Types of Chemical Changes
It also introduced the concept of equilibrium to acid–base chemistry: this concept states that reversible chemical reactions reach a point of balance, or equilibrium, at which the starting materials and the products are each regenerated by one of the two reactions as rapidly as they are consumed by the other.

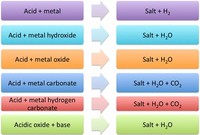
Acid–base reaction, a type of chemical process typified by the exchange of one or more hydrogen ions, H +, between species that may be neutral (molecules, such as water, H 2 O; or acetic acid, CH 3 CO 2 H) or electrically charged (ions, such as ammonium, NH 4 +; hydroxide, OH −; or carbonate, CO 3 2−).

Is baking a cake a chemical change? Next time you bake a cake, think about this: The cake dough isn't really a cake, but when it's heated in the oven, a chemical reaction occurs and new bonds are formed.

Burning of anything is a chemical change. The burning action changes the chemical makeup of the wood. The wood becomes a few different things, ash, smoke, energy, etc. They can’t go back to the wood and there isn’t any wood left in the burnt substances.

A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction is one of the most common types of chemical reactions. In a synthesis reaction two or more chemical species combine to form a more complex product. A + B → AB. In this form, a synthesis reaction is easy to recognize because you have more reactants than products.

Combustion is an exothermic reaction, so it releases heat, but sometimes the reaction proceeds so slowly that a temperature change is not noticeable. Good signs that you are dealing with a combustion reaction include the presence of oxygen as a reactant and carbon dioxide, water and heat as products.

Cooking an egg is considered a chemical change. If the cooking of an egg is just the physical change, the cooked state of it has to be able to be converted back to the previous form which existed earlier.
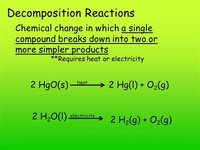
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a single chemical compound into its two or more elemental parts or to simpler compounds. Chemical decomposition is usually regarded and defined as the exact opposite of chemical synthesis.

The reactions may be classified on this basis as thermal decomposition reactions, electrolytic decomposition reactions, and catalytic reactions. A decomposition is the opposite or reverse process of a synthesis reaction.
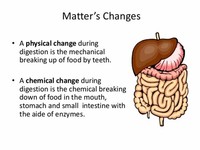
Because the process during digestion causes food to become a new substance, digestion is a chemical change. A physical change occurs when a subject changes its shape, size or... Because the process during digestion causes food to become a new substance, digestion is a chemical change.

A single-displacement reaction, also known as a single-replacement reaction, is a reaction by which one (or more) element(s) replaces an/other element(s) in a compound.It can be represented generically as:

Learn about double displacement reactions, or often referred to as salt metathesis, in chemistry with examples of representative chemical reactions. Learn about double displacement reactions, or often referred to as salt metathesis, in chemistry with examples of representative chemical reactions.

Exposure to heat initially melts the sugar into a syrup. This is the breakdown of the sugar into fructose and glucose, and it is marked by the aroma it creates. Continued exposure to heat alters the color of the melted sugar to yellow, then brown. The color change is caused by the further breakdown of the sugar molecules and formation of caramelin.

Adding a base to an acid or vice versa in changing the chemical properties of that solution. In both cases you are neuralizing the solution. There might be a physical change as well, but it would depend on what chemicals where mixing.

In rusting the Iron ore make a chemical reaction with the oxygen in the presence of water and environmental or atmospheric moisture to produce an Iron oxide. Iron oxide is otherwise called as rust. Rust has two different chemical composition Fe2O3nH2O (hydrated Iron Oxide) and (FeO (OH), Fe(OH)3) Iron oxide-hydroxide.

A single-displacement reaction, also known as a single-replacement reaction, is a reaction by which one (or more) element(s) replaces an/other element(s) in a compound.It can be represented generically as:

Souring milk is not something you can reverse, and the process of it souring produces new molecules. Some other examples of chemical changes would be things that involve burning, the creation of a new gas or bubbles, or change in color, like the formation of rust.

Chemical synthesis: Chemical synthesis, the construction of complex chemical compounds from simpler ones. It is the process by which many substances important to daily life are obtained. It is applied to all types of chemical compounds, but most syntheses are of organic molecules.