Types of Cytokines

Cytokines are signalling molecules produced by cell for specific biological functions. For example, interleukin is a type of cytokine produced by white cells as signalling molecules.

The substance that was found to stimulate formation of colonies of macrophages, for instance, was called macrophage colony-stimulating factor, for granulocytes, ...

Types of interferon ... also known as bird flu, has resistance to interferon and other anti-viral cytokines that is attributed to a single amino acid change in its ...

What are the classification methods which determine if a molecule is a cytokine or a interleukin? Also, how are prostaglandins classified (cytokines, interleukins or a hormone)?

Cytokines. Cytokines can be defined operationally as polypeptides secreted by leukocytes and other cells that act principally on hematopoietic cells, the effects of which include modulation of immune and inflammatory responses.

Transforming growth factor beta superfamily ... TGF-beta-1 is a peptide of 112 amino acid residues derived by proteolytic cleavage from the C-terminal of a ...
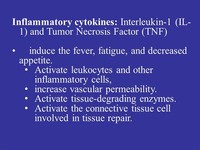
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, tumor necrosis factor alpha, TNFα, cachexin, or cachectin) is a cell signaling protein involved in systemic inflammation and is one of the cytokines that make up the acute phase reaction.It is produced chiefly by activated macrophages, although it can be produced by many other cell types such as CD4+ lymphocytes, NK cells, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, and ...