Types of Crystalloids
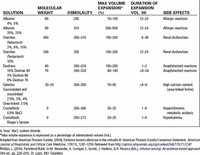
Colloid or Crystalloid: Any Differences in Outcomes? Tong J. Gan, ... and crystalloids that contribute to their effects. ... Table 1. Comparison of contents, ...

Gelofusine is a colloid volume expander that is used as a blood plasma replacement if a significant amount of blood is lost due to extreme hemorrhagia, trauma, dehydration, or a similar event. It is an intravenous colloid that behaves much like blood filled with albumins.

Glucose (dextrose) Intravenous sugar solutions, such as with glucose (also called dextrose), have the advantage of providing some energy, and may thereby provide the entire or part of the energy component of parenteral nutrition.

Crystalloid versus Hydroxyethyl Starch Trial (CHEST) Management Committee. The Crystalloid versus Hydroxyethyl Starch Trial: protocol for a multi-centre randomised controlled trial of fluid resuscitation with 6% hydroxyethyl starch (130/0.4) compared to 0.9% sodium chloride (saline) in intensive care patients on mortality.

Crystalloids. The most commonly used crystalloid fluid is normal saline, a solution of sodium chloride at 0.9% concentration, which is close to the concentration in the blood . Ringer's lactate or Ringer's acetate is another isotonic solution often used for large-volume fluid replacement.

Ringer's lactate solution has a lower rate of acidosis as compared with normal saline. Use is generally safe in pregnancy and breastfeeding. Ringer's lactate solution is in the crystalloid family of medication. It is the same tonicity as blood. Ringer's solution was invented in the 1880s with lactate being added in the 1930s.