Types of Body Cavities
abdominal cavity the cavity of the body between the diaphragm above and the pelvis below, containing the abdominal organs. absorption c's cavities in developing compact bone due to osteoclastic erosion, usually occurring in the areas laid down first.

Start studying Body Cavities. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.

- The cavity also enables he internal organs to grow and move independently of the outer body wall. If it were not for your coelom, for example, every beat of your heart or ripple of your intestine would wrap your body's surface.

body cavity Any space in the body that does not freely communicate with the outside. Body cavities are covered with specialised lining cells—e.g., mesothelial cells in the pericardium, peritoneum and pleura. Body cavity types • Major—Pericardial, pleural, peritoneal, cerebrospinal.
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.

Retroperitoneal Space Retroperitoneal space is the anatomical space in the abdominal cavity behind the parietal peritoneum. It extends from the 12 th thoracic vertebra and 12 th rib above to the sacrum and iliac crest below.

Serous fluid is secreted by both membranes and acts as a lubricant, allowing organs to slide in the cavity without causing friction. Typically, the serous membranes are named according to the cavity and organ they associate with. For instance, the parietal pericardium lines the pericardial cavity.
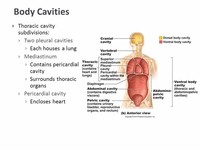
The thoracic cavity has three compartments: the mediastinum and two pleural cavities. The mediastinum is home to the heart, trachea, great vessels, and some other structures. The pleural cavities are on either side of the mediastinum and contain the lungs and the pleural linings.

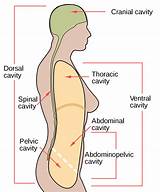
Human body cavities: Ventral body cavity is to the right The ventral body cavity is a human body cavity that is in the anterior (front) aspect of the human body. It is made up of the thoracic cavity, and the abdominopelvic cavity.

A body cavity is any fluid-filled space in a multicellular organism other than those of vessels (such as blood vessels and lymph vessels). The human body cavity normally refers to the ventral body cavity, because it is by far the largest.