Types of Amino Acids

Alanine (abbreviated as Ala or A; encoded by the codons GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.

Arginine (abbreviated as Arg or R) encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual.
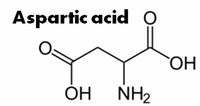
Aspartic acid is believed to help your body promote a robust metabolism. From time to time it is used to treat depression and fatigue. This amino acid plays a key role in the citric acid cycle (also known as Krebs cycle), within which a number of other amino acids and biochemicals are formed.

Glutamic acid, abbreviated as E or Glu, is an important amino acid for the synthesis of proteins. The salts and carboxylate anions associated with glutamic acid are referred to as glutamates. Glutamic acid contributes to the health of the immune and digestive systems, as well as energy production.

Glutamine and glutamic acid. The amino acids glutamine and glutamic acid are closely related in a chemical sense. The human body is able to produce L-glutamine itself, from L-glutamic acid through the glutamate ammonium ligase.
Lysine is an amino acid found in the protein of foods such as beans, cheese, yogurt, meat, milk, brewer's yeast, wheat germ, and other animal proteins. Proteins derived from grains such as wheat and corn tend to be low in lysine content.

Proline is formally NOT an amino acid, but an imino acid. Nonetheless, it is called an amino acid. The primary amine on the α carbon of glutamate semialdehyde forms a Schiff base with the aldehyde which is then reduced, yielding proline.

Like valine and isoleucine, leucine is a branched-chain amino acid. The primary metabolic end products of leucine metabolism are acetyl-CoA and acetoacetate; consequently, it is one of the two exclusively ketogenic amino acids, with lysine being the other.