Facts about Turtle

That is, the anapsid-like turtle skull is not a function of anapsid descent.

Some aquatic turtles, such as snapping turtles and soft-shelled turtles, have eyes closer to the top of the head.

The Australian bulldog ants, Myrmecia pilosula, are among the biggest and most primitive of ants.

Turtles are broken down into two groups, according to how they evolved a solution to the problem of withdrawing their neck into their shell.

Molecular studies have upheld this new phylogeny, though some place turtles closer to Archosauria (Zardoya and Meyer 1998).

Turtles are believed by some to be surviving anapsids, indeed the only surviving anapsids, as they also share this skull structure.

The first turtles are believed to have existed in the early Triassic period of the Mesozoic era, about 200 million years ago.

Turtles are thought to have exceptional night vision due to the unusually large amount of rod cells in their retinas.

Sea turtles lay their eggs on dry sandy beaches, and are highly endangered largely as a result of beach development and overhunting.

The leatherback sea turtle (Dermochelys coriacea), found in all tropical and subtropical oceans, has a shell that lacks the bony scutes of other turtles, comprising mainly of connective tissue.

Herbivorous turtles have serrated edged ridges that help them cut through tough plants.

Turtles are ectothermic or cold-blooded, which means that their body temperature changes with their environment.

Male turtles tend to have particularly long claws, and these appear to be used to stimulate the female while mating.

One of the most colorful turtles is the eastern painted turtle, which includes a yellow plastron and a black or olive shell with red markings around the rim.

Freshwater turtles are generally smaller, but with the largest species, the Asian softshell turtle Pelochelys cantorii, a few individuals have been reported to measure up to 200 centimeters (80 inches) (Das 1991).

Sea turtles possess glands near their eyes that produce salty tears that rid their body of excess salt taken in from the water they drink.

The Trionychidae family has members commonly referred to as "softshell turtles," such as with the North American genus Apalone, because their carapace (outer, upper covering) lacks scutes (scales).

The turtles can take up dissolved oxygen from the water using these papillae, in much the same way that fish use gills to respire.

The word "turtle" is widely used to describe all members of the order Testudines.

Growth requires molting of a turtle's skin, although not the scutes.
American snapping turtles and musk turtles have small, cross-shaped plastrons that give them more efficient leg movement for walking along the bottom of ponds and streams.
Others, citing genetic evidence, consider turtles, along with crocodiles, a more modern reptile group.

Some species of Australian freshwater turtles have large cloacal cavities that are lined with many finger-like projections.

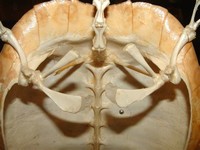
The inner layer of a turtle's shell is made up of about 60 bones that include portions of the backbone and the ribs, meaning the turtle cannot crawl out of its shell.

The earliest known modern turtle is proganochelys (family Proganochelyidae), that lived about 215 million years ago (EL 2007).

Turtles vary widely in size, although marine turtles tend to be relatively bigger animals than their land and freshwater relatives.

Two other species of small turtles are the American mud turtles and musk turtles that live in an area that ranges from Canada to South America.

Turtles, including terrapins, do not molt their skins all in one event, as snakes do, but continuously, in small pieces.

The carapace and plastron are joined together on the turtle's sides by bony structures called bridges.

Most turtles that spend most of their life on land have their eyes looking down at objects in front of them.

Turtles have historically served as food or skinned for leather.

Most aquatic turtles have flat, streamlined shells, which aid in swimming and diving.

Carnivorous turtles usually have knife-sharp ridges for slicing through their prey.
The amphibious turtles normally have limbs similar to those of tortoises except that the feet are webbed and often have long claws.

Tortoise is the common name for any land-dwelling turtle, especially those belonging to the family Testudinidae.

The largest known chelonian in the fossil record was Archelon ischyros, a Late Cretaceous sea turtle known to have been up to 4.6 meters (15 feet) long (Everhart 2007).

Turtles use their tongues to swallow food, but, unlike most reptiles, they cannot extend their tongues to catch food.

Turtles lay eggs, like other reptiles, which are slightly soft and leathery.

Researchers have recently discovered a turtle’s organs do not gradually break down or become less efficient over time, unlike most other animals.
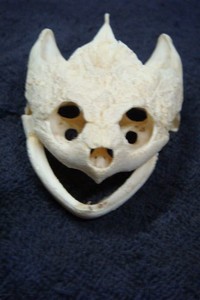
Instead of teeth, the upper and lower jaws of the turtle are covered by horny ridges.

Compared with freshwater turtles, sea turtles have very limited mobility on land, and apart from the dash from the nest to the sea as hatchlings, male sea turtles normally never leave the sea.

The Pleurodirans, also called the side-necked turtles, have long necks, and fold them sideways to align them with the shell.

Some species of Australian freshwater turtles have large cloacal cavities that are lined with many finger-like projections.

The upper shell or upper outer covering of a turtle is called the carapace.

When the turtles hatch they squirm their way to the surface and make for the water.

Ancestral turtles are believed to have not been able to retract their neck.

Turtles lay eggs, like other reptiles, which are slightly soft and leathery.

The shell of a leatherback turtle is extremely light because they lack scutes and contain many fontanelles.

Turtles are found in most parts of the world, and there are about 300 species alive today.

Sea turtles "fly" through the water, using the up-and-down motion of the front flippers to generate thrust; the back feet are not used for propulsion but may be used as rudders for steering.

Sea turtles are almost entirely aquatic and instead of feet they have flippers.

Turtle is any aquatic or terrestrial reptile of the order Testudines (or Chelonia), characterized by toothless jaws with horny beaks and generally having a body shielded by a special bony or cartilagenous shell.

American snapping turtles and musk turtles have small, cross-shaped plastrons that give them more efficient leg movement for walking along the bottom of ponds and streams.

The smallest turtle is the speckled padloper tortoise of South Africa.

Terrapin is the common name for large freshwater or brackish water turtles belonging to the family Emydidae, especially the genus Malaclemys, and sometimes the genus Pseudemys (or Chrysemys).
Sea turtles typically feed on jellyfish, sponge, and other soft-bodied organisms. Some species of sea turtle with stronger jaws have been observed to eat shellfish while some species, such as the green sea turtle, do not eat any meat at all and, instead, have a diet largely made up of algae.
turtle graphics - Computer Definition. A method for creating graphic images in the Logo programming language. The "turtle" is an imaginary pen that is given drawing commands, such as go forward and turn right. On screen, the turtle is shaped like a triangle. See Logo.
Alternatively referred to as turtle graphics, LOGO is pronounced as Low-go and is a high-level programming language known for its graphics capabilities, created by Seymour Papert in 1967. LOGO is often used for young school children as a basic method of programming instructions into a computer to create a graphic.Apr 26, 2017






