Types of Clean Energy

Unlike other renewable energy sources, biomass can be converted directly into liquid fuels - biofuels - for our transportation needs (cars, trucks, buses, airplanes, and trains). The two most common types of biofuels are ethanol and biodiesel.

What is Biomass? Biomass is fuel that is developed from organic materials, a renewable and sustainable source of energy used to create electricity or other forms of power. Some examples of materials that make up biomass fuels are: scrap lumber; forest debris; certain crops; manure; and; some types of waste residues.

Biomass is a renewable source of fuel to produce energy because: waste residues will always exist – in terms of scrap wood, mill residuals and forest resources; and properly managed forests will always have more trees, and we will always have crops and the residual biological matter from those crops.

Clean coal technology is a collection of technologies being developed to attempt to help lessen the environmental impact of coal energy generation and to mitigate worldwide climate change.

ENERGY SOURCES | Energy types include both the categories we use to group energy sources (like fossil fuels, alternatives, and renewables) and the resources we derive energy from (like oil, solar, and nuclear).

Fossil fuels—coal, natural gas, and oil—have powered America for more than a century, but their production and use have significant health and environmental impacts, including air and water pollution, environmental degradation, and global warming. Learn more about the technology and costs of fossil fuels.

Geothermal fields produce only about one-sixth of the carbon dioxide that a relatively clean natural-gas-fueled power plant produces, and very little if any, of the nitrous oxide or sulfur-bearing gases. Binary plants, which are closed cycle operations, release essentially no emissions. Geothermal energy is available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Geothermal power plants have average availabilities of 90% or higher, compared to about 75% for coal plants.

Geothermal power plants have average availabilities of 90% or higher, compared to about 75% for coal plants. Geothermal power is homegrown, reducing our dependence on foreign oil. Learn more on our Energy Basics page.
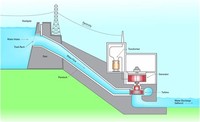
But hydroelectric power doesn't necessarily require a large dam. Some hydroelectric power plants just use a small canal to channel the river water through a turbine. Another type of hydroelectric power plant - called a pumped storage plant - can even store power. The power is sent from a power grid into the electric generators.

Hydroelectric power is a source of renewable energy. As a way of generating electricity, hydropower has several key advantages that contribute to its widespread usage: Hydroelectric power does not contribute to air pollution.

Hydrogen fuel cells power the shuttle's electrical systems, producing a clean byproduct - pure water, which the crew drinks. A fuel cell combines hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, heat, and water. Fuel cells are often compared to batteries. Both convert the energy produced by a chemical reaction into usable electric power.
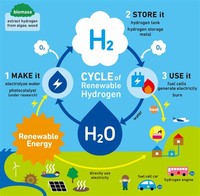
Renewable energy sources, like the sun and wind, can't produce energy all the time. But they could, for example, produce electric energy and hydrogen, which can be stored until it's needed. Hydrogen can also be transported (like electricity) to locations where it is needed.

Conventional hydropower, which accounts for nearly 8.2% of total U.S. electric generation, can provide low-emissions alternatives to fossil-fuel energy. But does that make it clean? It depends.

The Clean Energy Solution As the largest domestic distributor of natural gas fuel in North America, Clean Energy is proudly fueling our partners fleets, reducing our dependency on foreign oil, and providing solutions that are cleaner and make the American economy even stronger.

Nonrenewable and renewable energy sources Energy sources are classified as nonrenewable because they do not form or replenish in a short period of time. Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind replenish naturally in a short period of time.

The U.S. saw a boom in nuclear energy plants in the 195’s, when nuclear energy was widely regarded as the wave of the future. In 1979, however, the core reactor meltdown at the Three Mile Island nuclear facility near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, changed the nation’s optimistic views on nuclear power.

Most renewable energy comes either directly or indirectly from the sun. Sunlight, or solar energy, can be used directly for heating and lighting homes and other buildings, for generating electricity, and for hot water heating, solar cooling, and a variety of commercial and industrial uses.

Sometimes, petroleum and crude oil are used to mean the same thing, but petroleum itself is a broad range of petroleum products including crude oil itself. We use the term 'petroleum products after crude oil is refined in a factory. Crude oil can exist either deep down in the earth's surface or deep below the ocean beds.

Currently solar panels convert most of the visible light spectrum and about half of the ultraviolet and infrared light spectrum to usable solar energy. Solar energy technologies use the sun's energy and light to provide heat, light, hot water, electricity, and even cooling, for homes, businesses, and industry.

What is clean energy? Energy and the Environment; Tiki's Guide to Energy; Pearson Science: Energy Sources; CSIRO fact sheet: energy; CSIRO fact sheet: coal; CSIRO fact sheet: petroleum; CSIRO fact sheet: lp gas; Most of our electricity comes from power stations that use fossil fuels like coal and oil.

More About Solar Energy. Solar is one of the fastest-growing industries in America, employing 120,000 workers and generating an estimated 13 gigawatts (GW) of clean electricity – enough to effectively power 2 million homes. Installed solar capacity continues to grow as the cost of going solar drops.

Clean energy can be distinguished from renewable power in that clean power is focused on carbon emission reduction as a method of counteracting “dirty” energy as a primary goal whereas renewables would be, by definition, focused on the ability to reuse a resource as an ultimate goal.

Tidal energy or tidal power is a form of hydropower that uses the kinetic energy of the tides to spin an underwater turbine and generate clean electricity. Tidal energy is part of the alternative energy sources and is also considered a renewable energy source because the energy of the tides is continuous.

Tidal energy or tidal power is a form of hydropower that uses the kinetic energy of the tides to spin an underwater turbine and generate clean electricity. Tidal energy is part of the alternative energy sources and is also considered a renewable energy source because the energy of the tides is continuous.

Australian Government Clean Energy Future website; BTN story - Carbon; Clean energy cuts emissions; Watch video now Moving towards a clean energy world. We have already found ways to tap into the energy of the sun, wind, waves and water, amongst other things.

Ocean wave energy is captured directly from surface waves or from pressure fluctuations below the surface. Waves are caused by the wind blowing over the surface of the ocean. In many areas of the world, the wind blows with enough consistency and force to provide continuous waves along the shoreline.

Wind is a clean source of renewable energy that produces no air or water pollution. And since the wind is free, operational costs are nearly zero once a turbine is erected. Mass production and technology advances are making turbines cheaper, and many governments offer tax incentives to spur wind-energy development.