Types of Biodiversity

Biological diversity (or biodiversity) is the variety of life on Earth. It includes all living things, not just the plants and animals that are common or easily seen. It includes species that are not well known, such as microorganisms or invertebrates.

The Australian Government recognises the importance of biodiversity conservation and, in collaboration with states and territories, has set a national framework for biodiversity conservation over the next decade. Biodiversity, or biological diversity, is the variety of all species on earth.

Ecological diversity means diversity of ecosystems e.g. marine ecosystem, fresh water ecosystem, desert ecosystem. Biodiversity denote the diversity of species in an ecosystem by number of species. For example a freshwater lake may have algae, aquatic plants,fishes, birds etc.

Biodiversity is the variability among living organisms from all sources, including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species, and of ecosystems.

(1) The functional diversity within a trophic level enhanced the biomass of that trophic level, and (2) The functional diversity of the predators more effectively depressed the biomass of the herbivores, but only by modifying the functional diversity of the herbivores.
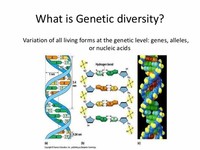
Genetic diversity refers to the diversity (or genetic variability) within species. Each individual species possesses genes which are the source of its own unique features: In human beings, for example, the huge variety of people's faces reflects each person's genetic individuality.

Human presence in the Great lakes ecosystem is a good example of this. The Great Lakes drain 20% of the world's freshwater. Despite their significant size, the biodiversity of the Great Lakes ecosystem is threatened for a number of reasons.

Species diversity is defined as the number of species and abundance of each species that live in a particular location. The number of species that live in a certain location is called species richness. If you were to measure the species richness of a forest, you might find 20 bird species, 50 plant species, and 10 mammal species.