Types of Common Stock

Common stock is a security that represents ownership in a corporation. Holders of common stock exercise control by electing a board of directors and voting on corporate policy.

A defensive stock is a stock that provides a constant dividend and stable earnings regardless of the state of the overall stock market. Because of the constant demand for their products, defensive stocks tend to remain stable during the various phases of the business cycle.

What is the 'Dividend Yield' A financial ratio that indicates how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price. Dividend yield is represented as a percentage and can be calculated by dividing the dollar value of dividends paid in a given year per share of stock held ...

A growth stock is a share in a company whose earnings are expected to grow at an above-average rate relative to the market. A growth stock usually does not pay a dividend, as the company would prefer to reinvest retained earnings in capital projects.

What is a 'New Issue' A new issue is a reference to a security that has been registered and issued and is being sold on a market to the public for the first time. The term does not necessarily refer to newly issued stocks, although initial public offerings (IPOs) are the most commonly known new issues.
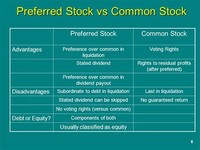
Preferred stock trades the same way as common stock, usually through a brokerage firm and with the same transaction costs. Because the properties generally associated with these stocks will affect the way investors value them, the prices of common and preferred stocks offered by the same company will differ.

What are 'Class A Shares' Class A shares refers to a classification of common stock that is accompanied by more voting rights than Class B shares, usually given to a company's management team. For example, one Class A share may be accompanied by five voting rights, while one Class B share may be accompanied by only one right to vote.