Types of Alzheimer's Disease
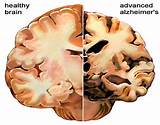
Alzheimer's and dementia basics . Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia, a general term for memory loss and other cognitive abilities serious enough to interfere with daily life. Alzheimer's disease accounts for 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases. Learn more: What We Know Today and Understanding Dementia.

Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) is a rare form of dementia that happens when a protein -- called a prion -- folds into an abnormal shape, and other prions start to do the same. This damages brain cells and triggers a fast mental decline.

Lewy body dementia (LBD) is one of the most common types of dementia, after Alzheimer’s disease. It usually happens to people who are 50 or over. There are two types: Dementia with Lewy bodies often starts when you have a hard time moving your body.

Lewy body dementia is a type of dementia, related to Alzheimer's disease. Learn about Lewy body dementia causes, signs and symptoms and treatment and get support resources.
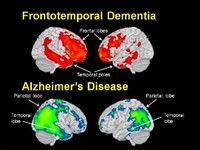
About frontotemporal dementia Arnold Pick, M.D., who described the first case of FTD. The nerve cell damage caused by frontotemporal dementia leads to loss of function in these brain regions, which variably cause deterioration in behavior and personality, language disturbances, or alterations in muscle or motor functions.

Huntington's Disease. Huntington's Disease (HD) is a progressive brain disorder caused by a defective gene. This disease causes changes in the central area of the brain, which affect movement, mood and thinking skills.

Mixed dementia is a term used when a person has more than one type of dementia. Often, mixed dementia consists of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia, but it also refers to a combination of Alzheimer's and any other type of dementia. Prevalence of Mixed Dementia. The prevalence of mixed dementia is difficult to determine. Traditionally, clinicians have identified one primary type of dementia when determining a diagnosis for a patient, such as Alzheimer's disease or vascular dementia.

Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a type of dementia, related to Alzheimer's disease. Learn about NPH causes, signs and symptoms, treatment and get information and support resources.

Parkinson's disease dementia is a type of dementia, related to Alzheimer's disease. Learn about Parkinson's disease signs and symptoms and treatment and get support resources.

Vascular brain changes often coexist with changes linked to other types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Several studies have found that vascular changes and other brain abnormalities may interact in ways that increase the likelihood of dementia diagnosis.