Facts about Tide

Terrestrial tides also need to be taken in account in the case of some particle physics experiments.

The semidiurnal tidal range (the difference in height between high and low tides over about a half day) varies in a two-week or fortnightly cycle.

The Isle of Wight is important, however, as it is responsible for the 'Young Flood Stand', which describes the pause of the incoming tide about three hours after low water.

The main result was the building of a tide-predicting machine (TPM) on using a system of pulleys to add together six harmonic functions of time.

The effects of the galactic tide on the Solar System's Oort cloud are believed to be the cause of 90 percent of all observed long-period comets.

High tide is reached simultaneously along the cotidal lines extending from the coast out into the ocean, and cotidal lines (and hence tidal phases) advance along the coast.

The galactic tide is the tidal force exerted by galaxies on stars within them and satellite galaxies orbiting them.

The changing distance of the Moon from the Earth also affects tide heights.

The semi-diurnal M2 Earth tides are nearly in phase with the Moon with tidal lag of about two hours.

The exact time and height of the tide at a particular coastal point is also greatly influenced by the local bathymetry.

Intertidal ecology is the study of intertidal ecosystems, where organisms live between the low and high tide lines.

An arrow on the tidal chart indicates the direction and the average flow speed (usually in knots) for spring and neap tides.

High tide rotates about once every 12 hours in the direction of rising cotidal lines, and away from ebbing cotidal lines.

The Earth's crust shifts (up/down, east/west, north/south) in response to the Moon's and Sun's gravitation, ocean tides, and atmospheric loading.

Euler realized that the horizontal component of the tidal force (more than the vertical) drives the tide.

The lines rotate around the amphidromic points counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere so that from Baja California to Alaska and from France to Ireland the M2 tide propagates northward.
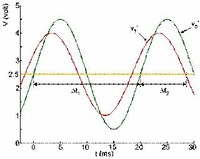
The difference of cotidal phase from the phase of a reference tide is the epoch.

Isaac Newton laid the foundations for the mathematical explanation of tides in the Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (1687).

Similarly, the two low tides each day are referred to as the higher low water and the lower low water.

Southampton in the United Kingdom has a double high tide caused by the interaction between the different tidal harmonics within the region.

The distance the tide will have moved the boat along this line is computed by the tidal speed, and this gives an "estimated position" or EP (traditionally marked with a dot in a triangle).

Tides cause changes in the depth of the marine and estuarine water bodies and produce oscillating currents known as tidal streams, making prediction of tides important for coastal navigation (see Tides and navigation).

Most coastline is dominated by semidiurnal tides, but some areas such as the South China Sea and the Gulf of Mexico are primarily diurnal.

At low tide, the intertidal is exposed (or ‘emersed’) whereas at high tide, the intertidal is underwater (or ‘immersed’).

More generally, tidal phenomena can occur in other systems besides the ocean, whenever a gravitational field that varies in time and space is present (see Other tides).

The exception is the Cook Strait where the tidal currents periodically link high to low tide.

Atmospheric tides are negligible from ground level and aviation altitudes, drowned by the much more important effects of weather.

At these points in the lunar cycle, the tide's range is minimum: this is called the neap tide, or neaps.

The first known sea-level record of an entire spring–neap cycle was made in 1831 on the Navy Dock in the Thames Estuary, and many large ports had automatic tide gages stations by 1850.

The resulting amplitudes and phases can then be used to predict the expected tides.

Tsunamis, the large waves that occur after earthquakes, are sometimes called tidal waves, but this name is due to their resemblance to the tide, rather than any actual link to the tide itself.

At spring tide the two effects add to each other to a theoretical level of 79 cm, while at neap tide the theoretical level is reduced to 29 cm.

An amphidromic point is at once cotidal with high and low tides, which is satisfied by zero tidal motion.

In 1740, the Acadйmie Royale des Sciences in Paris offered a prize for the best theoretical essay on tides.

Heights and times of low and high tide on each day are published in tide tables.

The actual depth of water at the given points at high or low water can easily be calculated by adding the charted depth to the published height of the tide.

From ancient times, tides have been observed and discussed with increasing sophistication, first noting the daily recurrence, then its relationship to the Sun and Moon.

Earth tides or terrestrial tides that affect the entire rocky mass of the Earth.

On the other hand M2 tide propagates counterclockwise around New Zealand, but this because the islands act as dam and permit the tides to have different heights on opposite sides of the islands.

Intertidal organisms are greatly affected by the approximately fortnightly cycle of the tides, and hence their biological rhythms tend to occur in rough multiples of this period.

Other phenomena unrelated to tides but using the word tide are rip tide, storm tide, hurricane tide, and black tide, referring to oil spills; or red tides, that refer to algae blooms.

Extremely small tides also occur for the same reason in the Gulf of Mexico and Sea of Japan.

Sea level measured by coastal tide gauges may also be strongly affected by wind.

Tidal heights are also very important; for example many rivers and harbors have a shallow "bar" at the entrance which will prevent boats with significant draft from entering at certain states of the tide.
The first major theoretical formulation for water tides was made by Pierre-Simon Laplace, who formulated a system of partial differential equations relating the horizontal flow to the surface height of the ocean.

Spring tides result in high waters that are higher than average, low waters that are lower than average, slack water time that is shorter than average and stronger tidal currents than average.

Each tidal constituent has a different pattern of amplitudes, phases, and amphidromic points, so the M2 patterns cannot be used for other tides.

The strip of seashore that is submerged at high tide and exposed at low tide, called the intertidal zone, is an important ecological product of ocean tides (see Intertidal ecology).

Tides are the cyclic rising and falling of the Earth's ocean surface caused by the tidal forces of the Moon and Sun acting on the oceans.