Types of Democracy

Authoritarianism is the antithesis of democracy because it marks an end to individual freedom and the value of an individual vote.

In the economic sphere, communism calls for the government to take control of all the capital and industry in the country in an effort to get rid of economic inequality. On the other hand, a democracy respects individuals' right to own property and means of production.

Democracy is a system of rule by laws, not by individuals. In a democracy, the rule of law protects the rights of citizens, maintains order, and limits the power of government. All citizens are equal under the law. No one may be discriminated against on the basis of their race, religion, ethnic group, or gender.

Democracy and dictatorship are two types of rule over a country. The person, who has complete power over a country, is called a dictator. A dictator enjoys an absolute rule over a country or a state.

Direct democracy is the opposite of the more common "representative democracy," under which the people elect representatives who are empowered to create laws and policies for them. Ideally, the laws and policies enacted by the elected representatives should closely reflect the will of the majority of the people.

Islamic democracy is a political ideology that seeks to apply Islamic principles to public policy within a democratic framework.

1. Monarchy is a form of government where a state is headed by a monarch while democracy is a government headed by elected representatives. 2. Power and position is passed through heritage and bloodline in Monarchy while democracy principally supports elections (people’s choice).
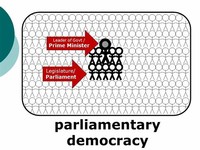
Parliamentary democracy, democratic form of government in which the party (or a coalition of parties) with the greatest representation in the parliament (legislature) forms the government, its leader becoming prime minister or chancellor. Executive functions are exercised by members of the parliament appointed by the prime minister to the cabinet.

Participatory democracy emphasizes the broad participation of constituents in the direction and operation of political systems. Etymological roots of democracy (Greek demos and kratos) imply that the people are in power and thus that all democracies are participatory.

Presidential Democracy Definition. A presidential system is a republican system of government where a head of government is also head of state and leads an executive branch that is separate from the legislative branch.

Simply put, a representative democracy is a system of government in which all eligible citizens vote on representatives to pass laws for them. A perfect example is the U.S., where we elect a president and members of the Congress. We also elect local and state officials.

A democratic republic is a form of government operating on principles adopted from a republic and a democracy. Rather than being a cross between two entirely separate systems, democratic republics may function on principles shared by both republics and democracies.

Social democracy is a political, social and economic ideology that supports economic and social interventions to promote social justice within the framework of a capitalist economy, as well as a policy regime involving a commitment to representative democracy, measures for income redistribution, and regulation of the economy in the general interest ...