Types of Connective Tissue

Adventitia consists of ordinary connective tissue in the shape of fibers that rests around the organ that the tissue supports. The serosa is also connective tissue, but its surface consists of mesothelium. It makes up the visceral peritoneum and extends over the abdominal wall, forming the parietal peritoneum.

There are two main types of bone tissue, compact bone and spongy bone. Individual bones in the body can be formed from both of these types of bone tissue. The diagram on the right shows the physical structure of a typical "long bone".

Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). Brown adipose tissue is found in almost all mammals. Classification of brown fat refers to two distinct cell populations with similar functions.

Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting of a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibres embedded in a rubbery ground substance. The matrix is produced by cells called chondroblasts, which become embedded in the matrix as chondrocytes. That is, mature cartilage cells are called chondrocytes.

Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting of a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibres embedded in a rubbery ground substance. The matrix is produced by cells called chondroblasts, which become embedded in the matrix as chondrocytes.

Cartilage Tissue - Anatomy & physiology revision about the structure and functions of human tissue types. Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting of a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibres embedded in a rubbery ground substance.

Simply put, fascia is the body’s connective tissue. It is a head to toe, inside to out, all-encompassing and interwoven system of fibrous connective tissue found throughout the body. Your fascia provides a framework that helps support and protect individual muscle groups, organs, and the entire body as a unit.
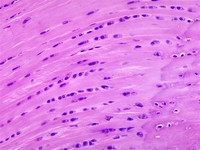
Fibrocartilage is a tough, dense, and fibrous material that helps fill in the torn part of the cartilage; however, it is not an ideal replacement for the smooth, glassy articular cartilage that normally covers the surface of joints.

Cartilage Tissue - Anatomy & physiology revision about the structure and functions of human tissue types. Cartilage is a connective tissue consisting of a dense matrix of collagen fibres and elastic fibres embedded in a rubbery ground substance.

In biology, adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages.