Types of Decision Making

Decision making without a group's input or a decision made regardless of the group's opinion is, naturally, an individual decision. This is the more traditional decision making approach and can work effectively for a manager when the group's input is not required or in certain cases, desired.

Long range impact on the organization is a major decision. 2. Impact of the decision on other functional area; If it affects one area that's a minor decision. Impact of the decision on other functional area; If it affects one area that's a minor decision.

Operational decisions relate to the daily operations of an organization. The countless interactions that take place on a daily basis represent the result of operational decisions. These decisions, therefore, can bog down an organization and make it ineffective.

Difference between Organizational and Personal Decisions Personal Decisions While making personal decisions, personal interests are kept in mind. Such decisions are made by managers on their own behalf. These decisions are personal in nature and hence, are biased and may not always be rational. There is no scope for delegation of such decisions in management.

Programmed Decision: Non-Programmed Decision: Used for frequent situations of organization; both internal and external. Used for unique and ill-structured situations of organization; both internal and external. Mostly Lower level managers are making these decisions. Mostly Upper-level managers are making these decisions.

Strategic Decisions or Policy Decisions These decisions are also known as Policy decisions. These are not repetitive in nature nor follow a routine manner. These are related to the long-term functioning of the company. The making of these decisions is guided by policy manuals but require high expertise and strategic knowledge. These decisions have a long-term impact and wide-scale repercussions and as a result they require long-term commitment of funds and resources.

DEFINE: The first step in making a decision or solving a problem is to define it. This first step is one of the most critical ones. You have to accurately and adequately define the constraints, the current operations, and the goals.

Decision making is the process of making choices by identifying a decision, gathering information, and assessing alternative resolutions. Using a step-by-step decision-making process can help you make more deliberate, thoughtful decisions by organizing relevant information and defining alternatives.

A range of creative policy or management alternatives designed to address the objectives is developed. Alternatives should reflect substantially different approaches to the problem or different priorities across objectives, and should present decision makers with real options and choices.

Using a step-by-step decision-making process can help you make more deliberate, thoughtful decisions by organizing relevant information and de˜ning alternatives. This approach increases the chances that you will choose the most satisfying alternative possible. Step 4: Weigh the evidence Draw on your information and emotions to imagine what it would be like if you carried out each of the alternatives to the end.

Essentials of Contemporary Management Chapter 5 - Decision Making. MGMT 3202, Essentials of Contemporary Management, ... Step 4: choose among alternatives Step 5: ...
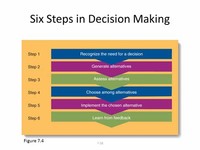
To complete the first step in the rational decision-making process, one must identify the problem and then state the desired outcome after the problem is solved. The next step is to identify the decision criteria by determining what factors are relevant in making the decision.

The first and the foremost step in the decision-making process are to define the real problem. A problem can be explained as a question for and appropriate solution. The manager should consider critical or strategic factors in defining the problem.

Strategic decision-making is the process of charting a course based on long-term goals and a longer term vision. By clarifying your company's big picture aims, you'll have the opportunity to align your shorter term plans with this deeper, broader mission -- giving your operations clarity and consistency.

Operational decisions are taken at lower levels of management. As the information is needed for helping the manager to take rational, well informed decisions, information systems need to focus on the process of managerial decision making.

Tactical decision making focuses on the big picture and the here and now. When making tactical decisions, the company as a whole is involved, according to Chron.com Small Business. Tactical decision making allows a company to evaluate its infrastructure and how it operates and make adjustments accordingly.