Types of cml

In the absence of intervention, CML typically begins in the chronic phase, and over the course of several years progresses to an accelerated phase and ultimately to a blast crisis. Blast crisis is the terminal phase of CML and clinically behaves like an acute leukemia.

Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), also called acute lymphoblastic leukemia, is a cancer that starts from the early version of white blood cells called lymphocytes in the bone marrow (the soft inner part of the bones, where new blood cells are made). Leukemia cells usually invade the blood fairly quickly.

Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML) Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML) Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) The rest of this document focuses on acute myeloid leukemias in adults only.

Blastic Myeloid Leukemia. Overview. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is the abnormal growth of relatively mature myeloid (white blood) cells. Half of all patients with CML are diagnosed after the age of 67. CML is associated with a chromosomal abnormality in which genetic material from chromosome 9 is transferred to chromosome 22.

Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia in adults. It's a type of cancer that starts in cells that become certain white blood cells (called lymphocytes) in the bone marrow. The cancer (leukemia) cells start in the bone marrow but then go into the blood.

Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myelogenous leukemia, is a type of cancer that starts in certain blood-forming cells of the bone marrow. In CML, a genetic change takes place in an early (immature) version of myeloid cells - the cells that make red blood cells, platelets, and most types of white blood cells (except lymphocytes).
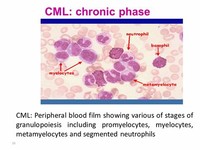
CML has three phases: Chronic phase Accelerated phase Blast crisis phase Each phase describes CML's progression, determined by the number of blast cells (white cells that don't fully form as they should, blocking production of functioning blood cells) in the blood and bone marrow.