicker inner layer called the dermis.

Reptiles and fish have hard protective scales on their skin for protection, and birds have hard feathers, all made of tough ?-keratins.

On some animals, the skin is very hard and thick, and can be processed to create leather.

Often, however, attractiveness based on external features ("skin deep") has been overemphasized versus the importance of internal character.

Estimates place the number of individual bacteria on the surface of one square inch of human skin at 50 million, although this figure varies greatly over the average 20 feet2 of human skin.

Amphibian skin is not a strong barrier to passage of chemicals and is often subject to osmosis.

Sunlight, water, and air play an important role in keeping the skin healthy.

The disinfected skin surface gets recolonized from bacteria residing in the deeper areas of the hair follicle, gut.

Despite these vast quantities, all of the bacteria found on the skin's surface would fit into a volume the size of a pea (Rosebury 1969).

Intensifying this effect is the decreasing ability of skin to heal itself.

The average square inch of skin holds 650 sweat glands, 20 blood vessels, 60,000 melanocytes, and more than a thousand nerve endings.
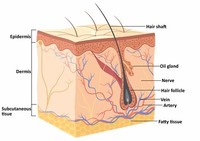
Hair mainly serves to augment the insulation the skin provides, but can also serve as a secondary sexual characteristic or as camouflage.

Damaged skin will try to heal by forming scar tissue, often giving rise to discoloration and depigmentation of the skin.

The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain.

Dermatology (from Greek derma, "skin") is a branch of medicine dealing with the skin and its appendages (hair, nails, sweat glands etc).

Individuals with African ancestry tend towards darker skin, while those of Northern European descent have paler skin.

Part of this is the result of the variations in the thickness of the skin on different parts of the human body.
Ask any child what color a polar bear is and s/he will exclaim, “white” with great enthusiasm, but truth be told, their fur is actually transparent and holds no color. It only appears white because it reflects visible light. They're nearly invisible under infrared photography.Feb 27, 2014
CLEAR! But if the Polar bear's skin is black, how come they don't look black in colour? Well, each of the longer guard hairs on the Polar bear's body is hollow and reflects visible light, much like snow. So when the sun is shining brightly, Polar bears appear bright white.Jan 4, 2012
Lions. It's not because they are out of shape! It's an adaptation for their protection. Loose belly skin allows animal to be kicked by prey with little chance of injury.
It helps them grind up food for digestion. Snood - the flap of skin that hangs over the turkey's beak. Turns bright red when the turkey is upset or during courtship. Tom - a male turkey.
Human hair is a simple thing made of keratin and dead skin cells. Its function is to prevent heat loss from a person's head, yet it also causes women to weep, men to buy Porsches and people to spend billions each year on its upkeep.Jan 22, 2009
Bed bugs pierce human skin with elongated beaks through which they extract blood. ... Bed bug bites occur most commonly on exposed skin, such as the upper body, neck, arms and shoulders. Bite Symptoms. Some individuals who are bitten by bed bugs develop itching, red welts or swelling the day after being bitten.
The bear's stark white coat provides camouflage in surrounding snow and ice. But under their fur, polar bears have black skin—the better to soak in the sun's warming rays. These powerful predators typically prey on seals.