Types of Blue Stones

Three-stone ring, 4 mm mined alexandrite and 3 mm emerald side stones. Set in a delicate 14k white gold band with trinity knot accents. © CustomMade. Used with permission.

Blue diamond is typically irradiated to obtain its color, though some very rare stones may be completely natural and untreated. Most blue diamond will exhibit a secondary greenish hue.
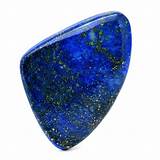
Lapis lazuli (/ ˈ l æ p ɪ s ˈ l æ zj ʊ l i, -l aɪ /), or lapis for short, is a deep blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.

Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide (α-Al 2 O 3). It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors.

Blue Topaz, the most commonly used Topaz color, is formed from colorless or lightly colored Topaz that is irradiated to make it blue, and then heat treated to stabilize the new color. Different forms of radiation treatment can produce different shades of blue.

For example, blue indicolite tourmaline is the only blue gemstone of any kind that will show a drag response when a neodymium magnet is applied. Any blue tourmaline that is diamagnetic can be identified as paraiba tourmaline colored by copper in contrast to magnetic blue tourmaline colored by iron.

Green stones from Myanmar may show more than forty lines, while orange gems from New South Wales, Australia may show only a few lines. Low zircon and heat-treated stones have a weaker display. Most zircons show a strong line at 6535 even in types where a strong spectrum is otherwise absent.