Types of 3d Printers

Binder Jetting is similar to traditional paper printing. The binder functions like the ink as it moves across the layers of powder, which like paper, forms the final product. Due to its ability to produce solid layers, Binder Jetting is often considered the best option for 3D printing.

Ceramic 3D Printer types: The smallest available ceramic 3D printer from Deltabots is the Micro-8, for ceramic 3D prints not bigger than 10 x 10 x 12 inches. The biggest machine is the XLS-2, with a whooping build volume of 72 inches diameter and 72 inches in height.

DLP Digital Light Processing rapid prototyping services is a form of stereolithography that is used in rapid prototyping services. The main difference between DLP and SLA rapid prototyping is the use of a projector light rather than a laser to cure photo-sensitive polymer resin.
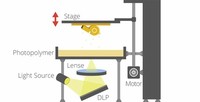
Digital Light Processing rapid prototyping services will produce parts with resolutions under 30 microns; the equivalent to other stereolithography machines. Ultimately, production time does depend on the size of the model. Compared to FDM, DLP 3D printing provides higher resolution and smoother surfaces.

Does 3D printing have the potential to significantly change the A&D value chain? Perhaps, but it ultimately will depend on how far 3D printing can improve its quality and its speed. 3D Printing and EBM (Electron Beam Melting) Product quality. Product quality is the Achilles’ heel of every production technology.

There are several different methods of 3D printing, but the most widely used is a process known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). FDM printers use a thermoplastic filament, which is heated to its melting point and then extruded, layer by layer, to create a three dimensional object.

Gold also dissolves in alkaline solutions of cyanide, which are used in mining and electroplating. Gold dissolves in mercury, forming amalgam alloys, but this is not a chemical reaction. A relatively rare element, gold is a precious metal that has been used for coinage, jewelry, and other arts throughout recorded history.

Laminated object manufacturing (LOM) is a method of 3D printing. It was developed by the California-based Helisys Inc. (now Cubic Technologies). During the LOM process, layers of plastic or paper are fused — or laminated — together using heat and pressure, and then cut into the desired shape with a computer-controlled laser or blade.

Polyamide 3D printing: Nylon Plastic Powder Material for SLS Polyamide is a plastic material used to print 3D objects. Printed from polyamide powder, this material is also known as nylon.

With total reviews from over 10,154 verified 3D printer owners having a collective 6,353 years of 3D printing experience, coupled with 1.48 million prints completed on 668 different 3D printer models, the result of our research is the 2018 3D Printer Guide – the most comprehensive 3D printer guide available.

SLM (Selective Laser Melting) : 3D Printing Metal Selective Laser Melting is an additive manufacturing technique that can print metal parts in 3D. A laser is used to melt metallic powder in specific places.

3D Systems’ Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Nylon Printers SLS technology uses a laser to harden and bond small grains of plastic, ceramic, glass, metal, or other materials into layers in a 3D structure.

Stainless steel is one of the most affordable materials in metal 3D printing. It’s very strong and can be used in a wide variety of industrial and even artistic/design applications. This type of steel alloy, which also contains cobalt and nickel, is particularly hard to break while at the same time having very high elastic properties.

Stereolithography (SL) is one of several methods used to create 3D-printed objects. It's the process by which a uniquely designed 3D printing machine, called a stereolithograph apparatus (SLA) converts liquid plastic into solid objects.

3D printing with metals has been around for a few years now, but as the technology and software that run 3D printers drop in price, it is starting to be adopted by a rapidly increasing number of industries.
