Types of Coping

Acting Out . Explanations > Behaviors > Coping > Acting Out. Description | Example | Discussion | So what? Description 'Acting out' means literally means acting out the desires that are forbidden by the Super ego and yet desired by the Id. We thus cope with the pressure to do what we believe is wrong by giving in to the desire.

The answer is compartmentalization. Psychology defines compartmentalization as a defense mechanism, or a coping strategy, which doesn’t impart a very good connotation. Put simply, it’s how our minds deal with conflicting internal standpoints simultaneously.

This type of denial is a helpful response to stressful information. You initially denied the distressing problem. But as your mind absorbed the possibility, you began to approach the problem more rationally and took action by seeking help.

Displacement . Explanations > Behaviors > Coping > Displacement. Description | Example | Discussion | So what? Description. Displacement is the shifting of actions from a desired target to a substitute target when there is some reason why the first target is not permitted or not available.

Dissociation is a coping skill used to separate the person from the traumatic event(s) and memories of the traumatic event(s). Children find it particularly easy to "step out of themselves" as their identity is still forming.
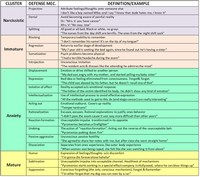
Projection . Explanations > Behaviors > Coping > Projection. Description | Example | Discussion | So what? Description. When a person has uncomfortable thoughts or feelings, they may project these onto other people, assigning the thoughts or feelings that they need to repress to a convenient alternative target.

Rationalization is related to our need to explain what happens and to maintain consistency between and amongst actions and thoughts. Our need for esteem also leads us to rationalize to others. Rationalization happens with bullies and victims. The bully rationalizes what they have done by saying that their victim 'deserved it'.

Reaction Formation . Explanations > Behaviors > Coping > Reaction Formation. Description | Example | Discussion | So what? Description. Reaction Formation occurs when a person feels an urge to do or say something and then actually does or says something that is effectively the opposite of what they really want.

Regression . Explanations > Behaviors > Coping > Regression. Description | Example | Discussion | So what? Description. Regression involves taking the position of a child in some problematic situation, rather than acting in a more adult way.

Repression . Explanations > Behaviours > Coping > Repression. Description | Example | Discussion | So what? Description. Repression involves placing uncomfortable thoughts in relatively inaccessible areas of the subconscious mind.

In psychology, sublimation is a mature type of defense mechanism, in which socially unacceptable impulses or idealizations are unconsciously transformed into socially acceptable actions or behavior, possibly resulting in a long-term conversion of the initial impulse.