Types of Body Scans

A bone scan is a good way to view and document abnormal metabolic activity in the bones. A bone scan can also be used to determine whether cancer has spread to the bones from another area of the body, such as the prostate or breast.
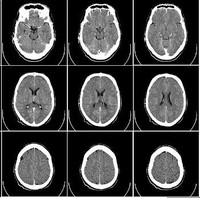
Computed tomography is an imaging procedure that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed pictures, or scans, of areas inside the body. It is also called computerized tomography and computerized axial tomography (CAT).

Computed tomography is an imaging procedure that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed pictures, or scans, of areas inside the body. It is also called computerized tomography and computerized axial tomography (CAT).

Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses sophisticated x-ray technology to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless, noninvasive and accurate. In emergency cases, it can reveal internal injuries and bleeding quickly enough to help save lives.

What is an endoscopic ultrasound scan (EUS) used for? EUS can be used for a wide range of different things, including to: Find gallstones. Diagnose diseases of the internal organs such as the pancreas. For example, to detect inflammation of the pancreas (chronic pancreatitis) or fluid-filled sacs (cysts) of the pancreas.

At Medical Imaging of Fredericksburg, we have ultrasounds, mammography, CT scans, several types of MRIs, PET scans, and PET-CT scans. The two most commonly used tests besides x-rays are CT scans and MRIs, both of which provide more detail than x-rays. If you need specialized imaging, it can be helpful to understand the operation and uses for a CT Scan vs. MRI. In some ways, these two tests are ...

What is a barium enema? A barium enema is a radiographic (X-ray) examination of the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The large intestine, including the rectum, is made visible on X-ray film by filling the colon with a liquid suspension called barium sulfate (barium). Barium highlights certain areas in the body to create a clearer picture.

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a test that uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and a computer to make detailed pictures inside your body. Your doctor can use this test to diagnose you or to see how well you've responded to treatment.

While technologies vary, the vast majority of these high-tech checkups use computed tomography (CT) scans to examine your entire body or specific parts, such as the heart and lungs, promising to catch dangerous diseases in earlier, more curable stages.

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a test that uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and a computer to make detailed pictures inside your body. Your doctor can use this test to diagnose you or to see how well you've responded to treatment.

A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging test that allows your doctor to check for diseases in your body. The scan uses a special dye that has radioactive tracers. These tracers are either swallowed, inhaled, or injected into a vein in your arm depending on what part of the body is being examined.

An ultrasound scan is a painless test that uses sound waves to create images of organs and structures inside your body. It is a very commonly used test. An ultrasound scan is a painless test that uses sound waves to create images of organs and structures inside your body.

The technique combines multiple X-ray images and with the aid of a computer produces cross-sectional views of your body. By examining the views, a doctor can look for early signs of abnormalities. The scans aren't cheap -- they run anywhere from $250 to $750 per scan and usually aren't reimbursed by insurance.