Facts about Star

Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a cluster or a galaxy.

Radial velocity is measured by the doppler shift of the star's spectral lines, and is given in units of km/s.

The most common of these are types L and T, which classify the coldest low-mass stars and brown dwarfs.

Small, dwarf stars such as the Sun generally have essentially featureless disks with only small starspots.

In 1584, Elizabeth I, granted a charter to Sir Walter Raleigh, for whom the state capital is named, for land in present-day North Carolina (then Virginia).

The oldest accurately dated star chart appeared in Ancient Egypt in 1,534 B.C.E.

Binary and multi-star systems consist of two or more stars that are gravitationally bound, and generally move around each other in stable orbits.

Due to the relatively vast distances between stars outside the galactic nucleus, collisions between stars are thought to be rare.

Many ancient astronomers believed that stars were permanently affixed to a heavenly sphere, and that they were immutable.

Stars are not spread uniformly across the universe, but are normally grouped into galaxies along with interstellar gas and dust.

The star with the lowest iron content ever measured is the dwarf HE1327-2326, with only 1/200,000th the iron content of the Sun.

The nearest star to the Earth, apart from the Sun, is Proxima Centauri, which is 39.9 trillion (1012) kilometers, or 4.2 light-years away.

The example below shows the amount of time required for a star of 20 solar masses to consume all of its nuclear fuel.

Giant stars have a much lower surface gravity than main sequence stars, while the opposite is the case for degenerate, compact stars such as white dwarfs.
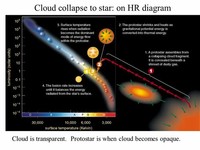
A star begins as a collapsing cloud of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements.

Some stars may even be close to 13.7 billion years old—the observed age of the universe.

When they occur within the Milky Way, supernovae have historically been observed by naked-eye observers as "new stars" where none existed before.

Red dwarf flare stars such as UV Ceti may also possess prominent starspot features.

Stars are formed within extended regions of higher density in the interstellar medium, although the density is still lower than the inside of an earthly vacuum chamber.

Almost everything about a star is determined by its initial mass, including essential characteristics such as luminosity and size, as well as the star's evolution, lifespan, and eventual fate.

Surface patches with a lower temperature and luminosity than average are known as starspots.

The Italian astronomer Geminiano Montanari recorded observing variations in luminosity of the star Algol in 1667.

The duration that a star spends on the main sequence depends primarily on the amount of fuel it has to fuse and the rate at which it fuses that fuel.

The heavier elements in these stars can work their way up to the surface, forming evolved objects known as Wolf-Rayet stars that have a dense stellar wind which sheds the outer atmosphere.

The magnetic field can act upon a star's stellar wind, however, functioning as a brake to gradually slow the rate of rotation as the star grows older.

The interior of a stable star is in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium: the forces on any small volume almost exactly counterbalance each other.

The surface temperature of a star, along with its visual absolute magnitude and absorption features, is used to classify a star (see classification below).

The twentieth century saw increasingly rapid advances in the scientific study of stars.

Islamic astronomers gave to many stars Arabic names which are still used today, and they invented numerous astronomical instruments which could compute the positions of the stars.

The proper motion of a star is determined by precise astrometric measurements in units of milli-arc seconds (mas) per year.

Ancient sky watchers imagined that prominent arrangements of stars formed patterns, and they associated these with particular aspects of nature or their myths.

The German astronomer Johann Bayer created a series of star maps and applied Greek letters as designations to the stars in each constellation.

Almost all elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were created by fusion processes in stars.

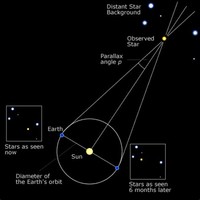
By determining the parallax of a star, the proper motion can then be converted into units of velocity.

Other stars are visible in the night sky, when they are not outshone by the Sun.

To explain why these stars exerted no net gravitational pull on the solar system, Isaac Newton suggested that the stars were equally distributed in every direction, an idea prompted by the theologian Richard Bentley.

The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing further under its own gravity.

Early stars of less than 2 solar masses are called T Tauri stars, while those with greater mass are Herbig Ae/Be stars.

From this he deduced that the number of stars steadily increased toward one side of the sky, in the direction of the Milky Way core.
The portion of a star that is visible to an observer is called the photosphere.

The electron-degenerate matter inside a white dwarf is no longer a plasma, even though stars are generally referred to as being spheres of plasma.

Larger, giant stars have much bigger, much more obvious starspots, and they also exhibit strong stellar limb darkening.

Among nearby stars, it has been found that population I stars have generally lower velocities than older, population II stars.

When the protostellar cloud has approximately reached the stable condition of hydrostatic equilibrium, a protostar forms at the core.

Many of the more prominent individual stars were also given names, particularly with Arabic or Latin designations.

Near the end of the star's life, fusion can occur along a series of onion-layer shells within the star.

Stars with several times the mass of the Sun have a convection zone deep within the interior and a radiative zone in the outer layers.

Smaller stars such as the Sun are just the opposite, with the convective zone located in the outer layers.
Due to their great distance from the Earth, all stars except the Sun appear to the human eye as shining points in the night sky that twinkle because of the effect of the Earth's atmosphere.

The color of a star, as determined by the peak frequency of the visible light, depends on the temperature of the star’s outer layers, including its photosphere.

Supernovae are so bright that they may briefly outshine the star's entire home galaxy.

Circa 1600, the names of the constellations were used to name the stars in the corresponding regions of the sky.

An example is the star Algol, which was thought to represent the eye of the Gorgon Medusa.

Of the intrinsically variable stars, the primary types can be subdivided into three principal groups.

Smaller bodies are called brown dwarfs, which occupy a poorly defined grey area between stars and gas giants.

The first direct measurement of the distance to a star (61 Cygni at 11.4 light-years) was made in 1838 by Friedrich Bessel using the parallax technique.

In 1913, the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram was developed, propelling the astrophysical study of stars.

The Rothko Chapel, a gallery of Mark Rothko's work, is located adjacent to the Menil Collection in Houston, Texas.

The disks of most stars are much too small in angular size to be observed with current ground-based optical telescopes, and so interferometer telescopes are required in order to produce images of these objects.

Stars can be much closer to each other in the centers of galaxies and in globular clusters, or much farther apart in galactic halos.

On both apparent and absolute magnitude scales, the smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star; the larger the magnitude number, the fainter.

The star's magnetic field and the stellar wind serve to slow down a main sequence star's rate of rotation by a significant amount as it evolves on the main sequence.

The explosion is created when the white dwarf accretes hydrogen from the companion star, building up mass until the hydrogen undergoes fusion.

Every star generates a stellar wind of particles that causes a continual outflow of gas into space.

By the following century the idea of the stars as distant suns was reaching a consensus among astronomers.

Stars spend about 90 percent of their lifetime fusing hydrogen to produce helium in high-temperature and high-pressure reactions near the core.
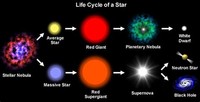
An evolved, average-size star will now shed its outer layers as a planetary nebula.

The activity levels of slowly rotating stars tend to vary in a cyclical manner and can shut down altogether for periods.

The only body which has been recognized by the scientific community as having the authority to name stars or other celestial bodies is the International Astronomical Union (IAU).

A star is a massive, luminous ball of plasma that is held together by its own gravity.

Once both rates of movement are known, the space velocity of the star relative to the Sun or the galaxy can be computed.

By convention, astronomers grouped stars into constellations and used them to track the motions of the planets and the inferred position of the Sun.

When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can have a significant impact on their evolution.

The motivation attributed to him was intending to immortalize his name by renaming Rome to "Neropolis."

Red dwarf stars with less than 0.4 solar masses are convective throughout, which prevents the accumulation of a helium core.

The least luminous stars that are currently known are located in the NGC 6397 cluster.

By contrast, the super-metal-rich star ? Leonis has nearly double the abundance of iron as the Sun, while the planet-bearing star 14 Herculis has nearly triple the iron.

The Gregorian calendar, currently used nearly everywhere in the world, is a solar calendar based on the angle of the Earth's rotational axis relative to the nearest star, the Sun.

The metallicity can influence the duration that a star will burn its fuel, control the formation of magnetic fields and modify the strength of the stellar wind.
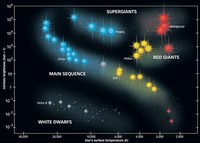
Stars on the main sequence convert hydrogen into helium, creating a slowly but steadily increasing proportion of helium in the core.
To the Ancient Greeks, some "stars," known as planets (Greek ???????? (plan?t?s), meaning "wanderer"), represented various important deities, from which the names of the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn were taken.

The spectra of stars were also successfully explained through advances in quantum physics.

In astronomy, luminosity is the amount of light, and other forms of radiant energy, a star radiates per unit of time.
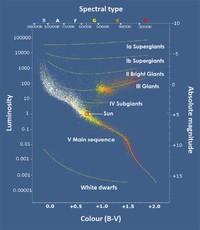
A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities, known as a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (H–R diagram), allows the age and evolutionary state of a star to be determined.

Edward Pickering discovered the first spectroscopic binary in 1899 when he observed the periodic splitting of the spectral lines of the star Mizar in a 104 day period.

The combination of the radius and the mass of a star determines the surface gravity.

Early European astronomers such as Tycho Brahe identified new stars in the night sky (later termed novae), suggesting that the heavens were not immutable.

A recent study of the Arches cluster suggests that 150 solar masses is the upper limit for stars in the current era of the universe.

Young, rapidly rotating stars tend to have high levels of surface activity because of their magnetic field.

The energy produced by stars, as a by-product of nuclear fusion, radiates into space as both electromagnetic radiation and particle radiation.

Edmond Halley published the first measurements of the proper motion of a pair of nearby "fixed" stars, demonstrating that they had changed positions from the time of the ancient Greek astronomers Ptolemy and Hipparchus.

Such stars are said to be on the main sequence and are called dwarf stars.

The faintest stars visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions are about magnitude +6.

Stars can also vary in luminosity because of extrinsic factors, such as eclipsing binaries, as well as rotating stars that produce extreme starspots.

Karl Schwarzschild discovered that the color of a star, and hence its temperature, could be determined by comparing the visual magnitude against the photographic magnitude.

The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily because massive stars have greater pressure on their cores, causing them to burn hydrogen more rapidly.
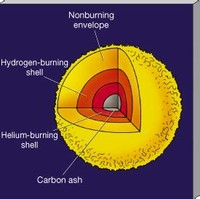
After the star has consumed the helium at the core, fusion continues in a shell around a hot core of carbon and oxygen.

The most massive stars last an average of about one million years, while stars of minimum mass (red dwarfs) burn their fuel very slowly and last tens to hundreds of billions of years.
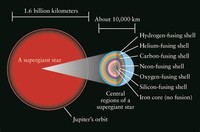
A variety of different nuclear fusion reactions take place inside the cores of stars, depending upon their mass and composition, as part of stellar nucleosynthesis.

A large portion of the star's angular momentum is dissipated as a result of mass loss through the stellar wind.

Numerous additional systems have since been created as star catalogues have appeared.

The first stars to form after the Big Bang may have been larger, up to 300 solar masses or more, due to the complete absence of elements heavier than lithium in their composition.

The balanced forces are inward gravitational force and an outward force due to the pressure gradient within the star.

Important conceptual work on the physical basis of stars occurred during the first decades of the twentieth century.

Observation of double stars gained increasing importance during the nineteenth century.

A typical galaxy contains hundreds of billions of stars, and there are more than 100 billion (1011) galaxies in the observable universe.

The star then evolves into a degenerate form, recycling a portion of the matter into the interstellar environment, where it will form a new generation of stars with a higher proportion of heavy elements.

The technique of gravitational microlensing will also yield the mass of a star.

Stars with high rates of proper motion are likely to be relatively close to the Sun, making them good candidates for parallax measurements.

The surface texture of p?hoehoe flows varies widely, displaying all kinds of bizarre shapes often referred to as lava sculpture.

The total mass of a star is the principal determinant in its evolution and eventual fate.
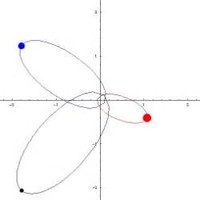
The first solution to the problem of deriving an orbit of binary stars from telescope observations was made by Felix Savary in 1827.

There also exist chemically peculiar stars that show unusual abundances of certain elements in their spectrum; especially chromium and rare earth elements.

The magnetic field of a star is generated within regions of the interior where convective circulation occurs.

The Sun is also a star, but it is close enough to the Earth to appear as a disk instead, and to provide daylight.

The blown-off outer layers of dying stars include heavy elements which may be recycled during new star formation.

The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth.

The outflow from supernovae and the stellar wind of large stars play an important part in shaping the interstellar medium.

Successful models were developed to explain the interiors of stars and stellar evolution.

The oldest star yet discovered, HE 1523-0901, is an estimated 13.2 billion years old.

The surface gravity can influence the appearance of a star's spectrum, with higher gravity causing a broadening of the absorption lines.

Small stars (called red dwarfs) consume their fuel very slowly and last tens to hundreds of billions of years.

The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the core through a combination of radiative and convective processes.

The star then follows an evolutionary path that parallels the original red giant phase, but at a higher surface temperature.

The brightest stars, on either scale, have negative magnitude numbers.

Degenerate stars have contracted into a compact mass, resulting in a rapid rate of rotation.

From the corona, a stellar wind of plasma particles expands outward from the star, propagating until it interacts with the interstellar medium.

The existence of a corona appears to be dependent on a convective zone in the outer layers of the star.

The components of motion of a star consist of the radial velocity toward or away from the Sun, and the traverse angular movement, which is called its proper motion.

The formation of a star begins with a gravitational instability inside a molecular cloud, often triggered by shockwaves from supernovae (massive stellar explosions) or the collision of two galaxies (as in a starburst galaxy).

In 1834, Friedrich Bessel observed changes in the proper motion of the star Sirius, and inferred a hidden companion.

The shockwave formed by this sudden collapse causes the rest of the star to explode in a supernova.

The most common multi-star system is a binary star, but systems of three or more stars are also found.

The current stellar classification system originated in the early 20th century, when stars were classified from A to Q based on the strength of the hydrogen line.

Pulsating variable stars vary in radius and luminosity over time, expanding and contracting with periods ranging from minutes to years, depending on the size of the star.

By precisely measuring the drop in brightness of a star as it is occulted by the Moon (or the rise in brightness when it reappears), the star's angular diameter can be computed.

Eruptive variables are stars that experience sudden increases in luminosity because of flares or mass ejection events.

Other than the Sun, the star with the largest apparent size is R Doradus, with an angular diameter of only 0.057 arcseconds.

Astronomers estimate that there are at least 70 sextillion (7Ч1022) stars in the observable universe.

The rapidly rotating star Vega, for example, has a higher energy flux at its poles than along its equator.

William Herschel was the first astronomer to attempt to determine the distribution of stars in the sky.

Historically, stars have been important to civilizations throughout the world.

The strength of the magnetic field varies with the mass and composition of the star, and the amount of magnetic surface activity depends upon the star's rate of rotation.

When stars form they are composed of about 70 percent hydrogen and 28 percent helium, as measured by mass, with a small fraction of heavier elements.

The motion of the Sun against the background stars (and the horizon) was used to create calendars, which could be used to regulate agricultural practices.

Using the stellar spectrum, astronomers can also determine the surface temperature, surface gravity, metallicity and rotational velocity of a star.

One of the most massive stars known is Eta Carinae, with 100–150 times as much mass as the Sun; its lifespan is very short—only several million years at most.
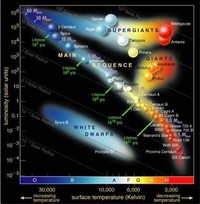
Most stars belong to the main sequence, which consists of ordinary hydrogen-burning stars.

Young stars can have a rapid rate of rotation greater than 100 km/s at the equator.

Comparison of the kinematics of nearby stars has also led to the identification of stellar associations.

The twentieth century saw increasingly rapid advances in the scientific study of stars.

The B-class star Achernar, for example, has an equatorial rotation velocity of about 225 km/s or greater, giving it an equatorial diameter that is more than 50 percent larger than the distance between the poles.
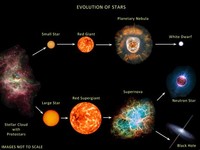
During their stellar evolution, some stars pass through phases where they can become pulsating variables.

Parallax measurements demonstrated the vast separation of the stars in the heavens.

The portion of heavier elements may also be an indicator of the likelihood that the star has a planetary system.

Instead, for stars of more than 0.4 solar masses, fusion occurs in a slowly expanding shell around the degenerate helium core.

The occurrence of convection in the outer envelope of a main sequence star depends on the mass.

Starting at zero-age main sequence, the proportion of helium in a star's core will steadily increase.

During the 1780s, he performed a series of gauges in 600 directions, and counted the stars observed along each line of sight.

Variable stars have periodic or random changes in luminosity because of intrinsic or extrinsic properties.

The outgoing flux of energy leaving any layer within the star will exactly match the incoming flux from below.

Astronomers can determine the mass, age, chemical composition and many other properties of a star by observing its spectrum, luminosity and motion through space.

The pressure gradient is established by the temperature gradient of the plasma; the outer part of the star is cooler than the core.

Detailed observations of many binary star systems were collected by astronomers such as William Struve and S. W. Burnham, allowing the masses of stars to be determined from computation of the orbital elements.

When they occur within the Milky Way, supernovae have historically been observed by naked-eye observers as "new stars" where none existed before.
Small, old stars can be at room temperature ex: WISE 1828+2650, so you could touch the surface without getting burned. Any star you can see in the sky with the naked eye, however, would be hot enough to destroy your body instantaneously if you came anywhere near them. No.Jun 27, 2017
data. Spica (/ˈspaɪkə/), also designated Alpha Virginis (α Virginis, abbreviated Alpha Vir, α Vir), is the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo and the 16th brightest star in the night sky.
Epsilon Sagittarii is a binary star approximately 143 light years distant. It is a blue class B giant with an apparent magnitude of 1.79 and a luminosity 375 times that of the Sun. Kaus Australis is the brightest star in the constellation Sagittarius and the 36th brightest star in the sky.
Sagittarius A* (pronounced "Sagittarius A-star", standard abbreviation Sgr A*) is a bright and very compact astronomical radio source at the center of the Milky Way, near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius.
Katie Campbell: Starfish lack a centralized brain, but they do have a complex nervous system and they can feel pain.Feb 24, 2014
Seastars can live up to 35 years in the wild! It really depends on the species. Their wild habitat includes coral reefs, rocky coasts, sandy bottom, or even the deep sea of all the world's oceans. There are approximately 1,800 different types of sea stars.Mar 6, 2009
A starfish is marine creature that normally inhabits the deep ocean floors. Some species are venomous to human beings. Starfish do not attack humans, but can inflict painful stings with the release of venom, when they are accidently stepped upon or handled.Dec 26, 2015
Regeneration. Starfish are unique among aquatic life because they have the ability to regenerate an arm when they lose one. It's not unusual for a predator to bite off part of an arm, and some species of starfish can break off their own arms where it connects to the central body to help escape from predators.
Canis Major contains Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, known as the "dog star". It is bright because of its proximity to the Solar System. In contrast, the other bright stars of the constellation are stars of great distance and high luminosity.
Jerry Seinfeld. Writer | Seinfeld. ... Shah Rukh Khan. Actor | Chennai Express. ... Tom Cruise. Actor | Top Gun. ... Tyler Perry. Writer | Diary of a Mad Black Woman. ... Johnny Depp. Actor | Pirates of the Caribbean: The Curse of the Black Pearl. ... Jack Nicholson. Actor | Chinatown. ... Tom Hanks. Producer | Cast Away. ... Bill Cosby. Actor | The Cosby Show.More items...
Is Star Wars Based on a Book? No. ... When the book was released (with George Lucas' name, but ghost-written by Alan Dean Foster), the film was already in production. Each subsequent film in the series has had a novelization released before the film, but was based entirely on the script of the film.Feb 25, 2006
Yoda was a legendary Jedi Master and stronger than most in his connection with the Force. Small in size but wise and powerful, he trained Jedi for over 800 years, playing integral roles in the Clone Wars, the instruction of Luke Skywalker, and unlocking the path to immortality.
Prequel trilogy. The 2002 film Star Wars: Episode II – Attack of the Clones revealed that Boba Fett is an unaltered child clone whom Jango Fett raises as his son. Boba helps Jango escape from Obi-Wan Kenobi, but later witnesses Jango's decapitation by Mace Windu.
Theatrical filmsFilmRelease dateDirector(s)Original trilogyEpisode IV – A New HopeMay 25, 1977George LucasEpisode V – The Empire Strikes BackMay 21, 1980Irvin KershnerEpisode VI – Return of the JediMay 25, 1983Richard Marquand8 more rows
Rogue One: A Star Wars Story. From Lucasfilm comes the first of the Star Wars standalone films, “Rogue One: A Star Wars Story,” an all-new epic adventure. In a time of conflict, a group of unlikely heroes band together on a mission to steal the plans to the Death Star, the Empire's ultimate weapon of destruction.
The answer is yes—to all of the above. It's the first standalone Star Wars story that doesn't fit directly in the Darth Vader-Luke-Rey storyline. Rogue One is set just before A New Hope and introduces an entirely new cast of characters—Rebel spies who set out to steal the plans to the Death Star.Dec 13, 2016
Rogue One is the first film in the Star Wars Anthology series, a series of stand-alone spin-off films in the Star Wars franchise. ... The spinoff movies, or we may come up with some other way to call those films, they exist within that vast universe that he created.
"Rogue One" is the first of three standalone "anthology" films set at different points within the "Star Wars" timeline. A new film will be released every other year, in between films in the new "Star Wars" trilogy. ... However, the anthology movies will all loosely relate to each other, with less overlap.Apr 7, 2016
Jyn Erso. Jyn Erso is a fictional character in the Star Wars franchise, portrayed by English actress Felicity Jones in the 2016 film Rogue One. Jyn is a former criminal who aids the Rebel Alliance in a desperate attempt to steal the plans to the Death Star, a powerful weapon possessed by the Empire.
You can use the Big Dipper to find Polaris, which is also known as the North Star. Notice that a line from the two outermost stars in the bowl of the Big Dipper points to Polaris. And notice that Polaris marks the tip of the handle of the Little Dipper. The northern sky is a large clock, with Polaris at its center.Sep 23, 2017
The North Star is the brightest star in the constellation known as the Little Dipper. It is so-called because of the special position it occupies relative to Earth's axis. If you were to stay up all night gazing at the stars, you'd slowly see them revolve around a point in the sky known as the North Celestial Pole.May 7, 2014
Frederick Douglass--Abolitionist Leader. After Douglass escaped, he wanted to promote freedom for all slaves. He published a newspaper in Rochester, New York, called The North Star. It got its name because slaves escaping at night followed the North Star in the sky to freedom.
n the brightest star in Ursa Minor; at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper; the northern axis of the earth points toward it. Synonyms: Polaris, polar star, pole star, polestar Example of: loadstar, lodestar. guiding star; a star that is used as a reference point in navigation or astronomy.
If you followed this axis out into space from the northern hemisphere on Earth, it would point toward a particular star in the sky. We call that star the "North Star" since it sits in the direction that the spin axis from the northern hemisphere of Earth points. At present, the star known as Polaris is the North Star.
This Day In History: Frederick Douglass Starts Anti-Slavery Newspaper The North Star. On this day in 1847, freed slave and abolitionist Frederick Douglass started a newspaper called The North Star.Dec 3, 2013
A star is born when atoms of light elements are squeezed under enough pressure for their nuclei to undergo fusion. All stars are the result of a balance of forces: the force of gravity compresses atoms in interstellar gas until the fusion reactions begin.
Stars are not scattered randomly through space, they are gathered together into vast groups known as galaxies. The Sun belongs to a galaxy called the Milky Way. Astronomers estimate there are about 100 thousand million stars in the Milky Way alone. Outside that, there are millions upon millions of other galaxies also!
The largest stars, in contrast, will be cool supergiants. Case in point, VY Canis Majoris is only 3,500 Kelvin, and a really big star would be even cooler. At 3,000 Kelvin, Humphreys estimates that cool supergiant would be as big as 2,600 times the size of the Sun.May 12, 2016
Star death. Most stars take millions of years to die. When a star like the Sun has burned all of its hydrogen fuel, it expands to become a red giant. This may be millions of kilometres across - big enough to swallow the planets Mercury and Venus.
Dying Stars. Like celestial chemical factories, stars spend their lives fusing hydrogen and helium atoms to forge heavier elements. In death, extremely massive stars explode in a supernova, blasting their chemical creations into space, and seeding the universe for a new generation of stars to grow.
A star begins its life as a cloud of dust and gas (mainly hydrogen) known as a nebula. A protostar is formed when gravity causes the dust and gas of a nebula to clump together in a process called accretion. ... If a critical temperature in the core of a protostar is reached, then nuclear fusion begins and a star is born.
Star birth. Like people, stars are born, they grow old and they die. Their birth places are huge, cold clouds of gas and dust, known as 'nebulas'. The most famous of these is the Orion nebula, which is just visible with the unaided eye.
Exploding Stars. ... When a star like the Sun dies, it casts its outer layers into space, leaving its hot, dense core to cool over the eons. But some other types of stars expire with titanic explosions, called supernovae. A supernova can shine as brightly as an entire galaxy of billions of "normal" stars.
The Black Star Line (1919−1922) was a shipping line incorporated by Marcus Garvey, the organizer of the Universal Negro Improvement Association (UNIA), and other members of the UNIA. ... It stands today as a major symbol for Garvey followers and African Americans in search of a way to get back to their homeland.
Black Star Line (1919-1923) The Black Star Line (BSL) was a steamship corporation established in 1919 by Pan-Africanist Marcus Garvey, the leader of the United Negro Improvement Association (UNIA).
What are stars made of? Basically, stars are big exploding balls of gas, mostly hydrogen and helium. Our nearest star, the Sun, is so hot that the huge amount of hydrogen is undergoing a constant star-wide nuclear reaction, like in a hydrogen bomb.
The Sun appears so large compared to the other stars because it is so much closer to us than any other star. The Sun is just an average sized star. For example, below is a list of some of the largest stars in our galaxy and how they compare to our Sun: Mu Cephi - about 1500 times the size of our sun.
Texas is nicknamed "The Lone Star State" to signify its former status as an independent republic, and as a reminder of the state's struggle for independence from Mexico. The "Lone Star" can be found on the Texas state flag and on the Texan state seal.






