Types of Biology

Anatomy, a field in the biological sciences concerned with the identification and description of the body structures of living things. Gross anatomy involves the study of major body structures by dissection and observation and in its narrowest sense is concerned only with the human body.

Biology is easy and Biochem is more challenging because of Pchem and analytical chemistry. I was wondering if it is better to have a little bit of lower gpa and a biochem major or a higher gpa and a Biology major.

Biophysics is a vibrant scientific field where scientists from many fields including math, chemistry, physics, engineering, pharmacology, and materials sciences, use their skills to explore and develop new tools for understanding how biology—all life—works.

Modern biotechnology provides breakthrough products and technologies to combat debilitating and rare diseases, reduce our environmental footprint, feed the hungry, use less and cleaner energy, and have safer, cleaner and more efficient industrial manufacturing processes.

Botany, also called plant science(s), plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field.

Cell biology. Cell biology (formerly called cytology, from the Greek κυτος, kytos, "vessel") is a branch of biology that studies the different structures and functions of the cell and focuses mainly on the idea of the cell as the basic unit of life.

In biological classification, class (Latin: classis) is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order.
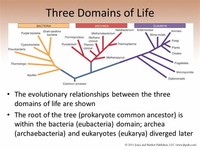
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese et al. in 1977 that divides cellular life forms into archaea, bacteria, and eukaryote domains. In particular, it emphasizes the separation of prokaryotes into two groups, originally called Eubacteria (now Bacteria) and Archaebacteria (now Archaea).

Ecology is the scientific study of the distribution and abundance of organisms, the interaction among organisms, and the interactions between organisms and their abiotic environment. Ecologists try to understand the inner workings of natural ecosystems and the species they contain.

Though entomology is the study of insects, medical entomology has a broader scope in that it incorporates other arthropods that may affect human health - this means arachnids such as spiders, mites, ticks and also come under the scope of a medical entomology researcher.

Ethology is the scientific and objective study of animal behaviour, usually with a focus on behaviour under natural conditions, and viewing behaviour as an evolutionarily adaptive trait.

Family (biology) In biological classification, family (Latin: familia, plural familiae) is one of the eight major taxonomic ranks; it is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks above the rank of genus.

In binomial nomenclature, the genus is used as the first word of a scientific name. The genus name is always capitalized and italicized. For example, the binomial name of lion is Panthera leo. The first part, Panthera, is the genus name whereas the second part, leo, is the specific epithet.

How to be a Herpetologist So you want to be a herpetologist? That is an admirable choice, but you should have a strong desire to study reptiles and amphibians for the road to a career in herpetology is not an easy one — but it is an interesting one. Below is a description of how to become a herpetologist, originally written in 1985, but still ...

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world.

Ichthyology (from Greek: ἰχθύς, ikhthus, "fish"; and λόγος, logos, "study"), also known as fish science, is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish. This includes bony fish (Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha).

Mammalogy is the branch of biology that deals with the study of mammals. It encompasses such diverse areas as the structure, function, evolutionary history, ethology, taxonomy, management and economics of mammals. Approximately 4,200 species of living mammals and numerous extinct species comprise the material for study.

Microbiology (from Greek μῑκρος, mīkros, "small"; βίος, bios, "life"; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, parasitology, mycology and bacteriology.

In biological classification, the order (Latin: ordo) is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, family, genus, and species, with order fitting in between class and family.

Examples: Class Mammalia , Class Aves and Class Ascidiacea (sea squirts) all belong to Chordate Phylum, which is a group of animals that have notochords at some time in their life cycle. Aside from Chordata, other well known phyla are the Mollusca, Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Arthropoda and Echinodermata, which all belong to Kingdom Animalia.

Species - smallest classification The domain is the broadest category, while species is the most specific category available. The taxon Domain was only introduced in 1990 by Carl Woese, as scientists reorganise things based on new discoveries and information.

Zoology (/zuːˈɒlədʒi/, zoo-OL-luh-jee or /zoʊˈɒlədʒi/, zoh-OL-luh-jee) or animal biology is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems.