Facts about Volcano

Active mud volcanoes tend to involve temperatures much lower than those of igneous volcanoes, except when a mud volcano is actually a vent of an igneous volcano.

The buildup of these layers form a broad volcano with gently sloping sides called a shield volcano.

Supplemental oxygen used as prescribed (20+ hours/day) is the only non-surgical treatment that has been shown to prolong life in emphysema patients.

Interestingly, hotspot volcanoes are also found elsewhere in the Solar System, especially on rocky planets and moons.

Hawaii and Iceland are examples of places where volcanoes extrude huge quantities of basaltic lava that gradually build a wide mountain with a shield-like profile.

Typical examples for this kind of volcano are the volcanoes in the Pacific Ring of Fire, Mount Etna.

Confusion however, can arise because many volcanoes which scientists consider to be active are referred to as dormant by laypersons or in the media.

The Roman name for the island Vulcano has contributed the word for volcano in most modern European languages.

By contrast, volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past each other.

A volcano is an opening, or rupture, in the Earth's surface or crust, which allows hot, molten rock, ash, and gases to escape from deep below the surface.

Dormant volcanoes are those that are not currently active (as defined above), but could become restless or erupt again.

The Earth's Moon has no large volcanoes and no current volcanic activity, although recent evidence suggests it may still possess a partially molten core.

The study of volcanoes is called volcanology, sometimes spelled vulcanology.

Some volcanoes have rugged peaks formed by lava domes rather than a summit crater, whereas others present landscape features such as massive plateaus.

Cassini-Huygens also found evidence of a methane-spewing cryovolcano on the Saturnian moon Titan, which is believed to be a significant source of the methane found in its atmosphere.

Other types of volcanoes include cryovolcanos (or ice volcanoes), particularly on some moons of Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune; and mud volcanoes, which are formations often not associated with known magmatic activity.

Volcanic cones or cinder cones result from eruptions that throw out mostly small pieces of scoria and pyroclastics (both resemble cinders, hence the name of this volcano type) that build up around the vent.

Stratovolcanoes are tall conical mountains composed of lava flows and other ejecta in alternate layers, the strata that give rise to the name.
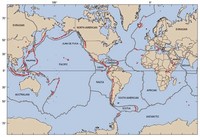
Volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates pull apart or come together.

The Pacific Ring of Fire has examples of volcanoes caused by "convergent tectonic plates"—that is, plates coming together.

The concentrations of different volcanic gases can vary considerably from one volcano to the next.

Another way of classifying volcanoes is by the composition of material erupted (lava), since this affects the shape of the volcano.

Where the mid-oceanic ridge comes above sea-level, volcanoes like the Hekla on Iceland are formed.
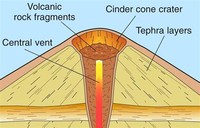
Cinder cones may form as flank vents on larger volcanoes, or occur on their own.

The most common perception of a volcano is of a conical mountain, spewing lava and poisonous gases from a crater in its top.

Scientists usually consider a volcano active if it is currently erupting or showing signs of unrest, such as unusual earthquake activity or significant new gas emissions.
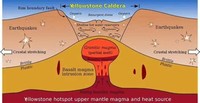
Large igneous provinces are also considered supervolcanoes because of the vast amount of basalt lava erupted.

In 1989 the Voyager 2 spacecraft observed cryovolcanos (ice volcanoes) on Triton, a moon of Neptune, and in 2005 the Cassini-Huygens probe photographed fountains of frozen particles erupting from Enceladus, a moon of Saturn.

Complicating the definition are volcanoes that become restless (producing earthquakes, venting gases, or other non-eruptive activities) but do not actually erupt.

Many scientists also consider a volcano active if it has erupted in historic time.

A supervolcano is the popular term for a large volcano that usually has a large caldera and can potentially produce devastation on an enormous, sometimes continental, scale.

Extinct volcanoes are those that scientists consider unlikely to erupt again.
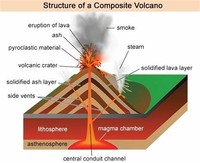
The most common perception of a volcano is of a conical mountain, spewing lava and poisonous gases from a crater in its top.

The lifespan of a volcano can vary from months to several million years, making such a distinction sometimes meaningless when compared to the lifespans of humans or even civilizations.

Olympus Mons is the largest shield volcano on Mars, and is the tallest known mountain in the solar system.

Various explanations were proposed for volcano behavior before the modern understanding of the Earth's mantle structure as a semisolid material was developed.

Finally, volcanoes can be caused by "mantle plumes," so-called "hotspots."

Very good examples of this type of volcano can be seen in Iceland, however, there are also tuyas in British Columbia.

A mid-oceanic ridge, like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has examples of volcanoes caused by "divergent tectonic plates"—that is, plates pulling apart.
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
A volcano is a mountain from where the molten rocks or magma erupt through the surface. In simple terms, a volcano is an opening in the earth's surface from which the molten rocks and gases escape out. Once the magma erupts through the Earth's surface, it is called lava.Jun 13, 2013
Volcanoes happen when magma rises to the surface of the earth, which causes bubbles of gas to appear in it. This gas can cause pressure to build up in the mountain, and it eventually explodes. When the magma bursts out of the earth, it is called lava.







